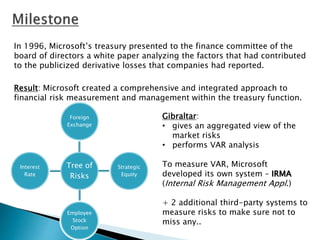
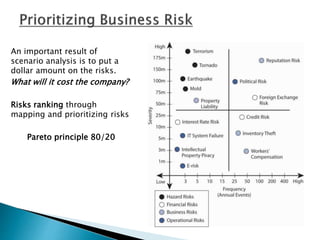
Microsoft established its risk management group (RMG) in 1997 within the treasury department to develop a comprehensive approach to risk identification, measurement, and management across the enterprise. The RMG worked to bring non-financial risk management practices in line with the more mature financial risk management processes. Microsoft developed internal risk measurement systems and consulted third parties to ensure all risks were captured. The company encouraged a culture of transparency around risk through accessible internal reporting and education for all employees.