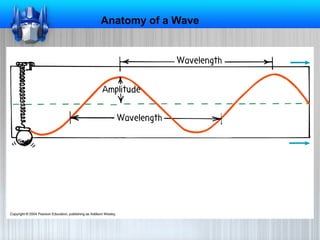
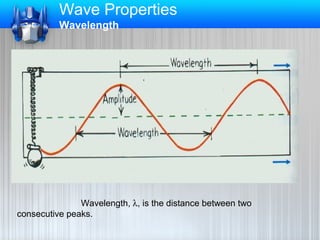
This document discusses different types of waves and their properties. It explains that waves are disturbances that transfer energy through matter or space, using examples like ripples in water and sound waves. Waves travel through a medium and involve the movement of that medium. The size of a wave determines how much energy it carries - larger waves carry more energy. As waves spread out, their energy becomes distributed over a larger area. Most waves are caused by vibrating objects, and the vibration of particles in the medium allows the wave to pass through.