Embed presentation
Downloaded 67 times



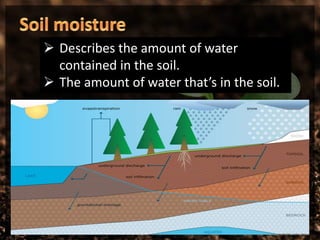
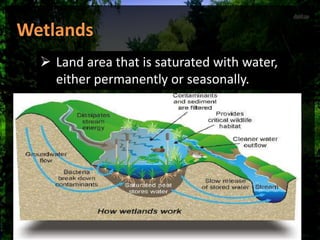
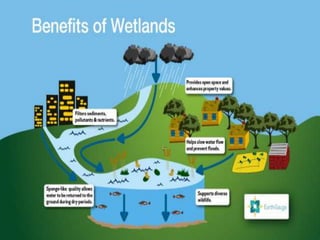


Water is stored naturally in groundwater aquifers, soil water, wetlands, and artificially in small ponds, tanks, and reservoirs behind dams. Groundwater is water found underground in cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rock. Soil water describes the amount of water contained in the soil. Wetlands are land areas saturated with water permanently or seasonally. Artificial storage includes community or household ponds and tanks filled by rainwater, groundwater, or surface runoff, as well as reservoirs behind dams used for electricity or water supply.







