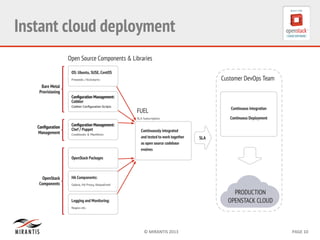
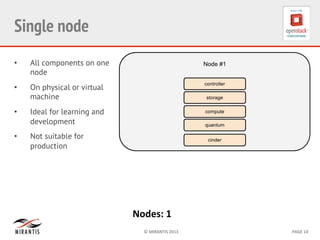
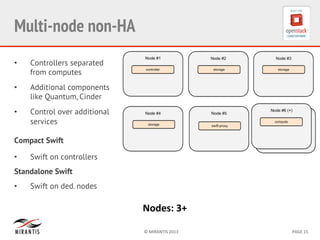
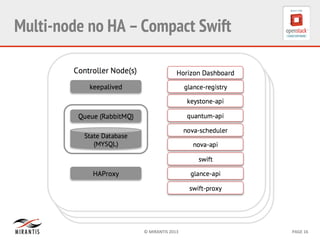
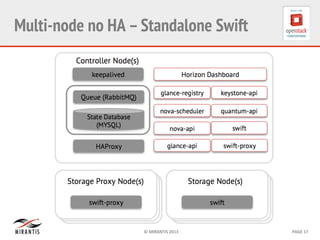
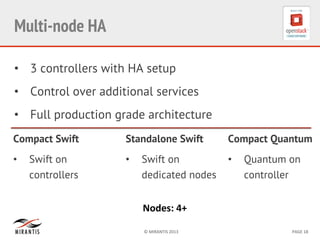
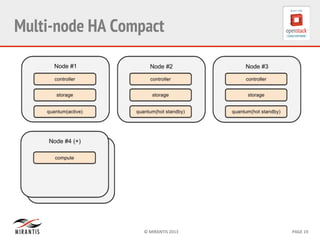
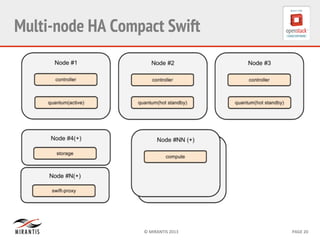
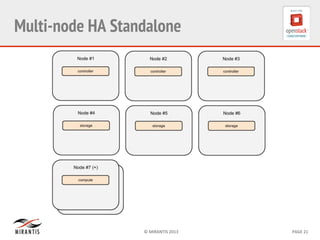
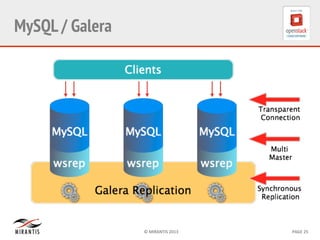
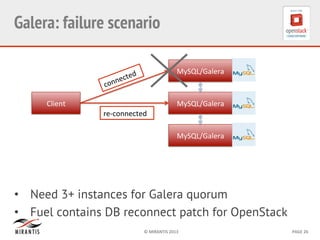
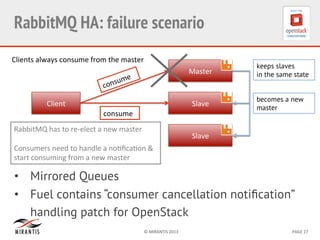
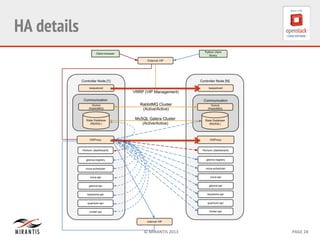
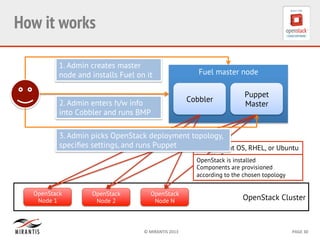
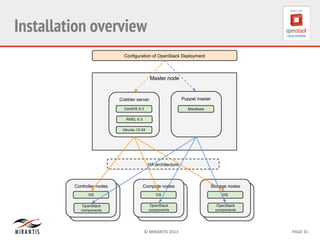
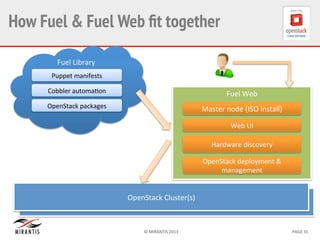
Mirantis developed Fuel to automate OpenStack deployments. Fuel uses tools like Cobbler and Puppet to provision hardware and deploy OpenStack in an automated, error-proof manner. It supports various deployment topologies including single-node, multi-node non-HA, and multi-node HA. Fuel Web provides a web-based interface for managing OpenStack clusters deployed using Fuel.