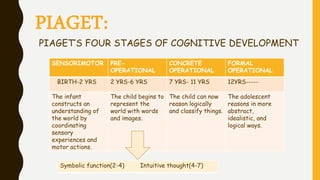
This document compares the theories of Vygotsky and Piaget on child cognitive development. Vygotsky emphasized the social context of learning and believed that language acquisition shapes thought, while Piaget saw cognition as directing language development. Piaget outlined four stages of cognitive development from infancy to adulthood focused on adapting to the environment. In contrast, Vygotsky did not define strict stages and emphasized the zone of proximal development and language as a cultural tool. The theories have different implications for education, with Vygotsky seeing it as central to language learning and Piaget viewing it as refining an individual's language.