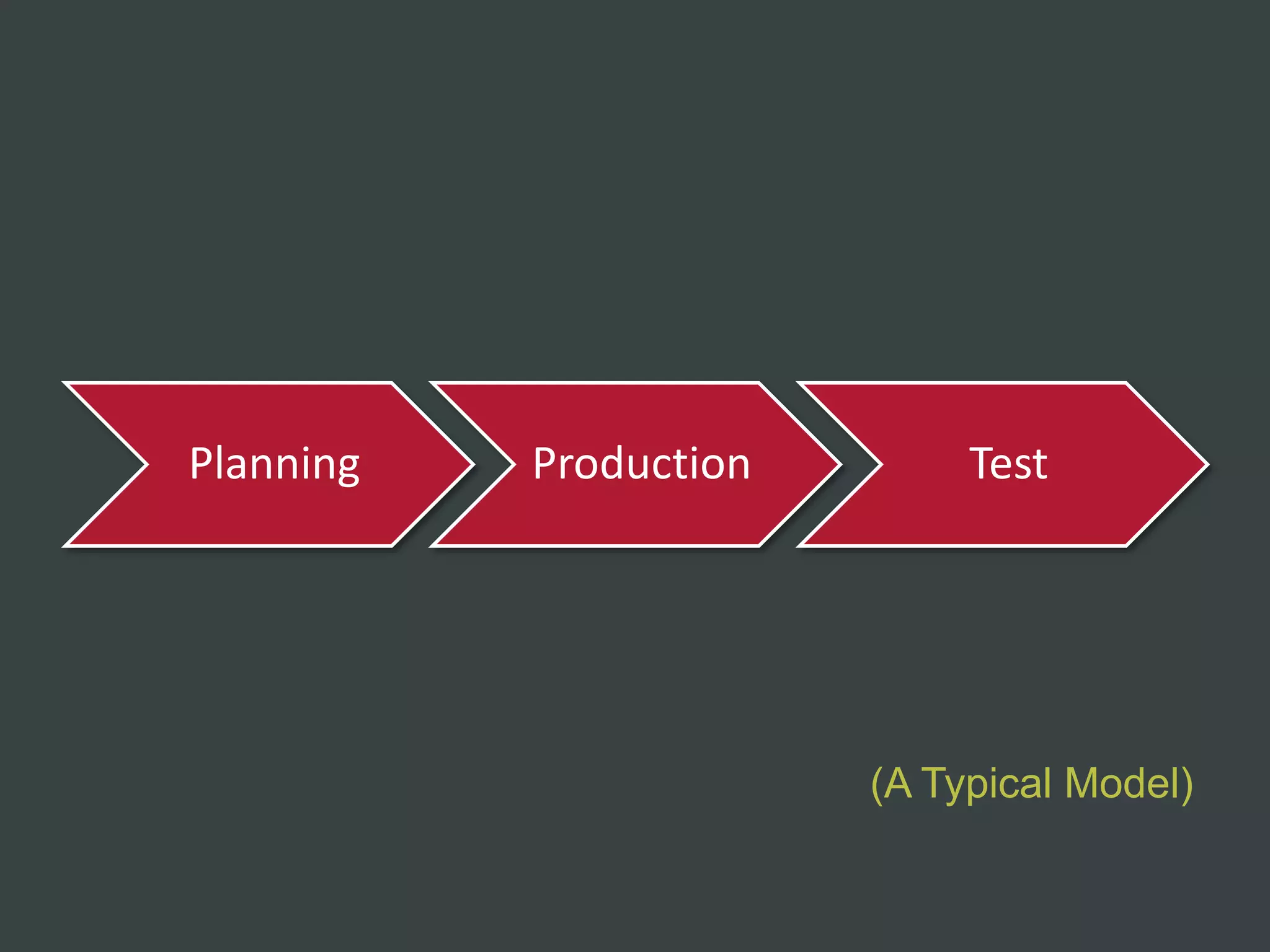
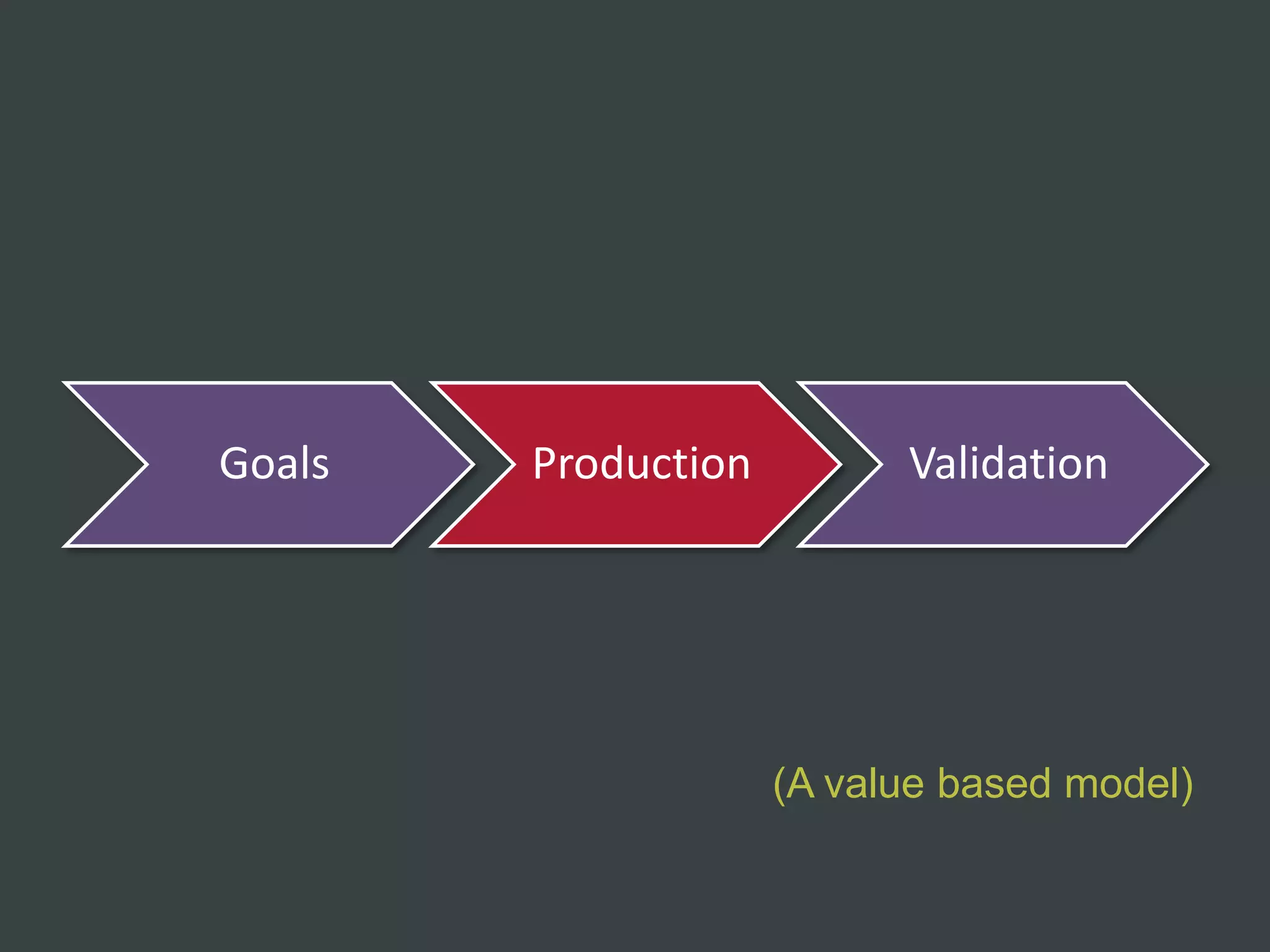
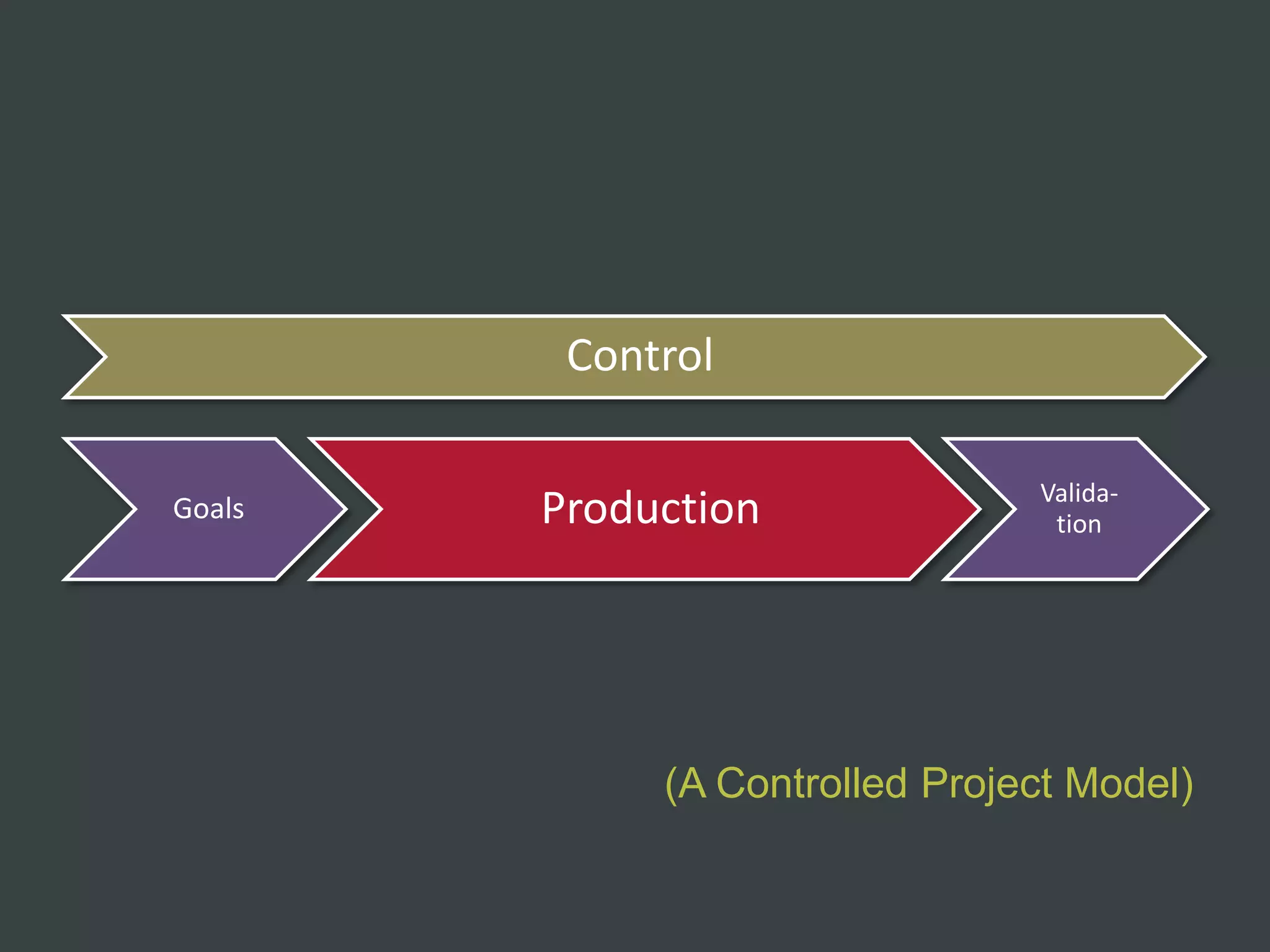
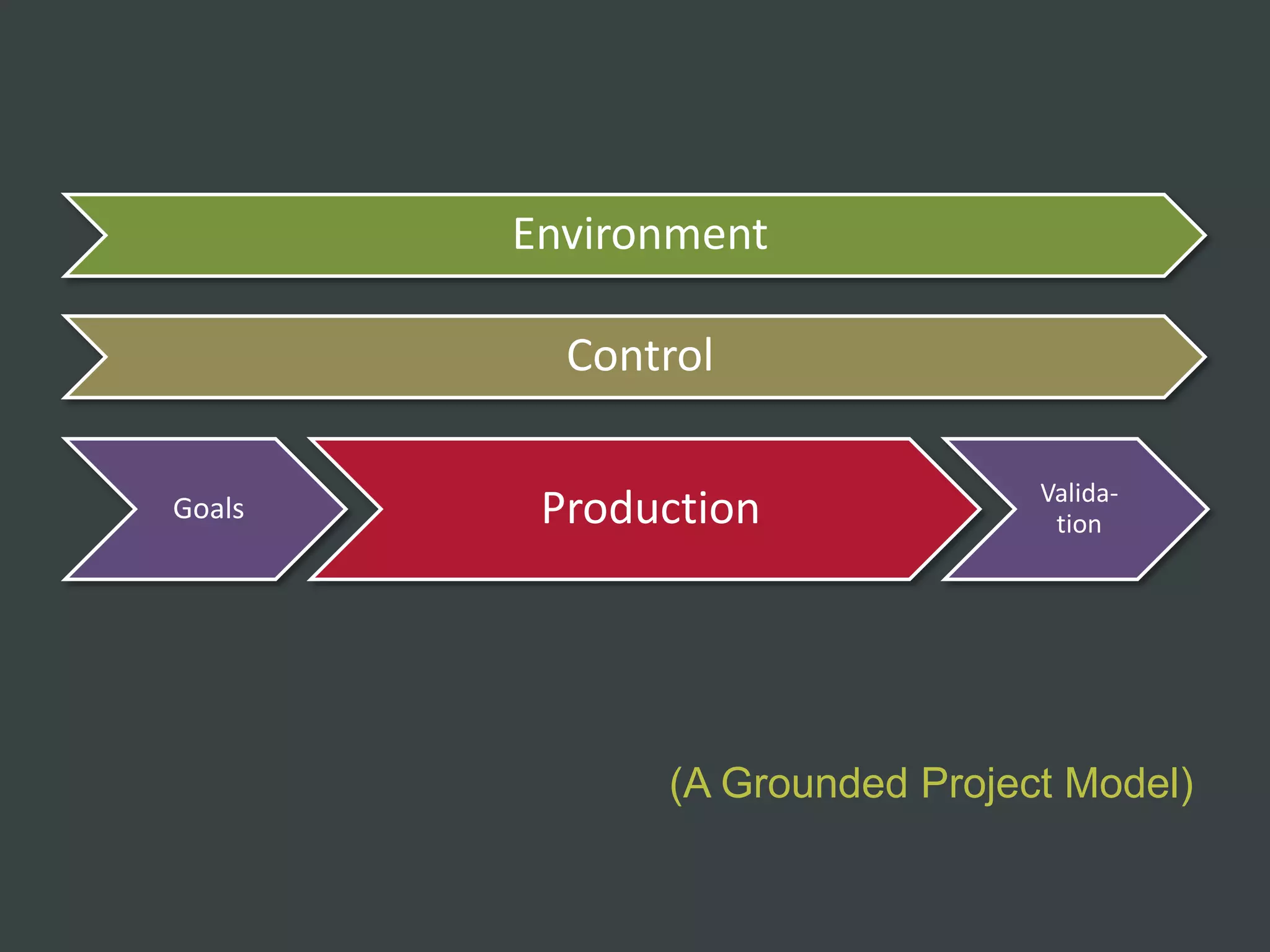
