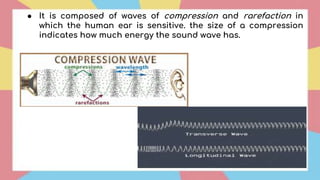
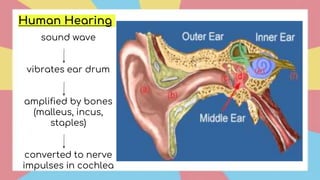
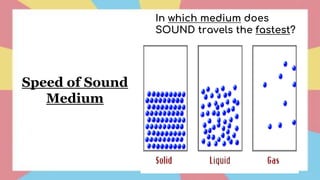
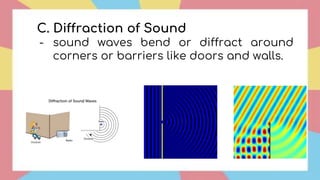
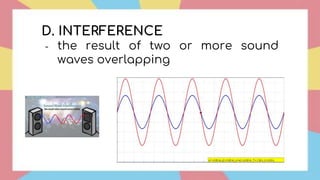
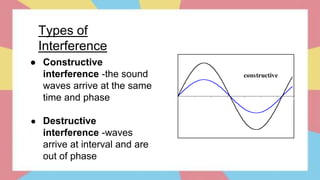
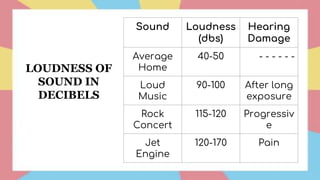
Sound is a form of energy that propagates as mechanical waves, requiring a medium such as air, water or solid material to transmit energy. It is caused by vibrations which create pressure variations that propagate outward as a wave at the speed of sound. The speed of sound depends on factors like the density, elasticity and temperature of the medium, being fastest in solids and slowest in gases. Sound exhibits properties like reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference as it travels and interacts with surfaces and other sounds.