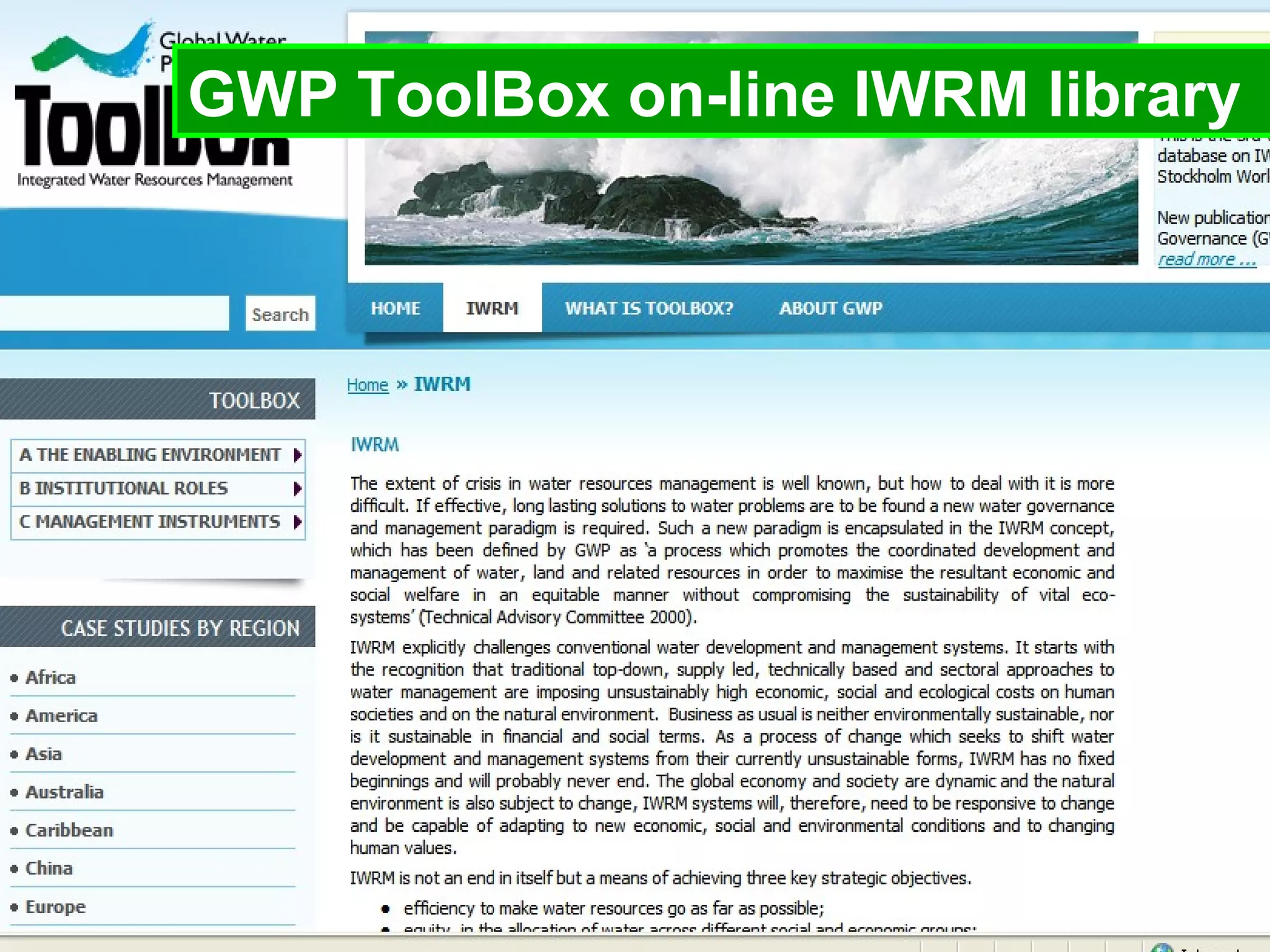
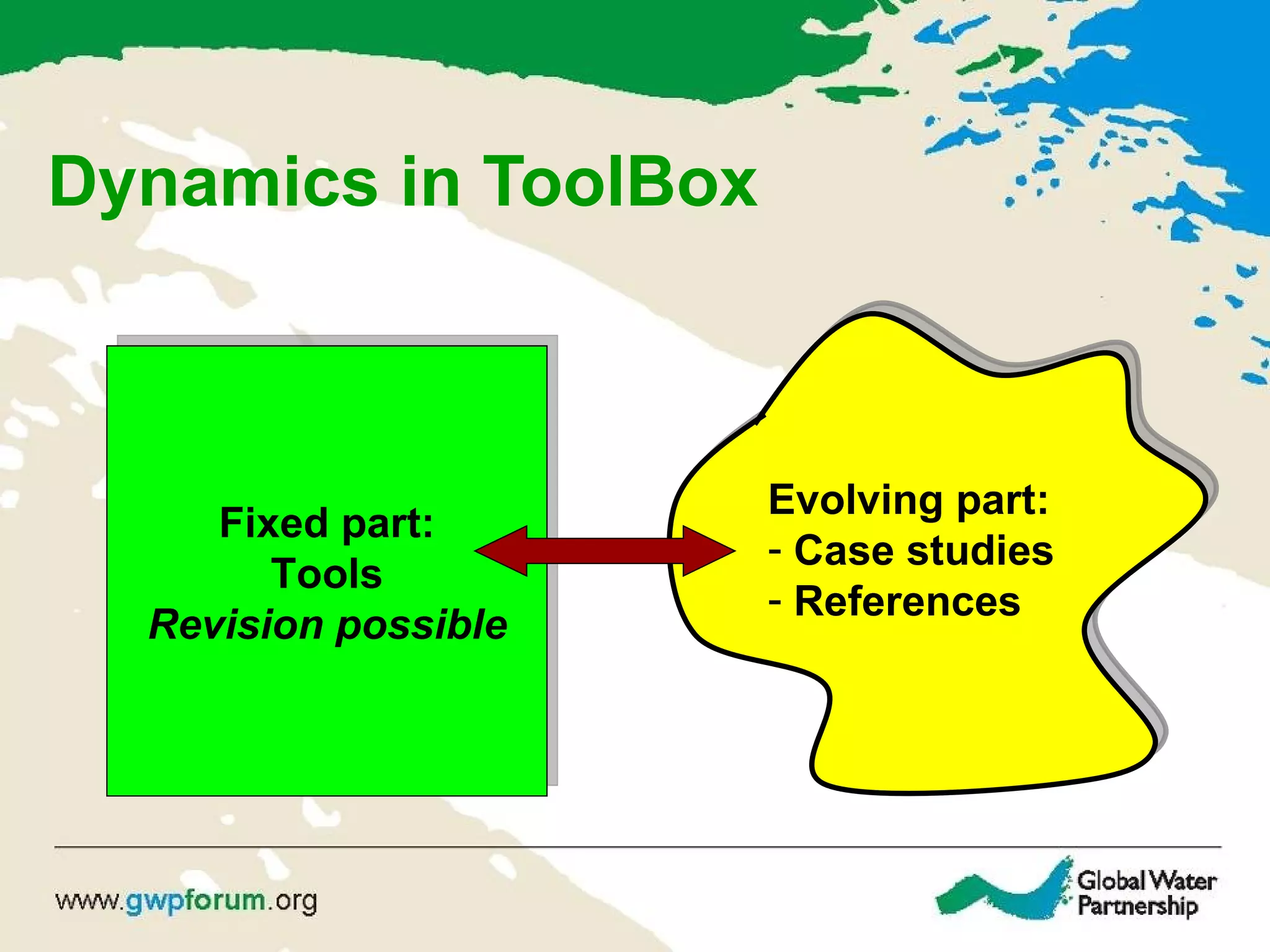
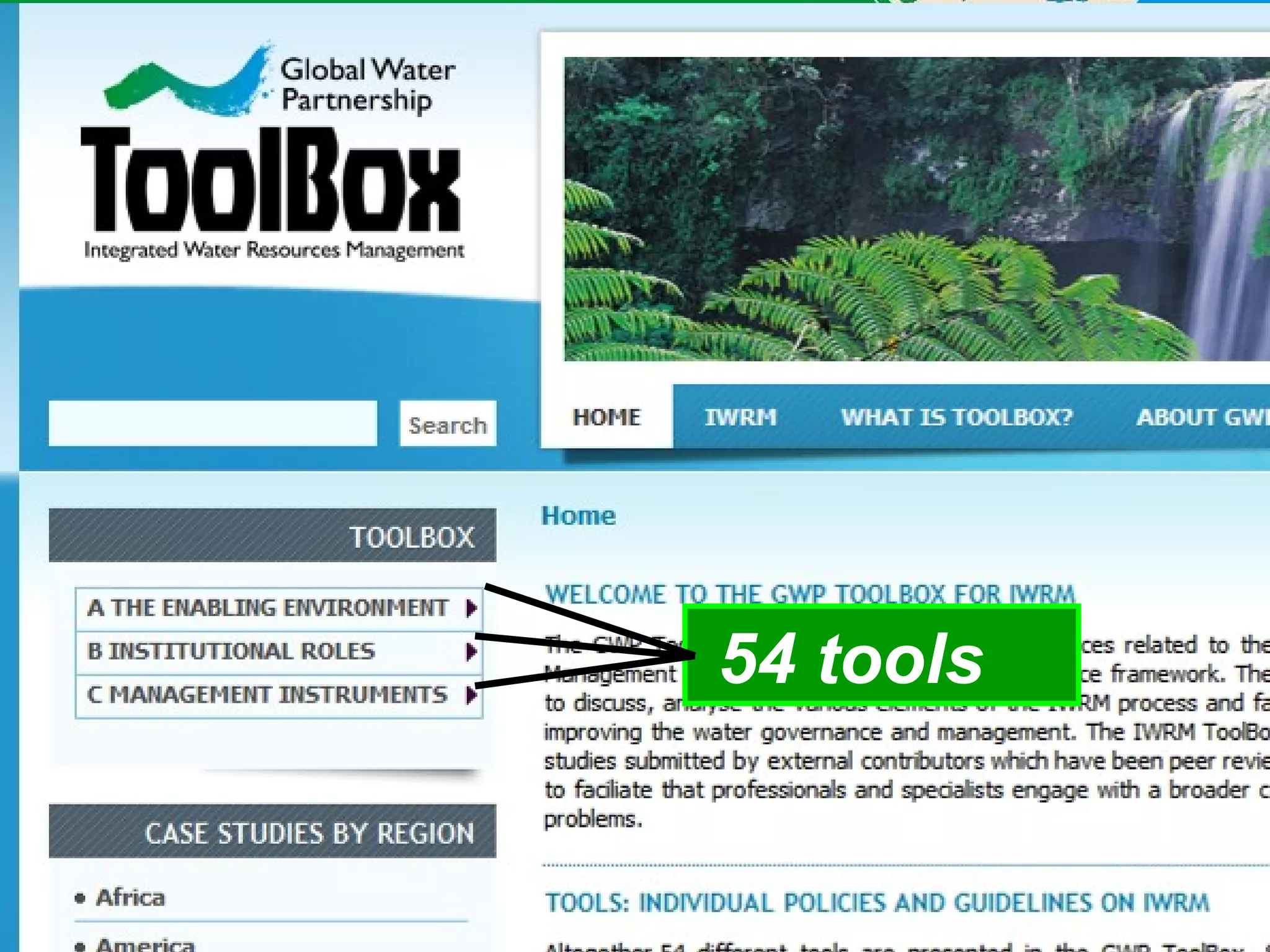
