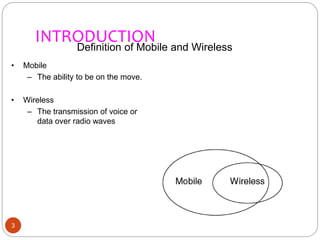
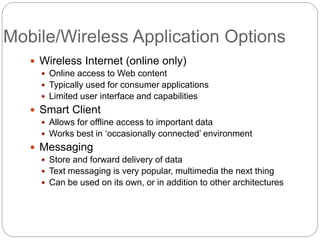
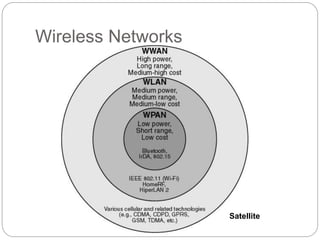
This document discusses web services on mobile platforms. It begins with an abstract that outlines how web services fulfill needs in web development and mobile accessibility. It then introduces web services, their role in mobile environments, types of web services, and middleware components. The document covers defining mobile and wireless technologies, why mobile is chosen, mobile/wireless application options, and services on the web. It discusses challenges in the mobile environment like coverage, bandwidth, reliability and costs. The document concludes that web services can improve individual performance and efficient use of resources on mobile devices.