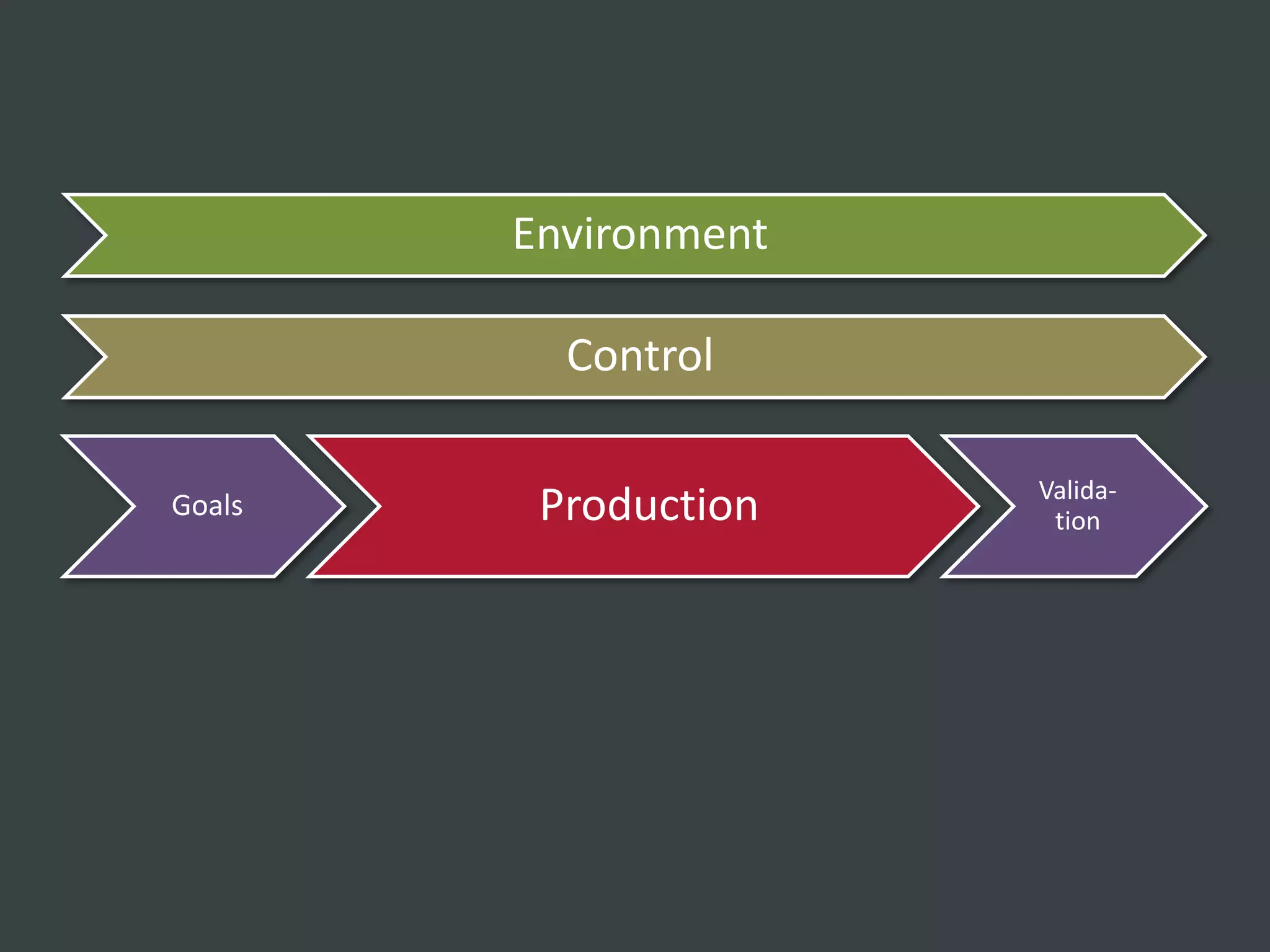
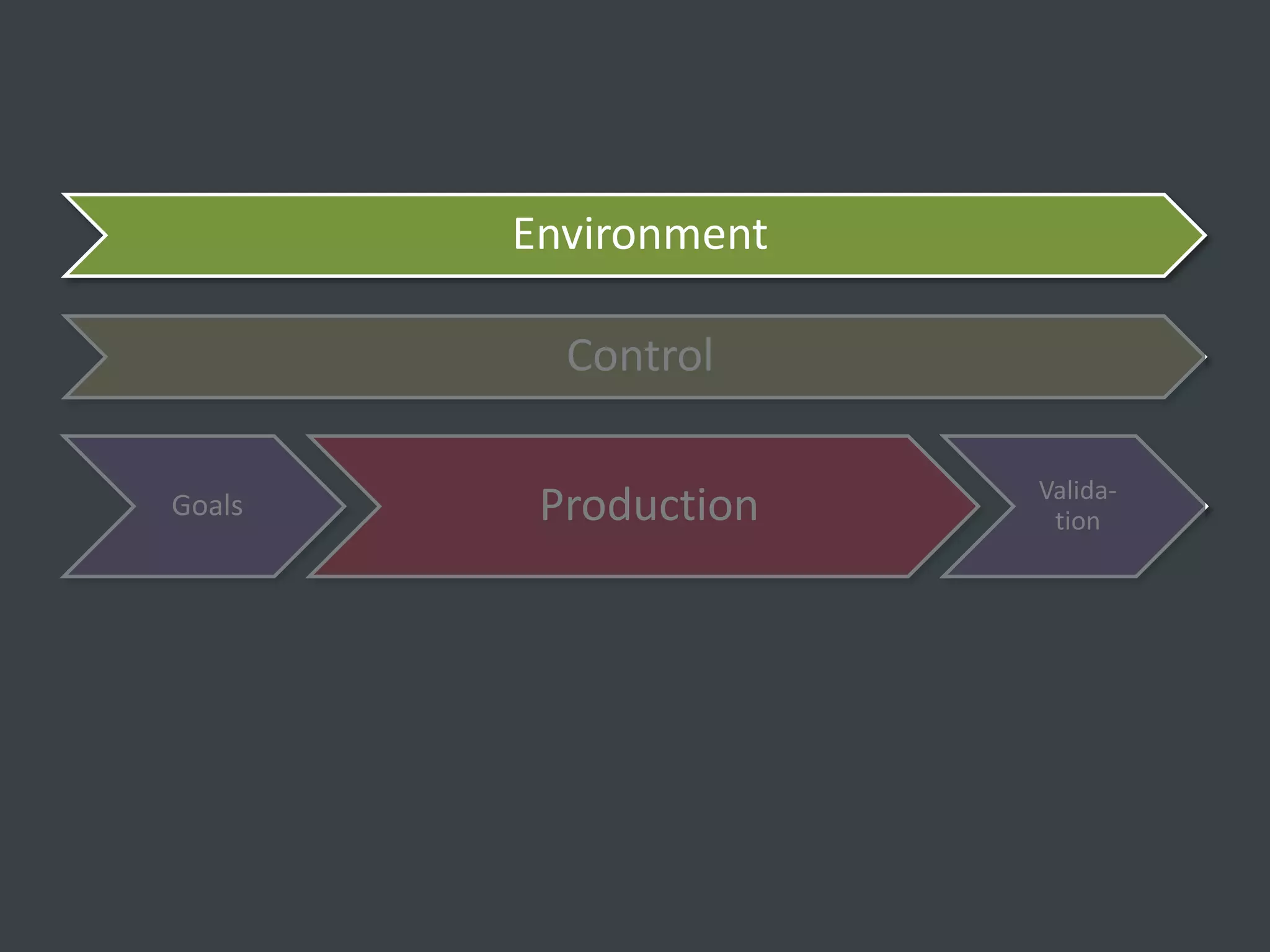
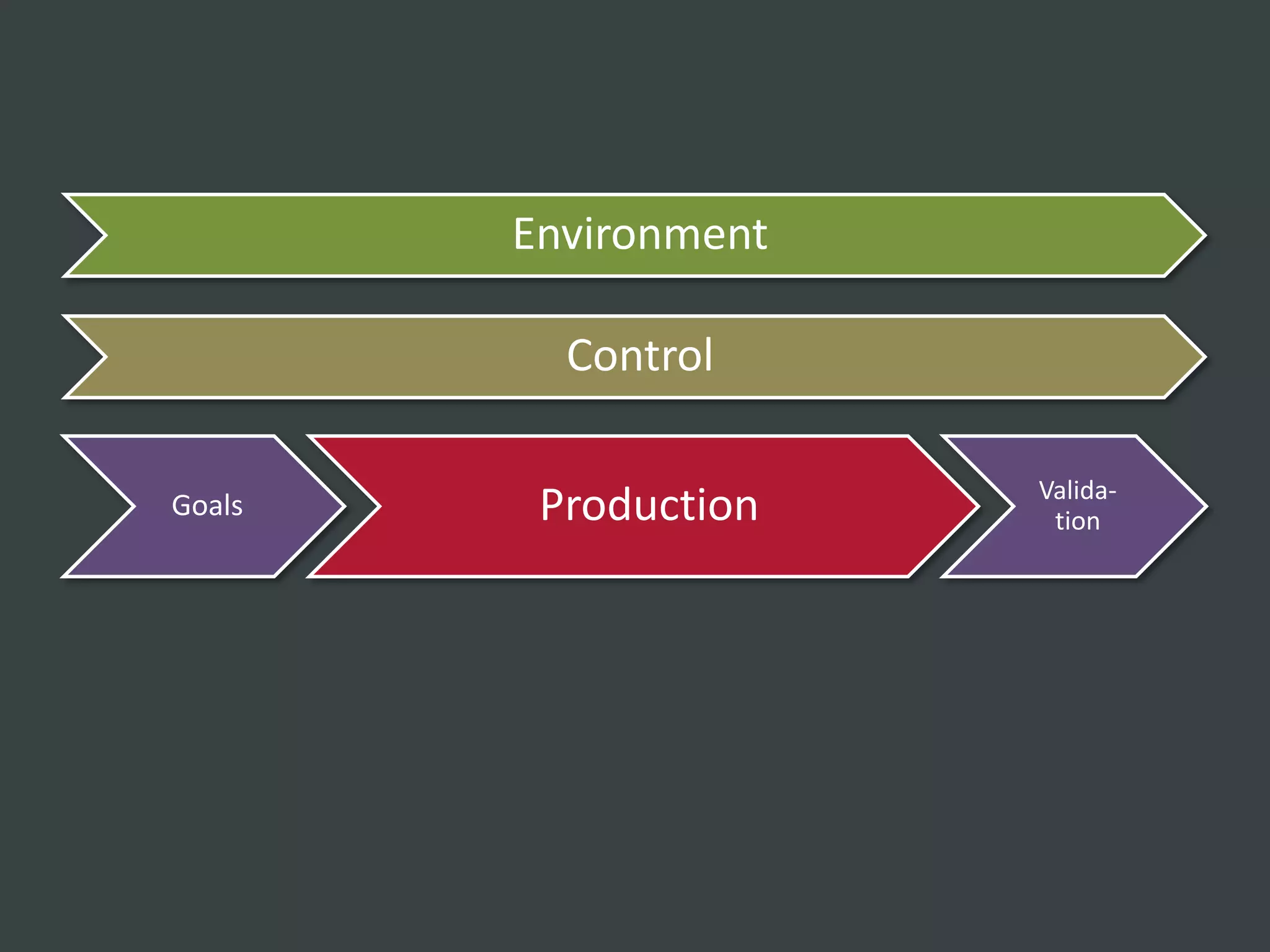
