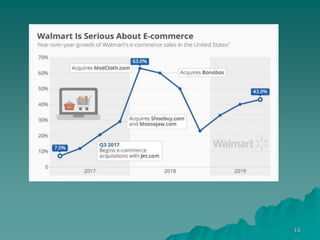
1. Walmart was the largest retailer in the world in 2018 with $514 billion in sales, followed by Amazon, Schwarz Group, and Carrefour.
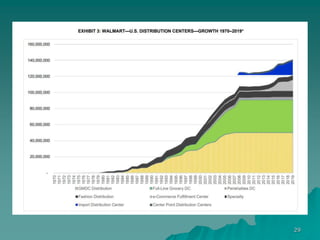
2. Founded by Sam Walton in 1962, Walmart pioneered the use of a centralized distribution system and data-driven decision making. By 1984, it had 640 stores in the US.
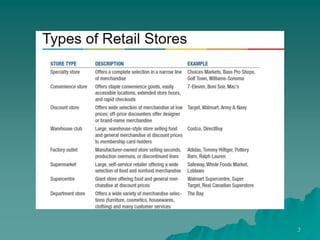
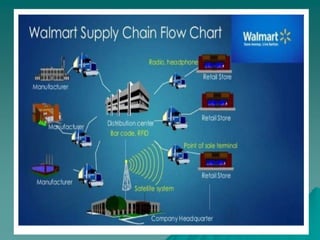
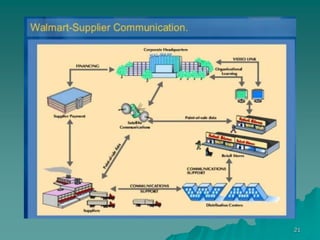
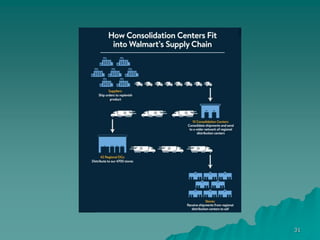
3. Currently, Walmart has over 11,000 stores globally and 2.2 million employees. It focuses on reducing costs through efficient supply chain management and using technologies like RFID tags and AI to enhance its operations.