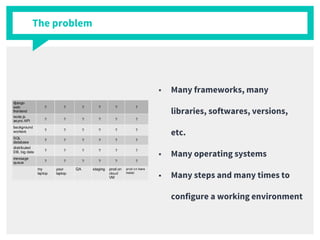
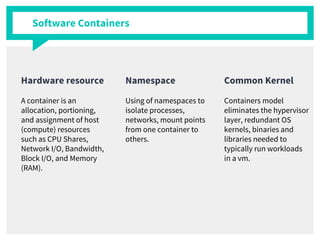
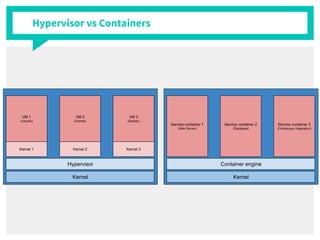
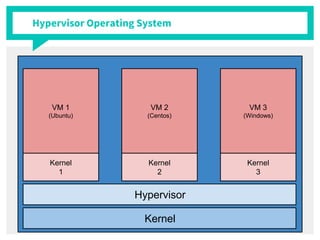
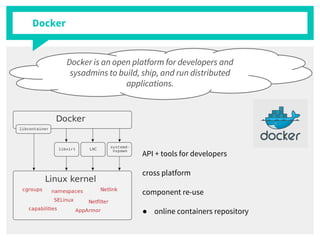
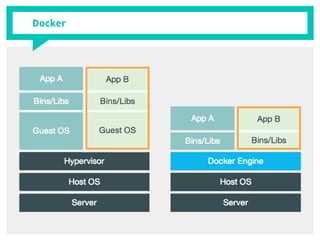
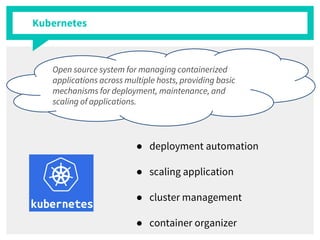
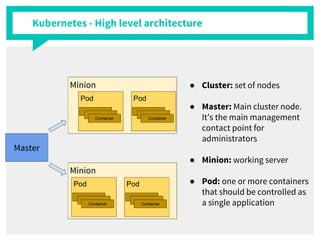
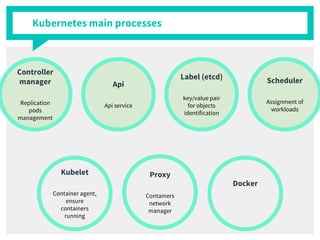
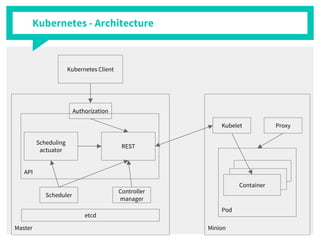
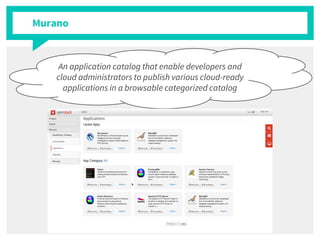
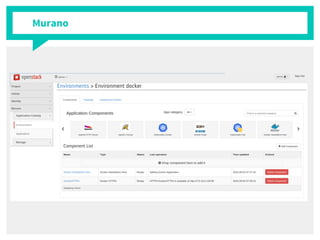
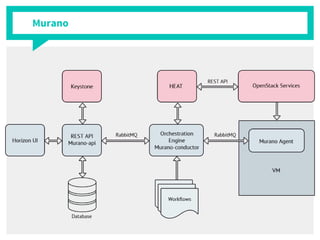
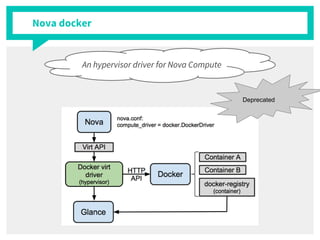
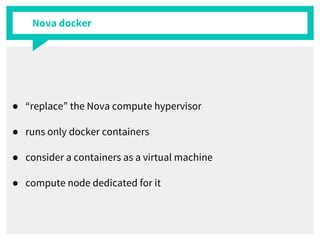
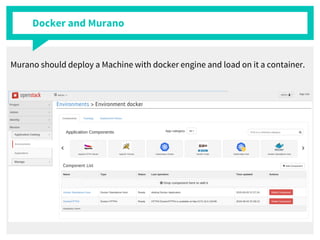
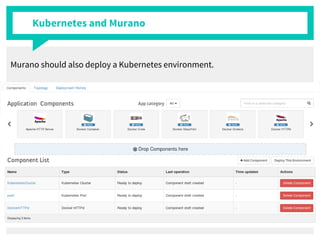
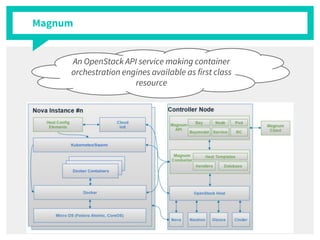
The document discusses container management within the OpenStack ecosystem, covering topics such as the definition, implementation, and advantages of containers like Docker and Kubernetes. It explains how OpenStack integrates with these technologies through services like Murano and Magnum to facilitate application deployment and orchestration. Finally, it provides an overview of a webinar along with links to video demos and additional resources for further learning.














![Reference
[1] https://www.docker.com/whatisdocker
[2] http://www.slideshare.net/jpetazzo/introduction-docker-linux-containers-lxc
[3] https://linuxcontainers.org/lxc/introduction/
[4] https://coreos.com/blog/rocket/
[5] http://kubernetes.io/v1.0/docs/whatisk8s.html
[6] https://docs.docker.com/swarm/
[7] https://coreos.com/
[8] http://www.projectatomic.io/
[9] https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Docker
[10] https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Murano
[11] https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Magnum
[12] http://kubernetes.io/v1.0/docs/whatisk8s.html
[13] http://aucouranton.com/2014/06/13/linux-containers-parallels-lxc-openvz-docker-and-more/
[14] http://www.socallinuxexpo.org/sites/default/files/presentations/Jerome-
Scale11x%20LXC%20Talk.pdf
[15] http://martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html
[16] https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/an-introduction-to-kubernetes
[17] https://blog.risingstack.com/operating-system-containers-vs-application-containers/
[18] https://github.com/appc/spec/blob/master/SPEC.md
[19] http://media.wix.com/ugd/295986_d5059f95a78e451db5de3d54f711e45d.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinarcontainermanagement-151215134746/85/Webinar-container-management-in-OpenStack-41-320.jpg)