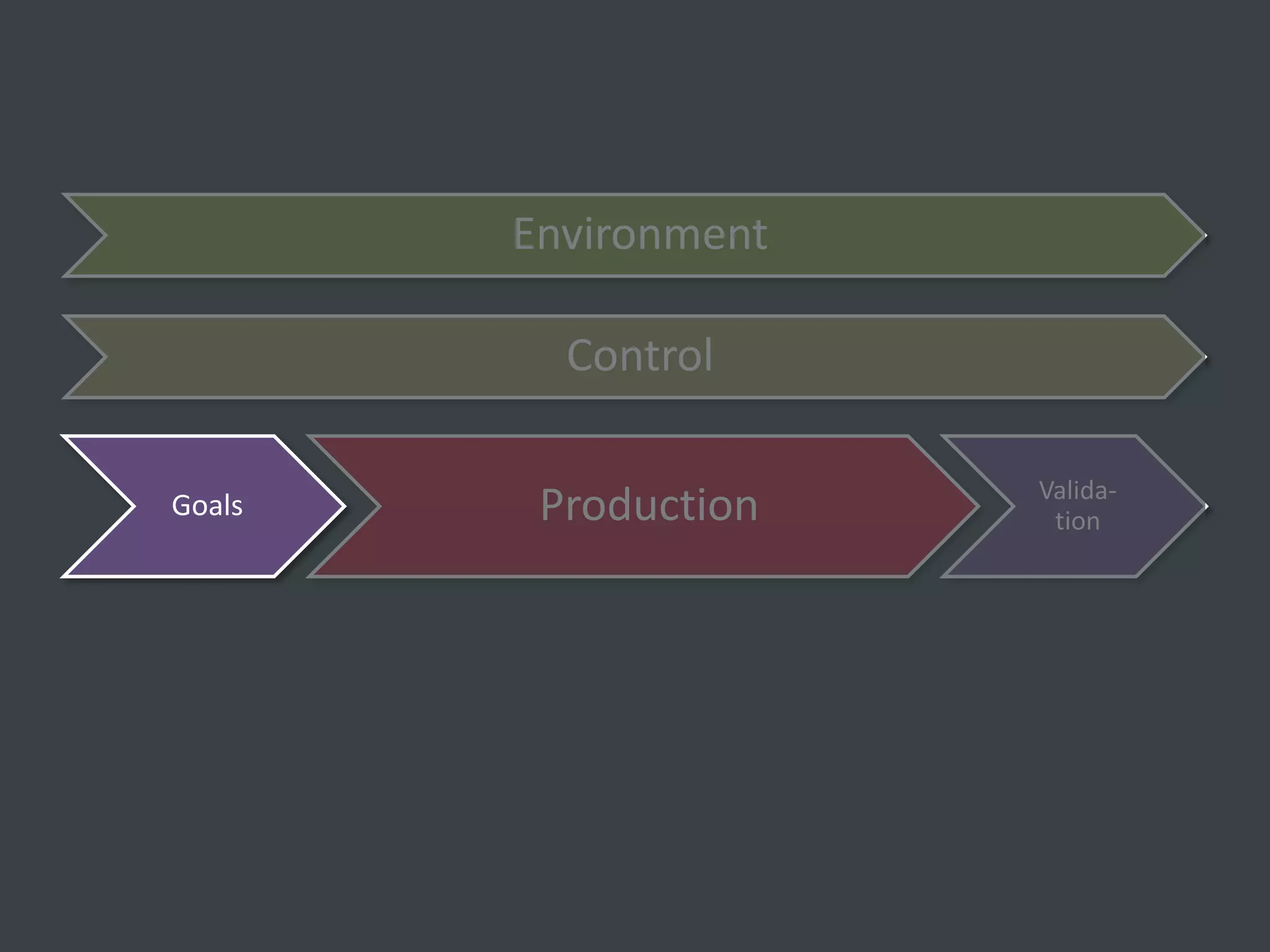
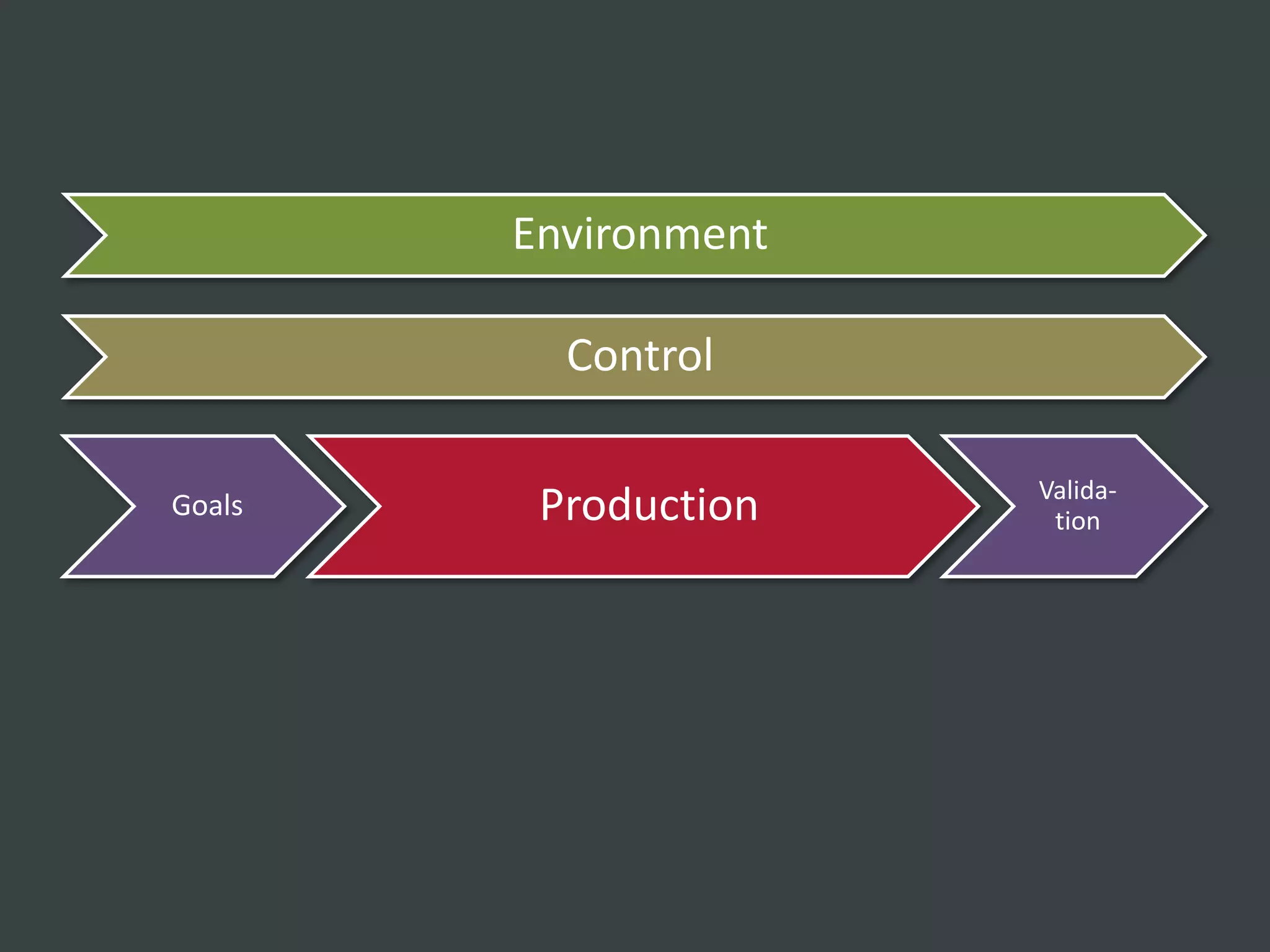
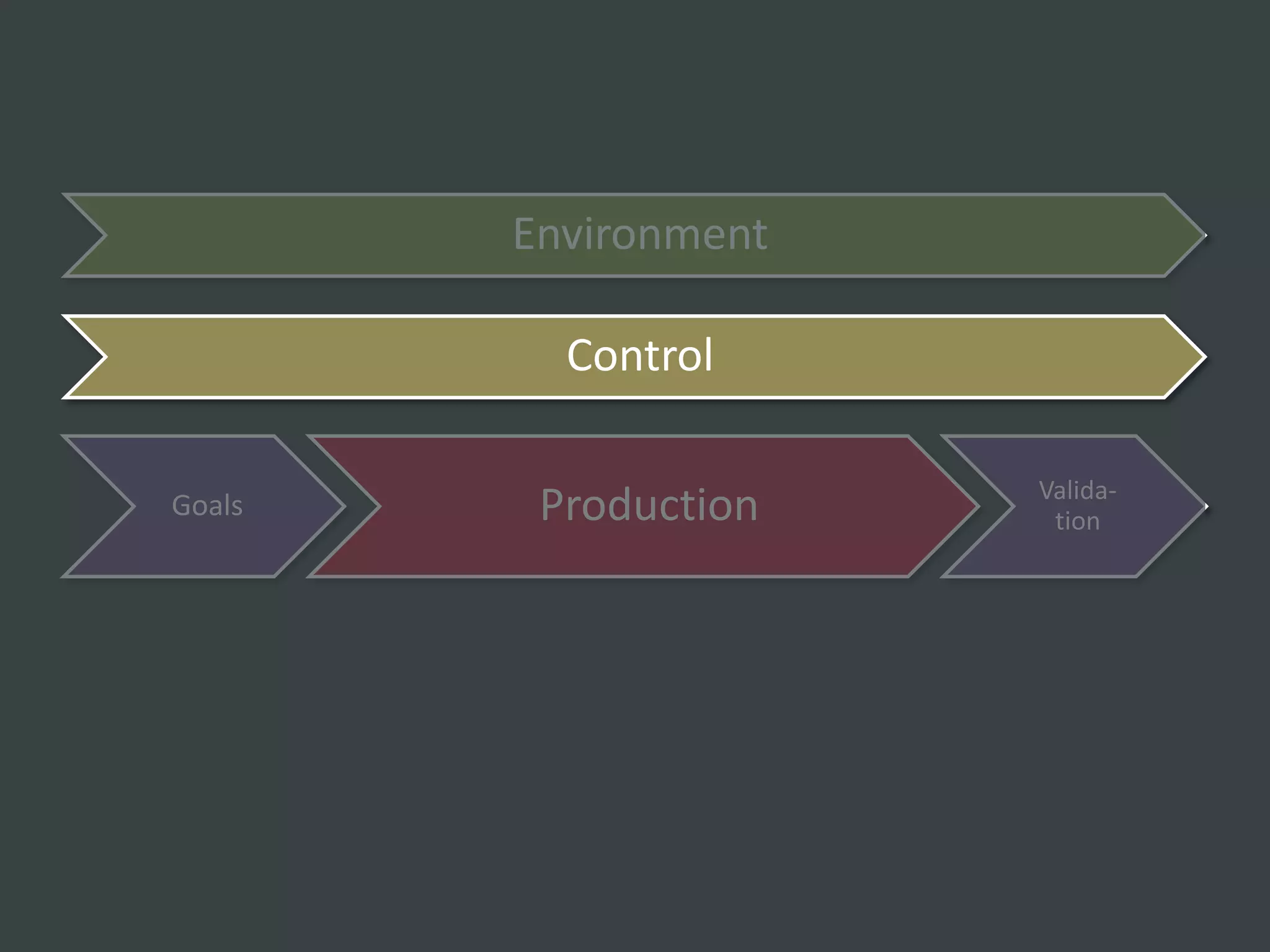
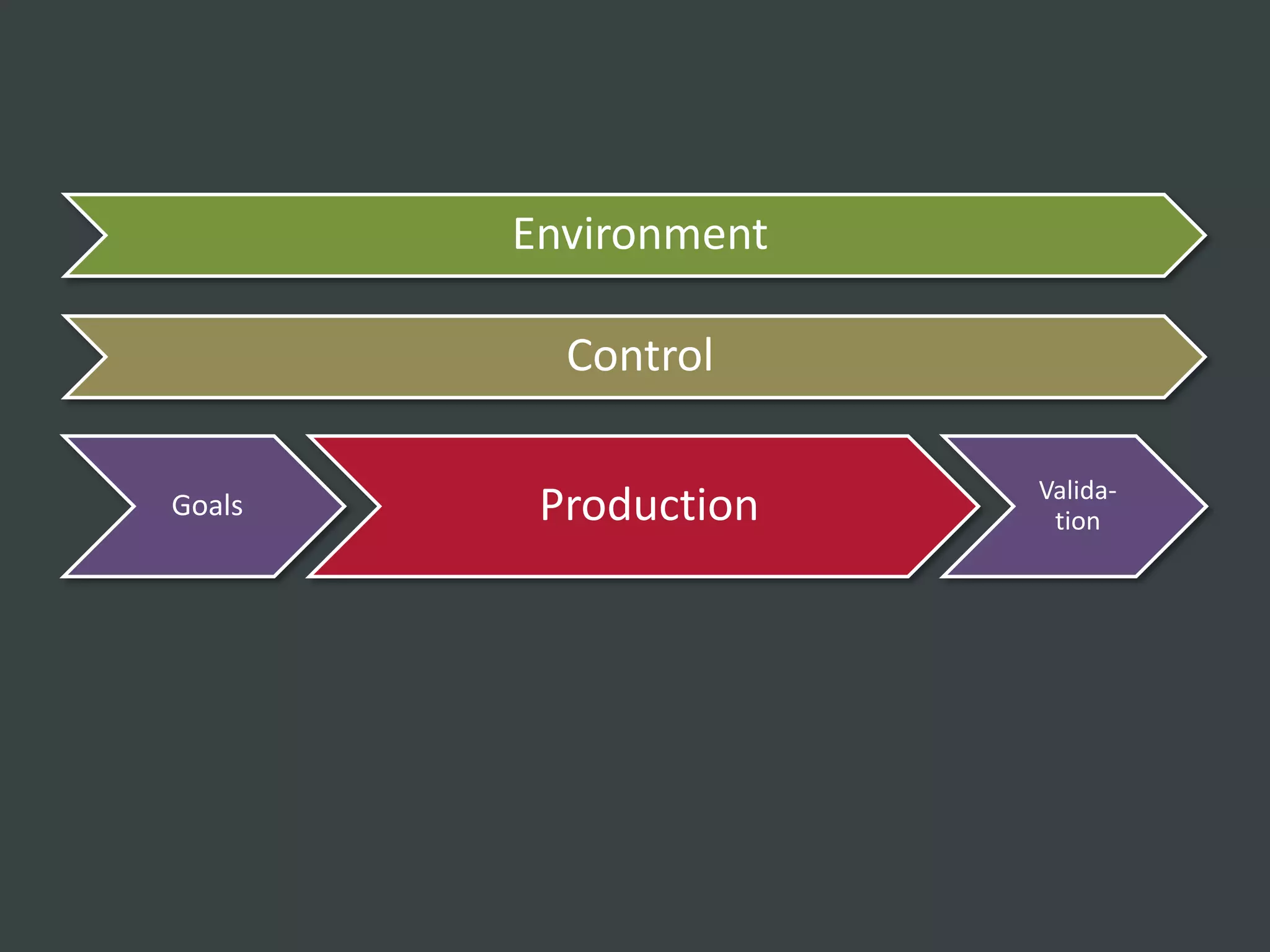