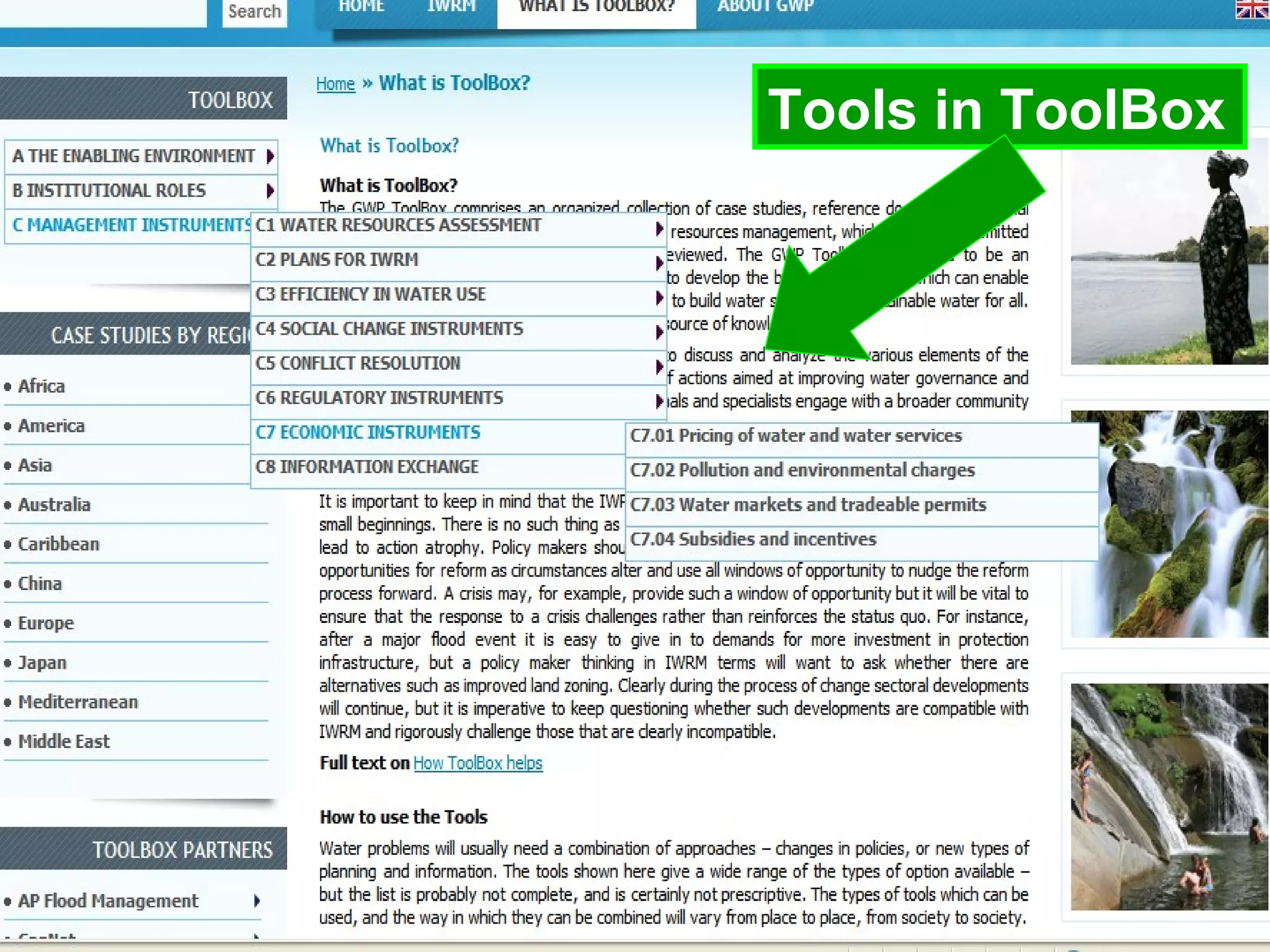
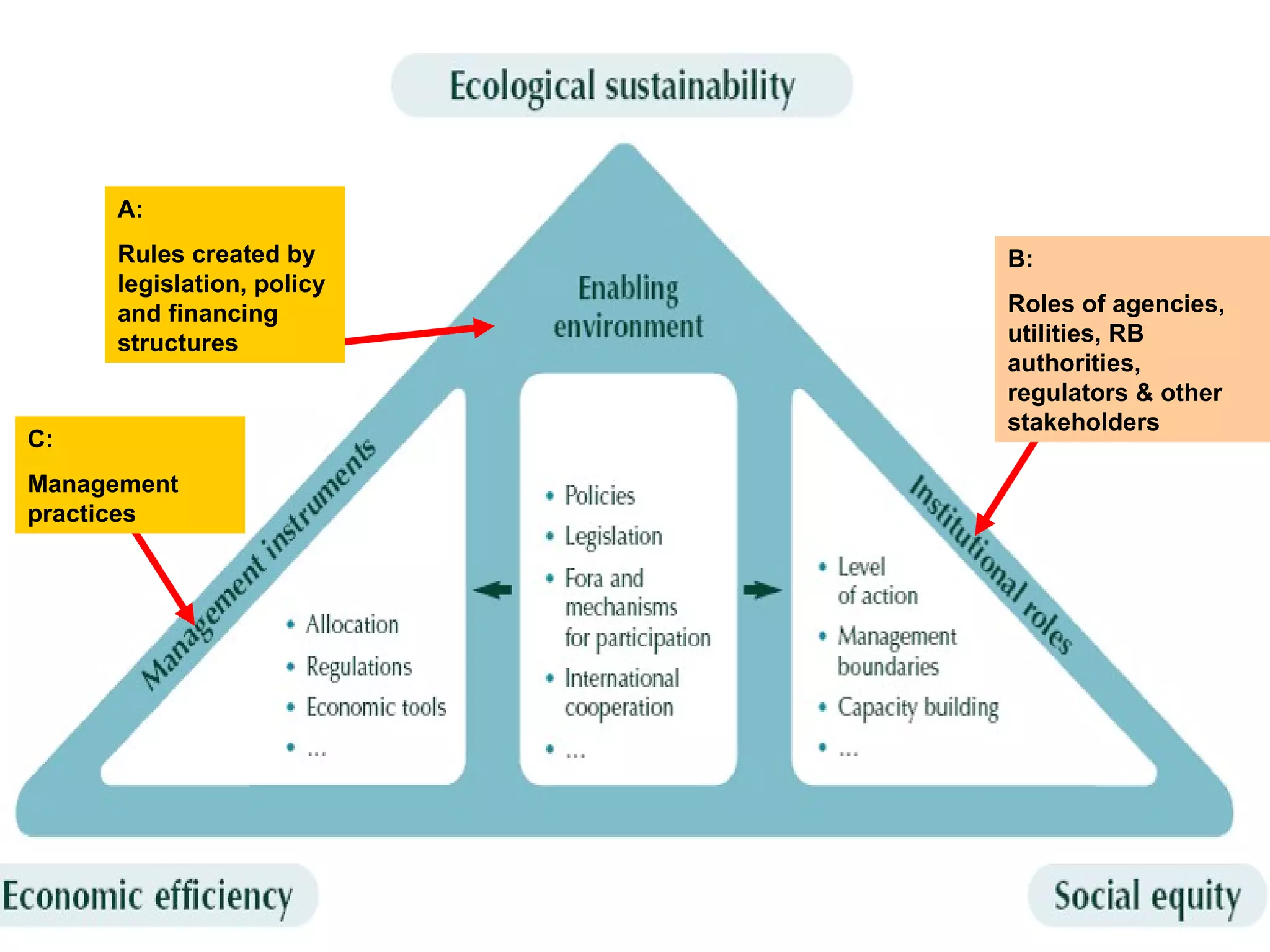
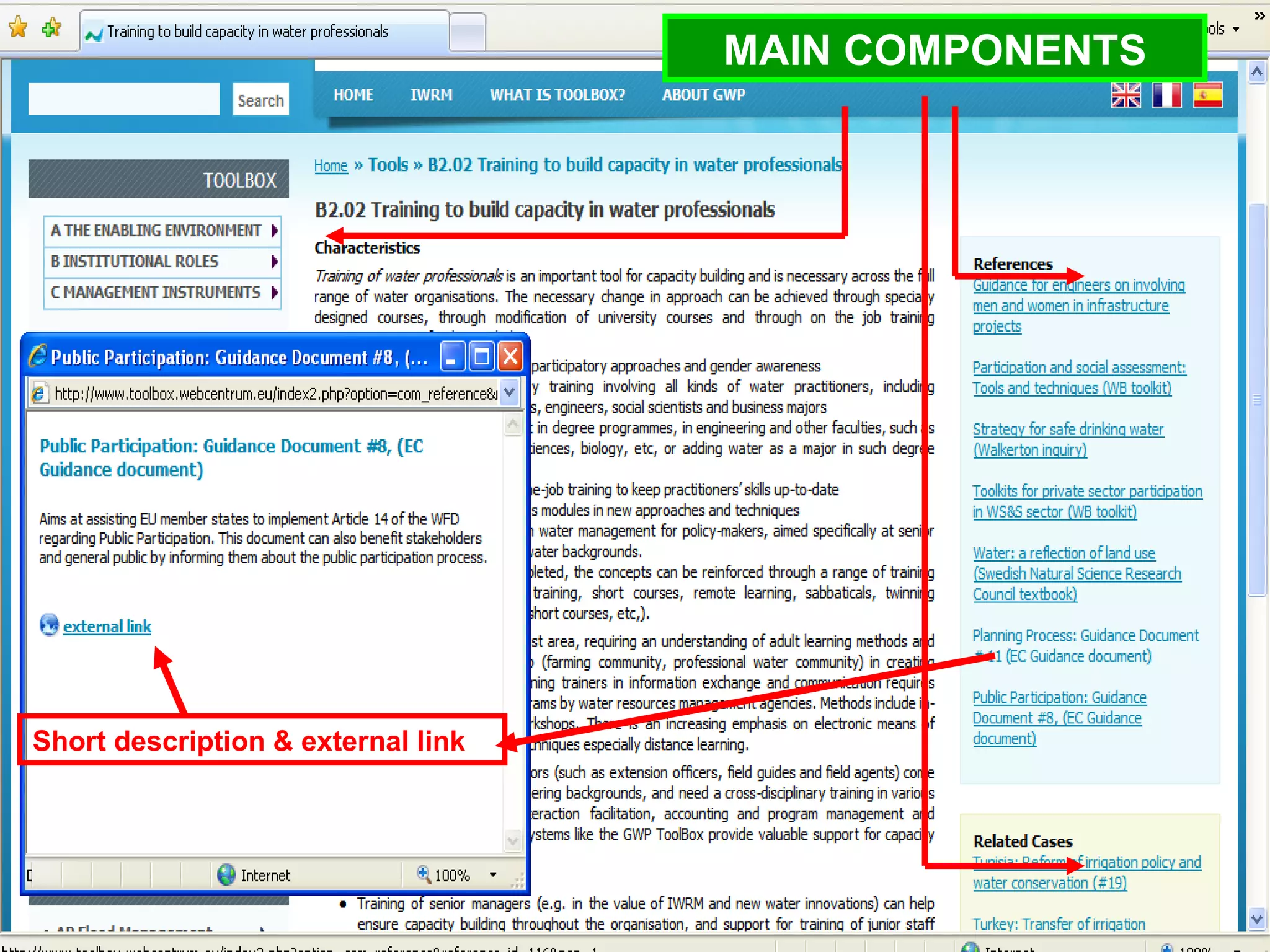
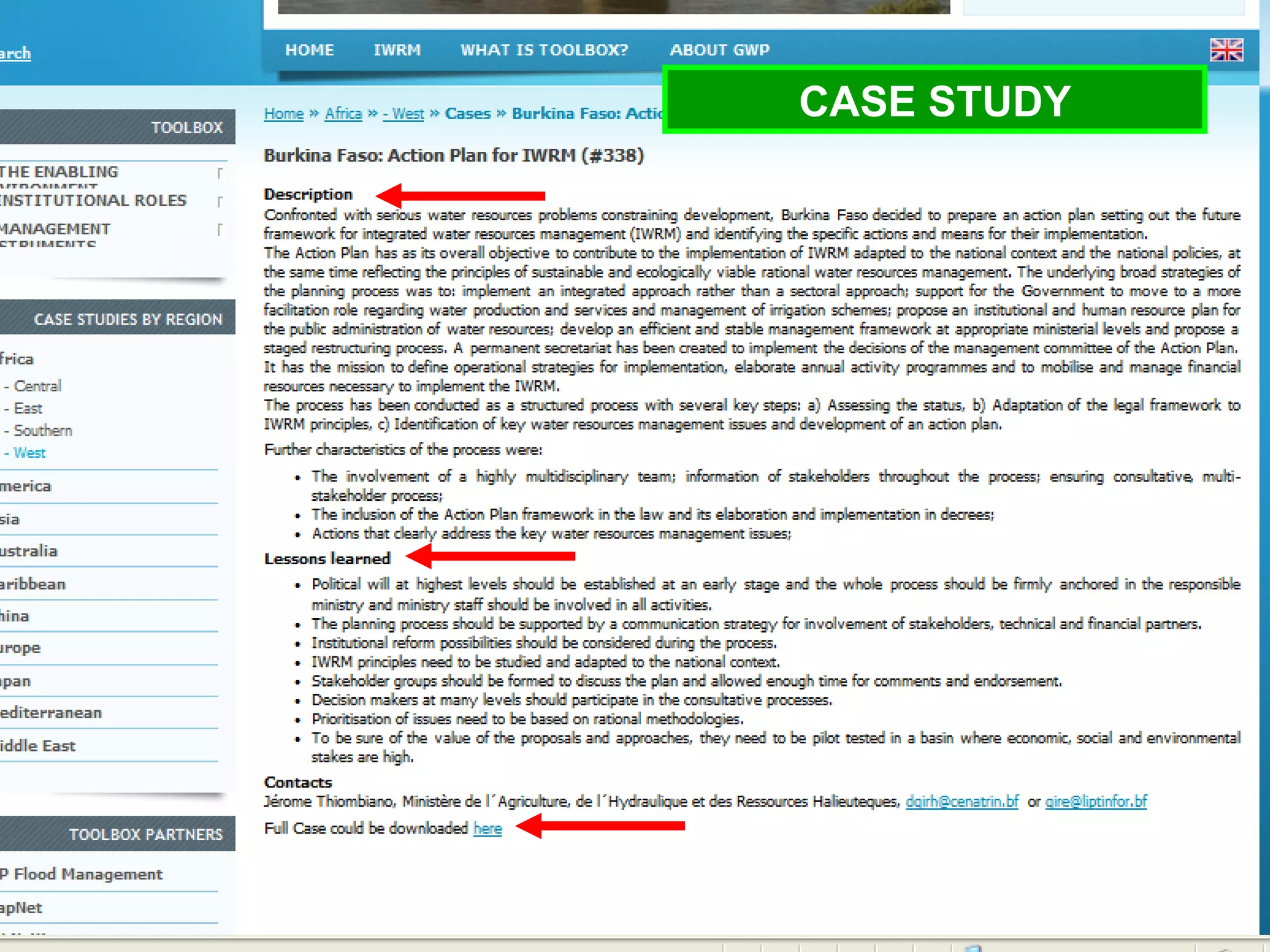
