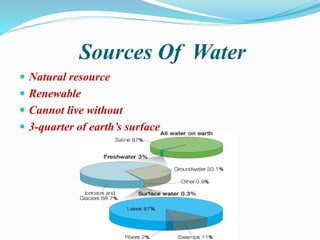
A water footprint is the amount of water used directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, or community on a daily basis. It includes water used for household needs, food consumption, and other activities. Most of the Earth's water is salty and located in oceans, with only a small fraction being freshwater available for human use. Freshwater sources include groundwater stored underground in aquifers, and surface water found in lakes, rivers, and streams. Water can exist in three states - liquid, gas (water vapor), and solid (ice) - and moves continuously through the water cycle by changing states and flowing across and within the Earth. Water is essential for human survival and is used for domestic, agricultural, industrial, and