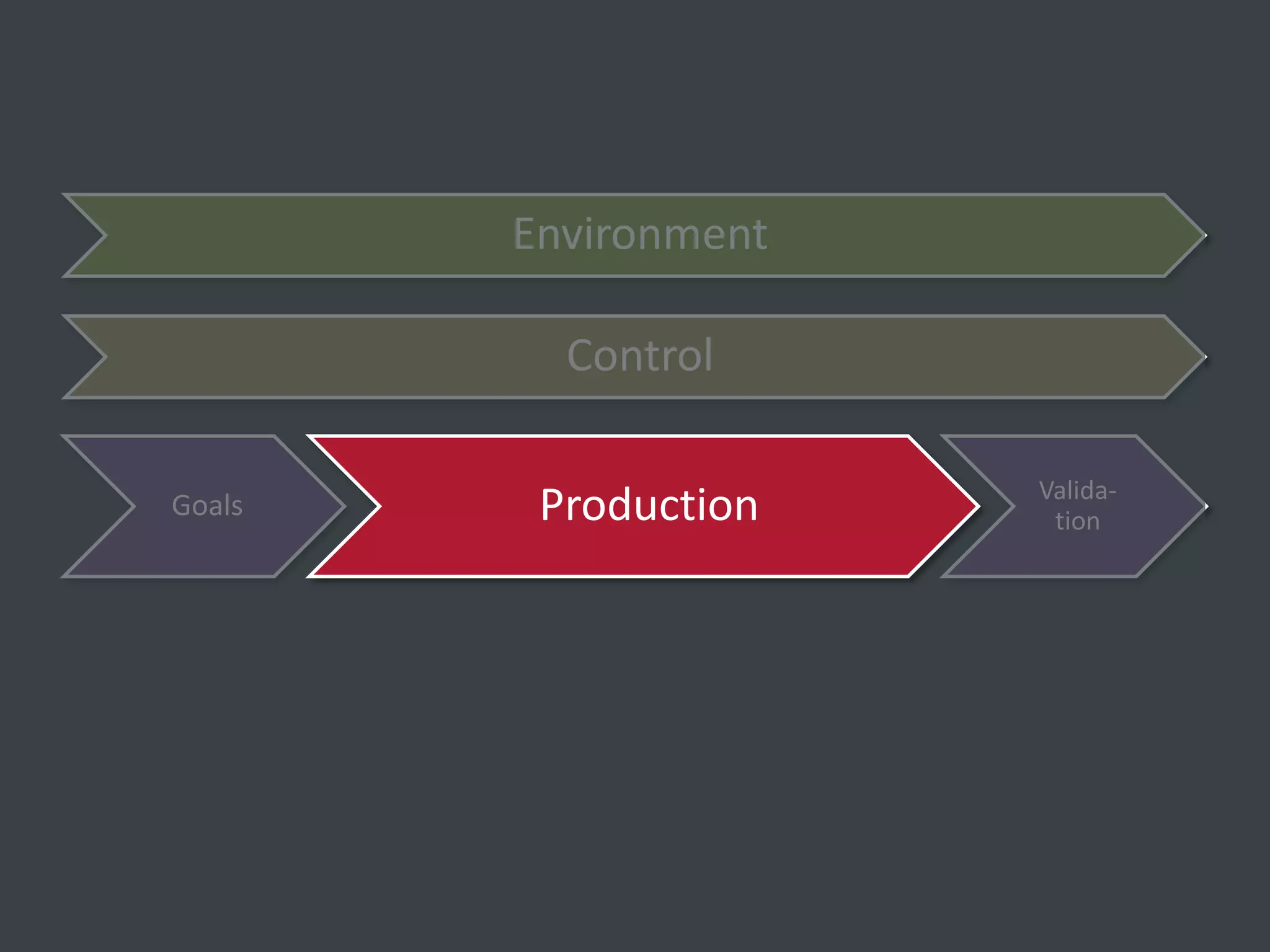
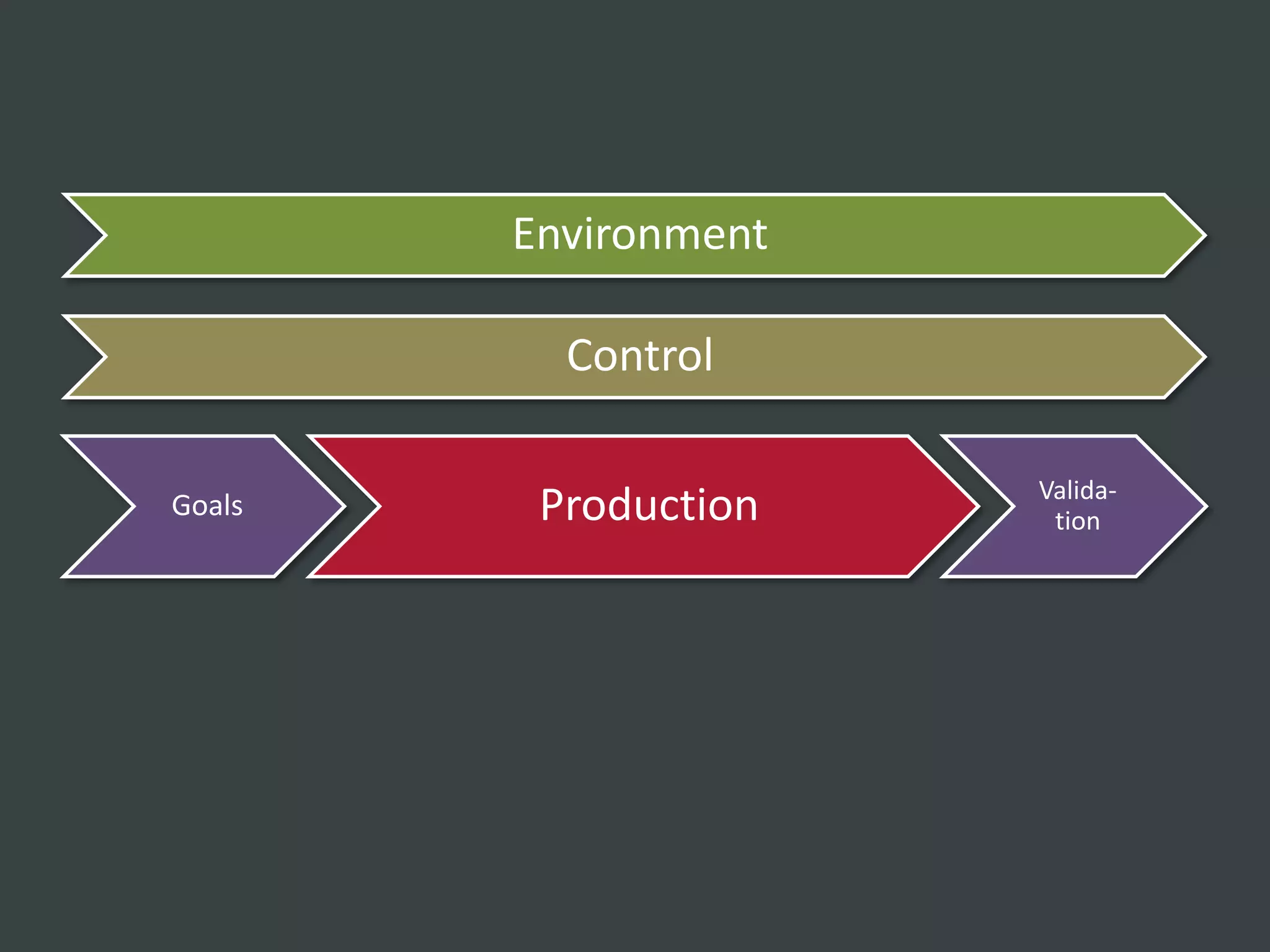
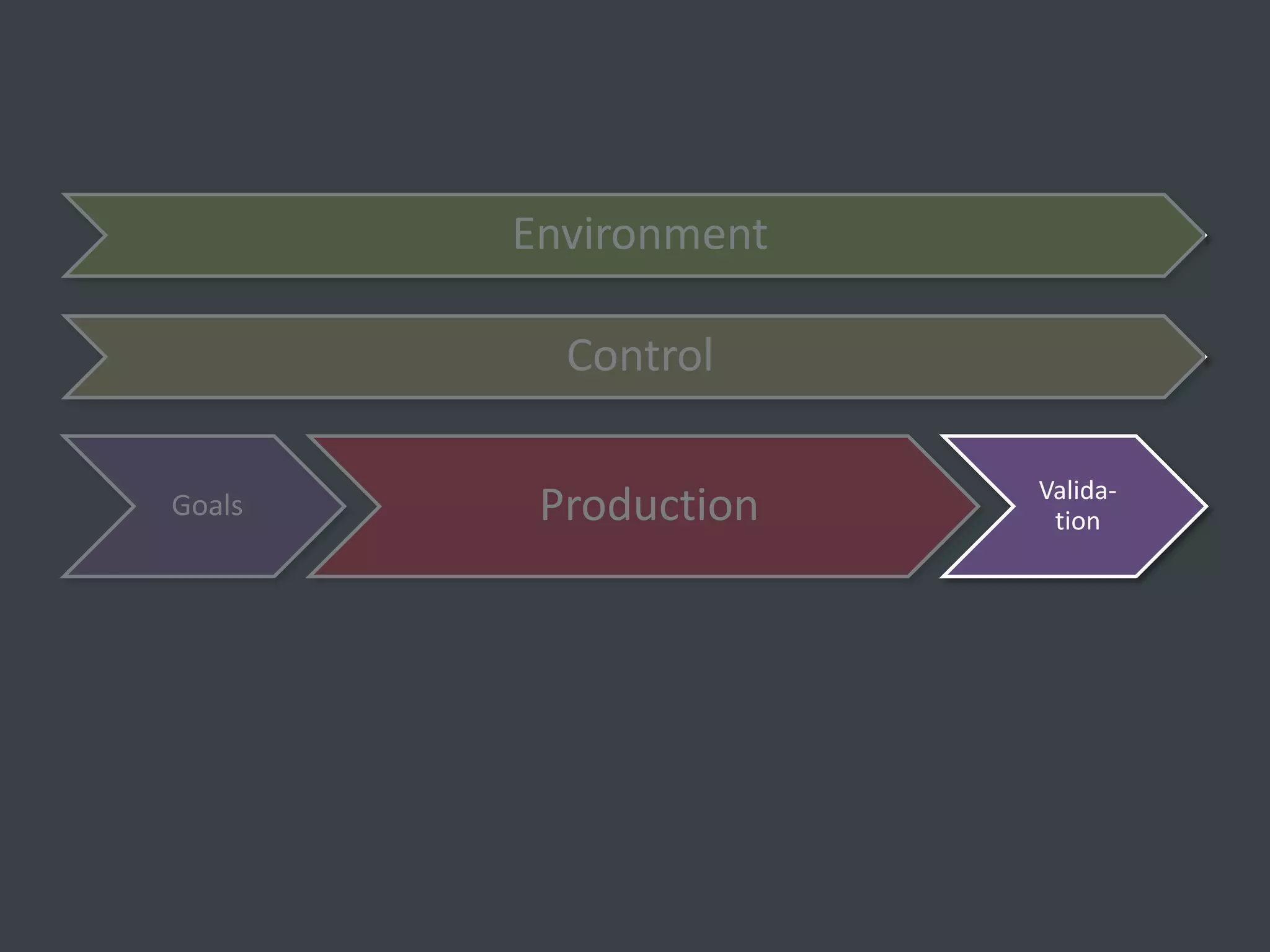
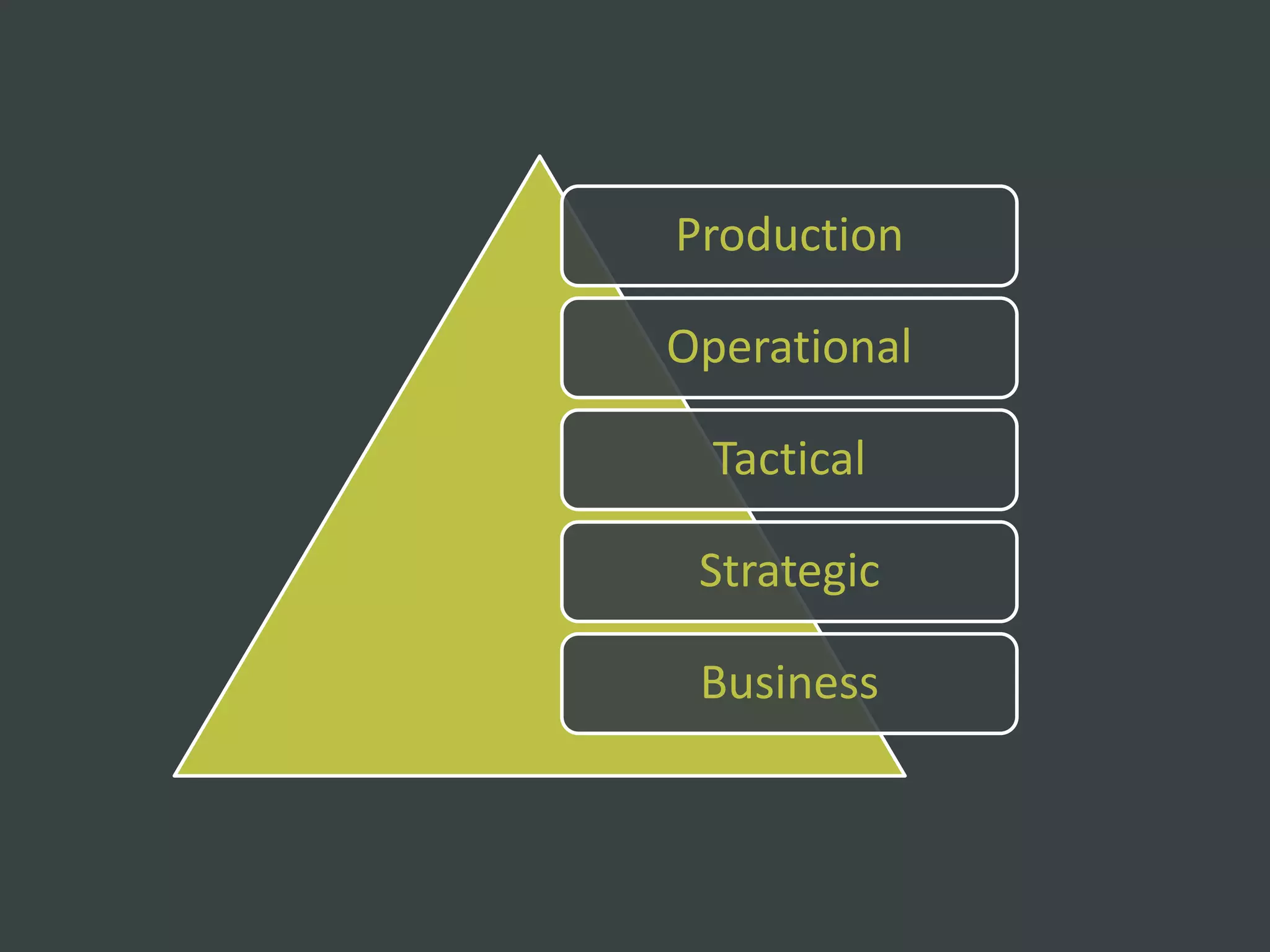
The document discusses how to structure web projects for success. It emphasizes understanding both the internal project environment and client environment. A successful project requires defining goals and metrics, establishing control structures like status meetings and issue tracking, structuring production into defined phases, and validating deliverables through testing and signoff. Roles and responsibilities must also be divided among strategic, tactical, operational, and production levels to ensure proper support, escalation procedures, and respect for each team member's area.