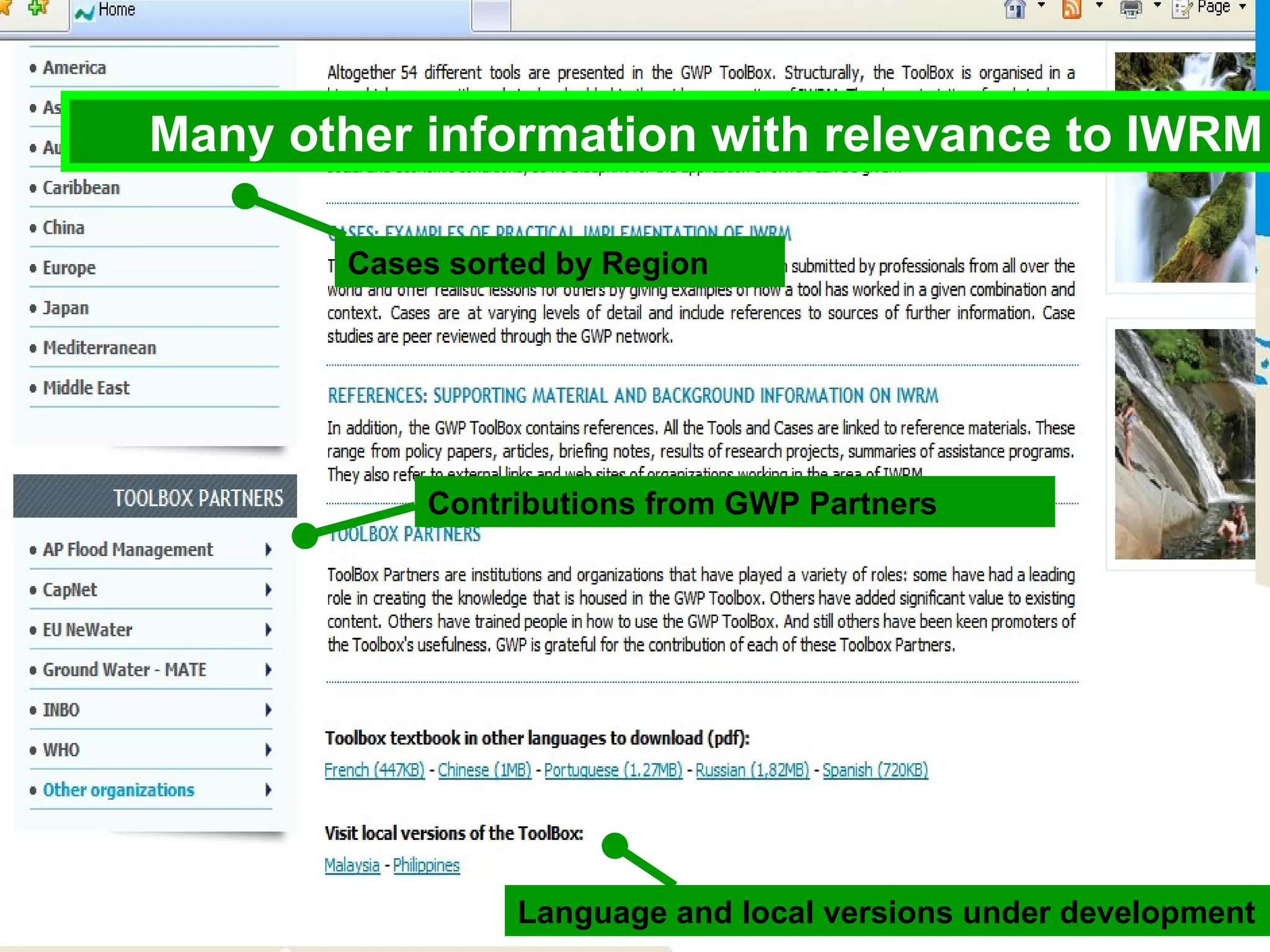
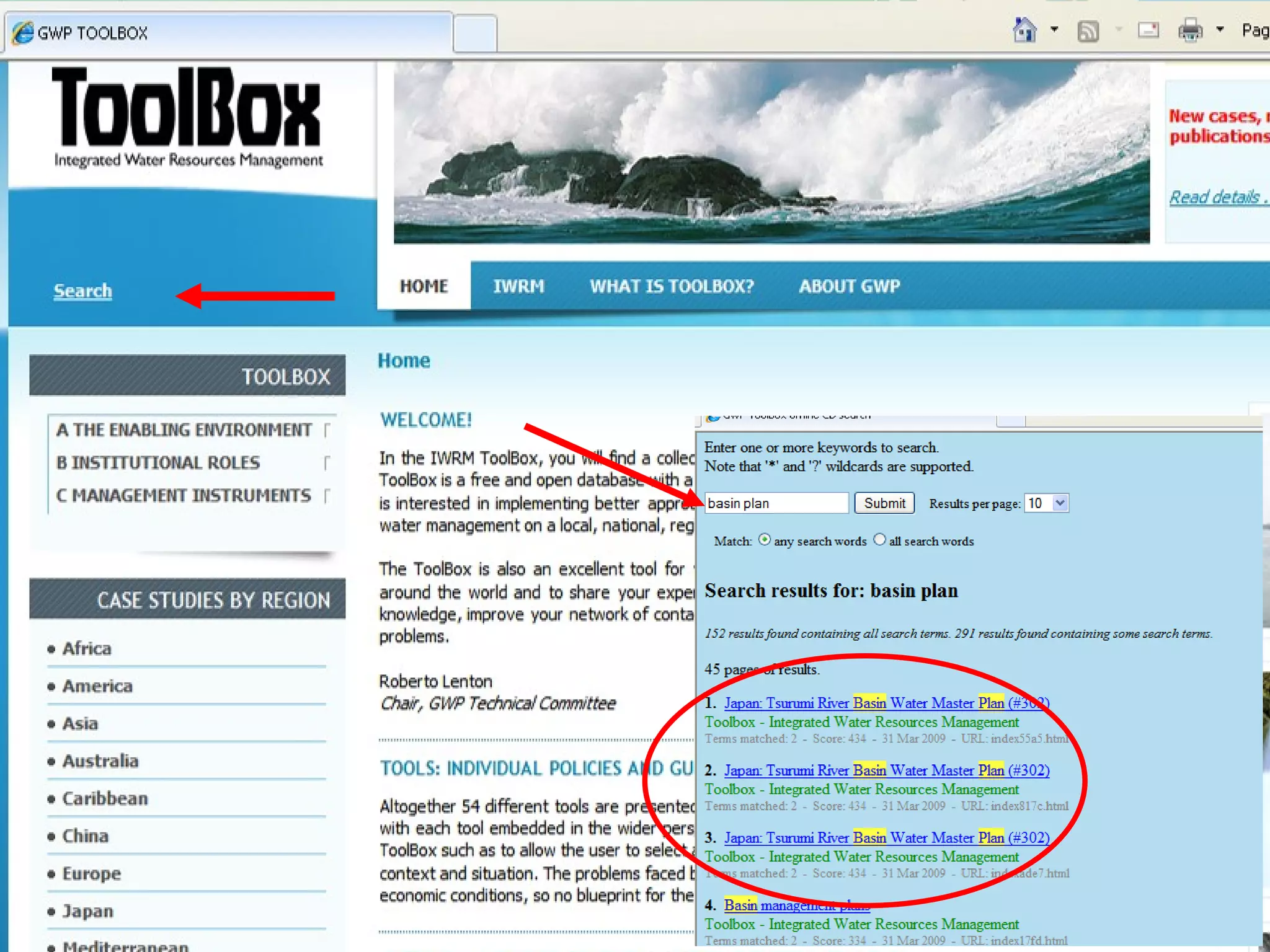
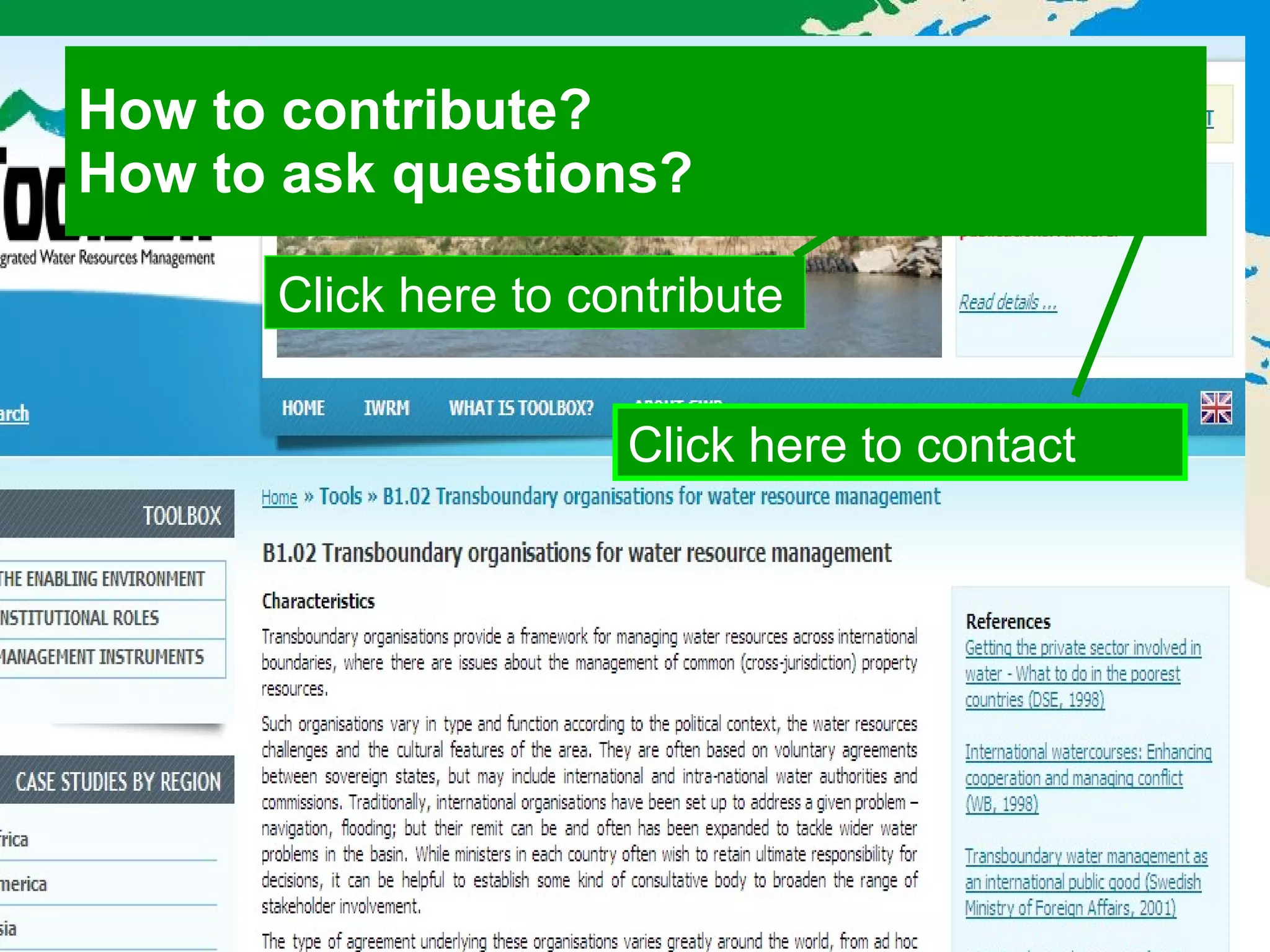
