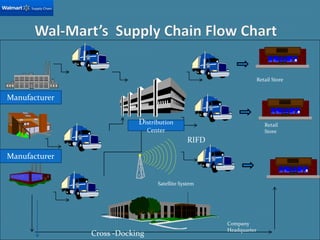
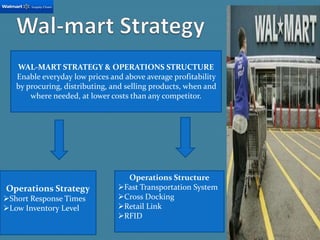
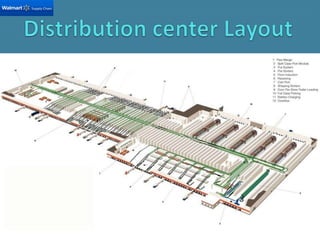
Wal-Mart has become the largest retailer and private employer in the world through strategic operations and a focus on low prices. It generates over $444 billion in annual sales, more than many countries' GDP. Key aspects of Wal-Mart's success include efficient procurement directly from manufacturers, a fast transportation network, cross-docking to reduce inventory costs, and sophisticated IT systems to track sales and replenish stores. This allows Wal-Mart to offer consistently low prices while maintaining high profitability.