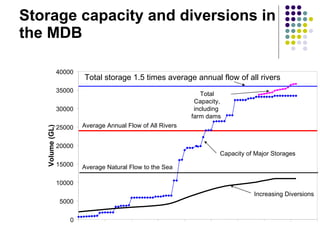
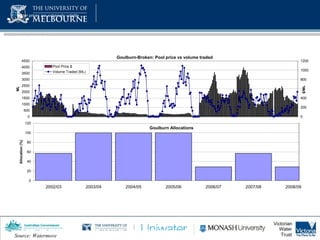
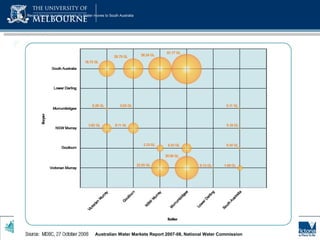
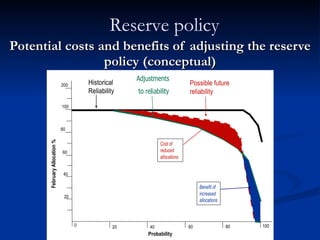
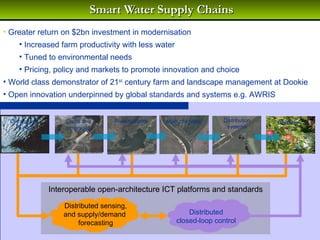
1) Total storage capacity in the Murray-Darling Basin (MDB) has increased to 1.5 times the average annual flow of all rivers in the basin between 1920-2010 due to increased development of major storages and farm dams.
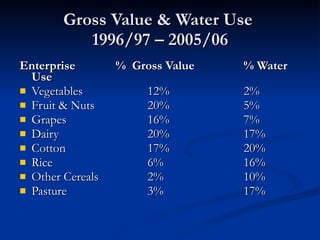
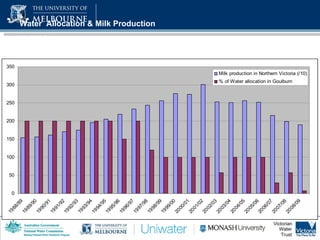
2) Dairy production accounts for 20% of the gross value of production but uses 17% of water in the MDB, while cotton accounts for 17% of value but uses 20% of water.
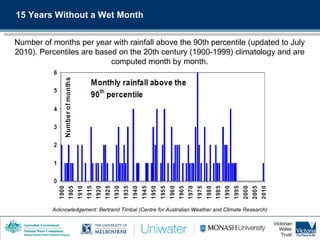
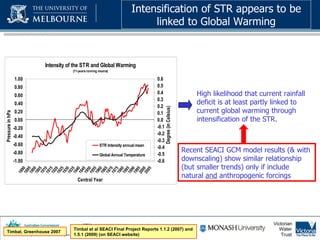
3) Recent climate trends in the MDB show a decrease in the number of wet months per year and an intensification of drought conditions linked to global warming.