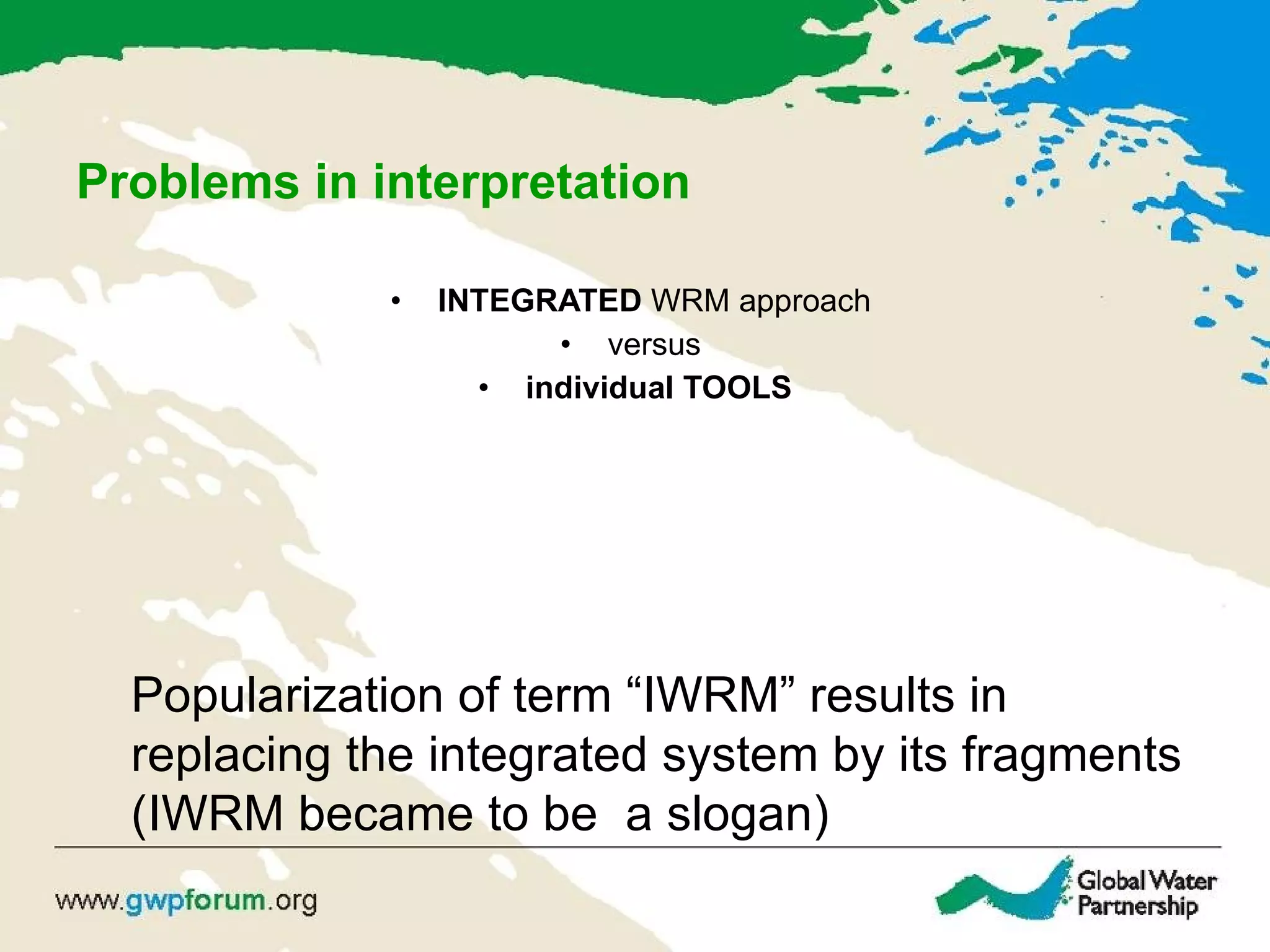
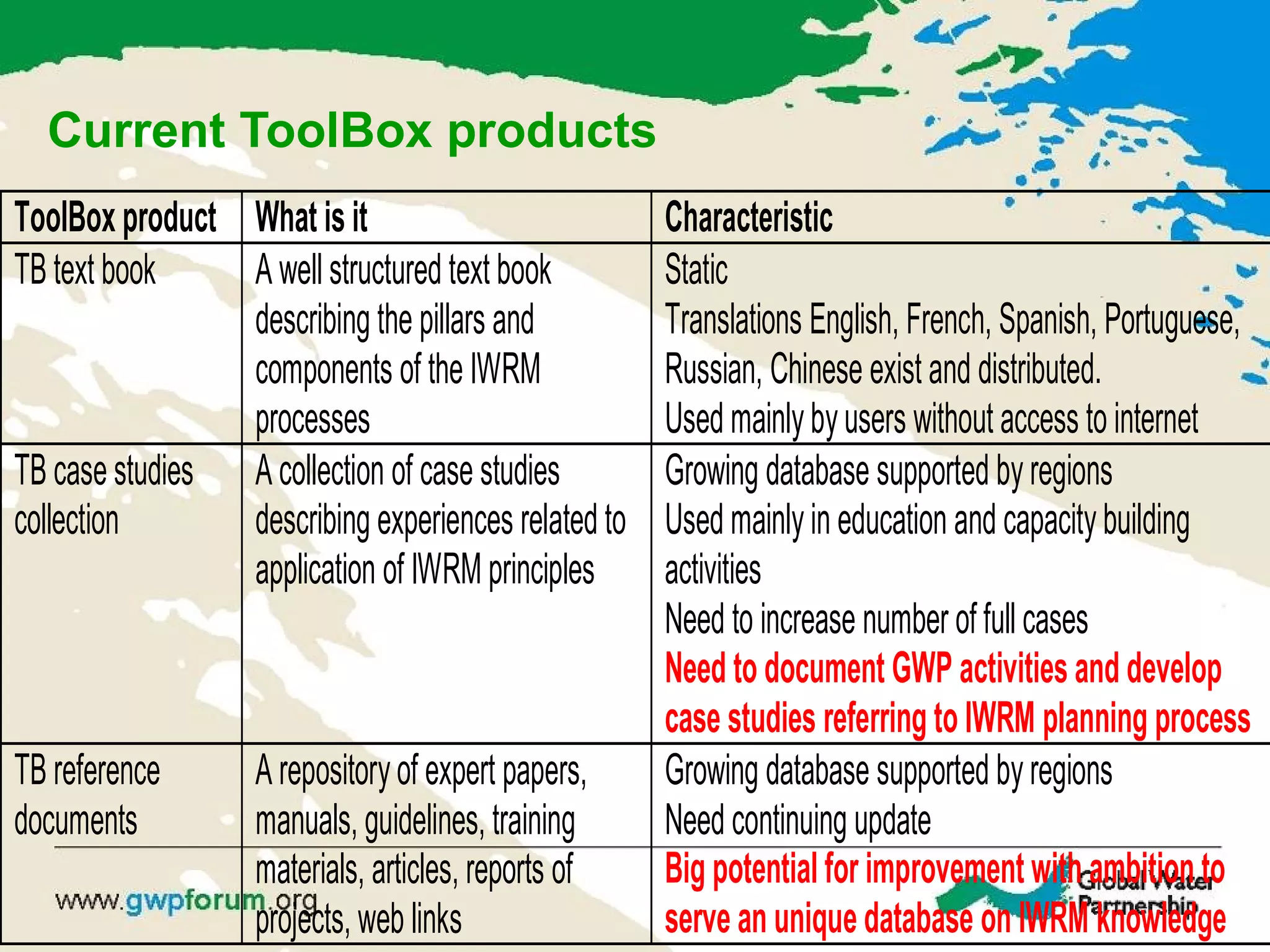
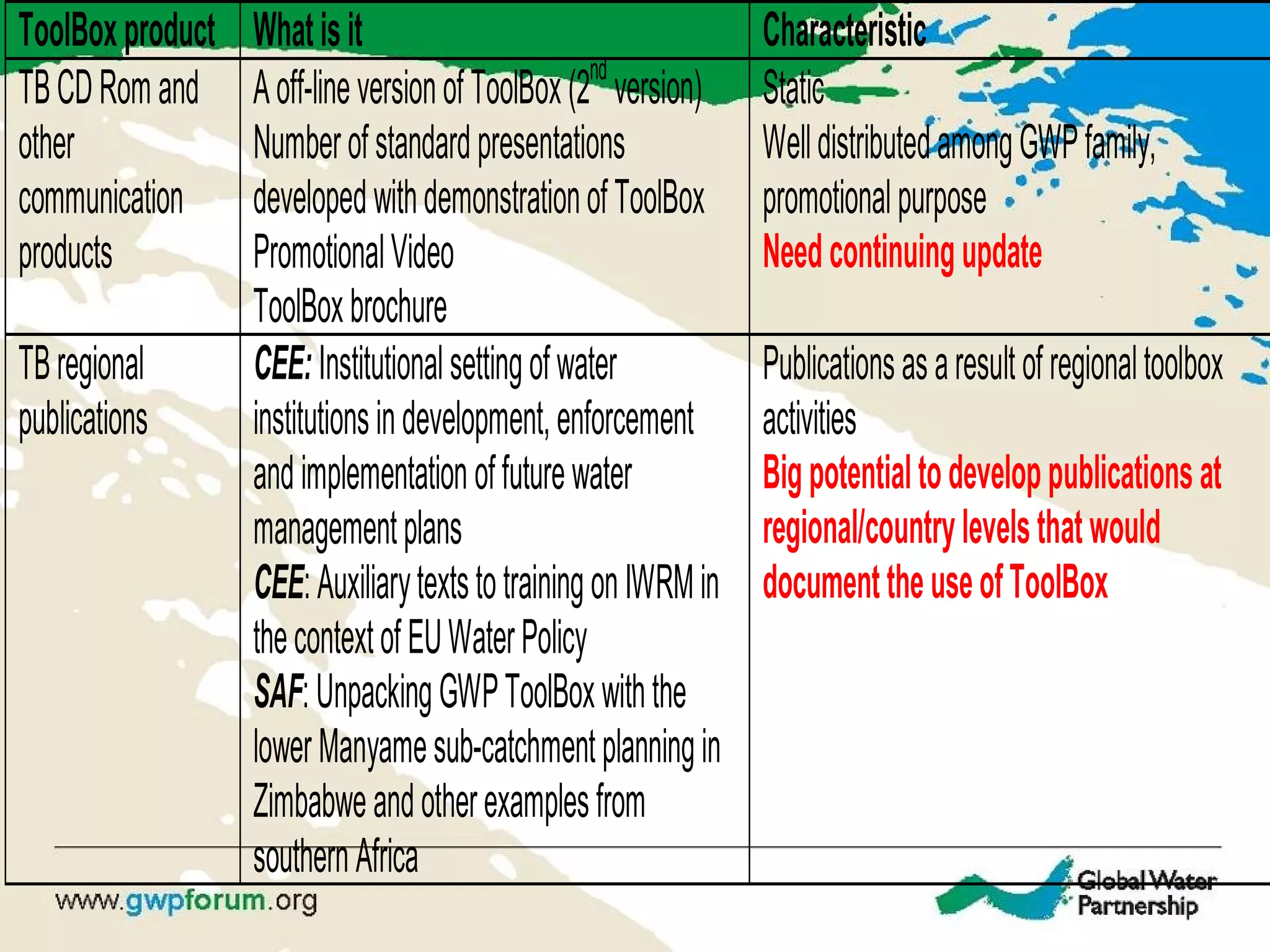
The document describes the GWP ToolBox, an online knowledge sharing tool for integrated water resources management (IWRM). It contains three main components: 1) 54 tools that provide guidelines for implementing IWRM; 2) 193 case studies that illustrate how the tools work in practice; 3) 178 references like documents, manuals, and papers to support IWRM knowledge. The ToolBox aims to establish a global platform for sharing IWRM knowledge and building capacity. It provides best practices, case studies, and relevant publications. Users can contribute additional case studies, references, and questions.