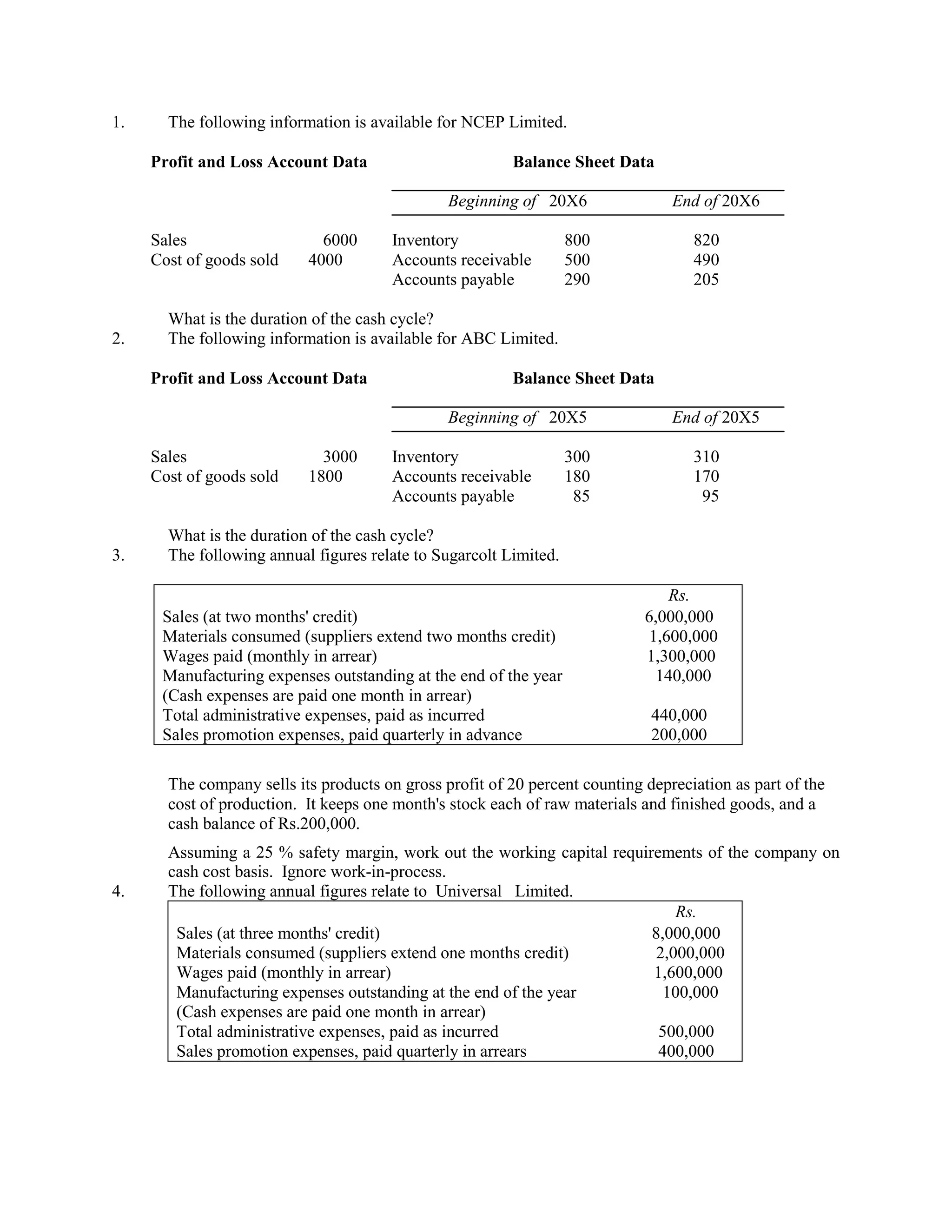
1. The document provides profit/loss and balance sheet data for NCEP Limited and ABC Limited for two years, and asks to calculate the duration of the cash cycle for each. It also provides annual figures for Sugarcolt Limited and asks to calculate working capital requirements.
2. The document provides annual sales, material consumption, wage, expense and promotion figures for Universal Limited and asks to calculate working capital requirements assuming a 20% safety margin. It also provides data on inventory levels and cash balances.
3. The document presents 7 inventory management problems involving calculating economic order quantities and total inventory costs under different order sizes and discount scenarios. It