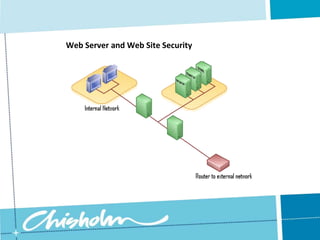
This document discusses various topics related to web server and website security including demilitarized zones (DMZs), firewalls, intrusion detection systems, secure web protocols like SSL and HTTPS, common gateway interfaces (CGIs), web form validation, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS) prevention. It explains that a DMZ is a network area between an internal and external network that allows limited connections, firewalls filter incoming network traffic using methods like packet filtering and stateful inspection, and an IDS monitors network traffic for malicious activity. It also describes secure web protocols that encrypt data transmission and how to properly validate web forms and user input to prevent vulnerabilities like SQL injection and XSS attacks.