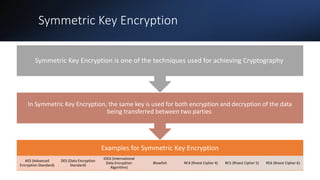
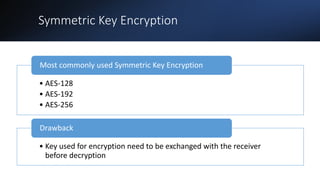
The document discusses web application security testing. It defines security testing as identifying vulnerabilities in software, databases, operating systems, and organizations to protect information from hackers. Effective security practices need to be implemented through security testing to avoid losses and protect organizations' reputations from data breaches. Security testing includes vulnerability assessments to find security issues and penetration tests to simulate hacker activities and evaluate vulnerabilities' impacts. The goals of security testing are to achieve confidentiality, integrity, and availability as defined in the CIA security triad.