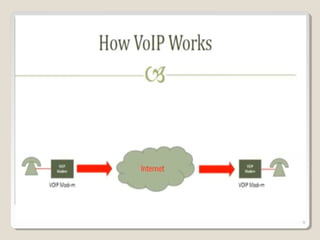
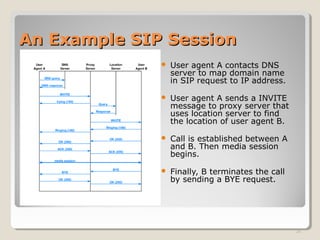
This document summarizes Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology. It begins by defining VoIP as using Internet Protocol networks to deliver voice communications. It then explains how VoIP works by continuously sampling and digitizing audio for transmission over the Internet in packets. The document outlines key advantages of VoIP such as lower costs compared to traditional phone service. It also discusses some disadvantages like reliance on internet connectivity and potential for lost audio. Additionally, it provides overviews of important VoIP standards and protocols including SIP, IP telephone systems, and how telephone numbers are mapped and routed over the Internet.