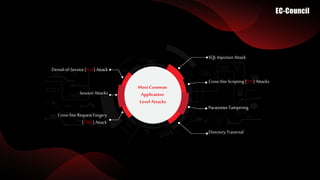
The document outlines the most common application-level attacks, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), parameter tampering, directory traversal, denial-of-service (DoS), session hijacking, and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). It emphasizes the significant risks posed by these attacks, such as unauthorized access to sensitive data and disruption of application interactions. Each type of attack is briefly described, highlighting its method and potential impact on security.