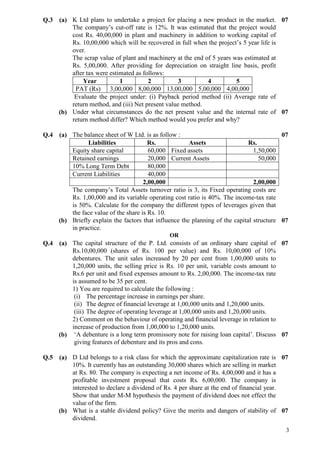
This document contains a sample exam for a Financial Management course, with 5 multiple choice questions covering various topics in corporate finance. Question 1 has two parts asking about debenture pricing and calculating present value of rental income. Question 2 covers sources of working capital and calculating optimal order quantity. Question 3 covers project evaluation techniques and weighted average cost of capital. Question 4 addresses leverage calculation and factors influencing capital structure. Question 5 discusses dividend policy and the Modigliani-Miller hypothesis.