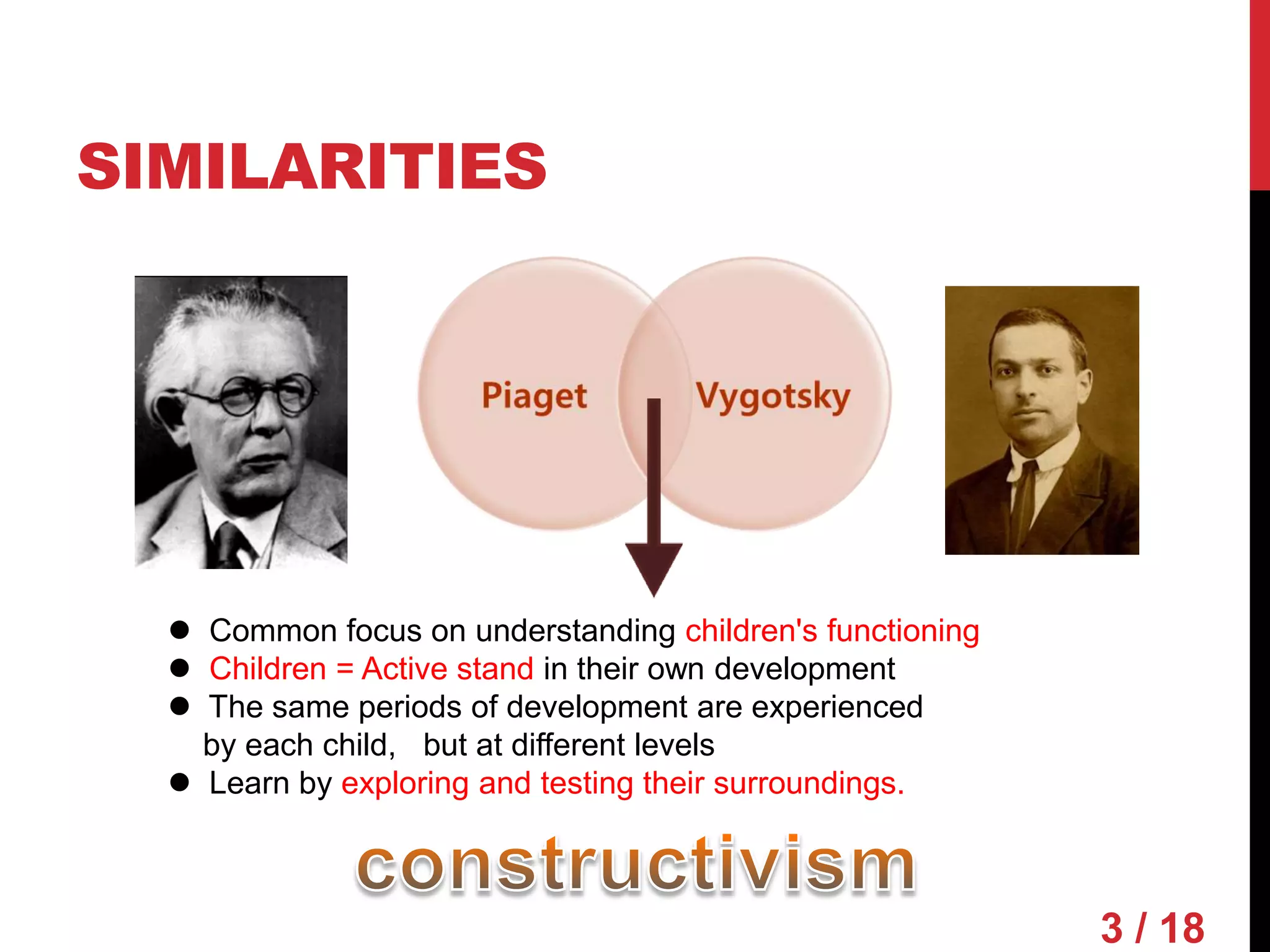
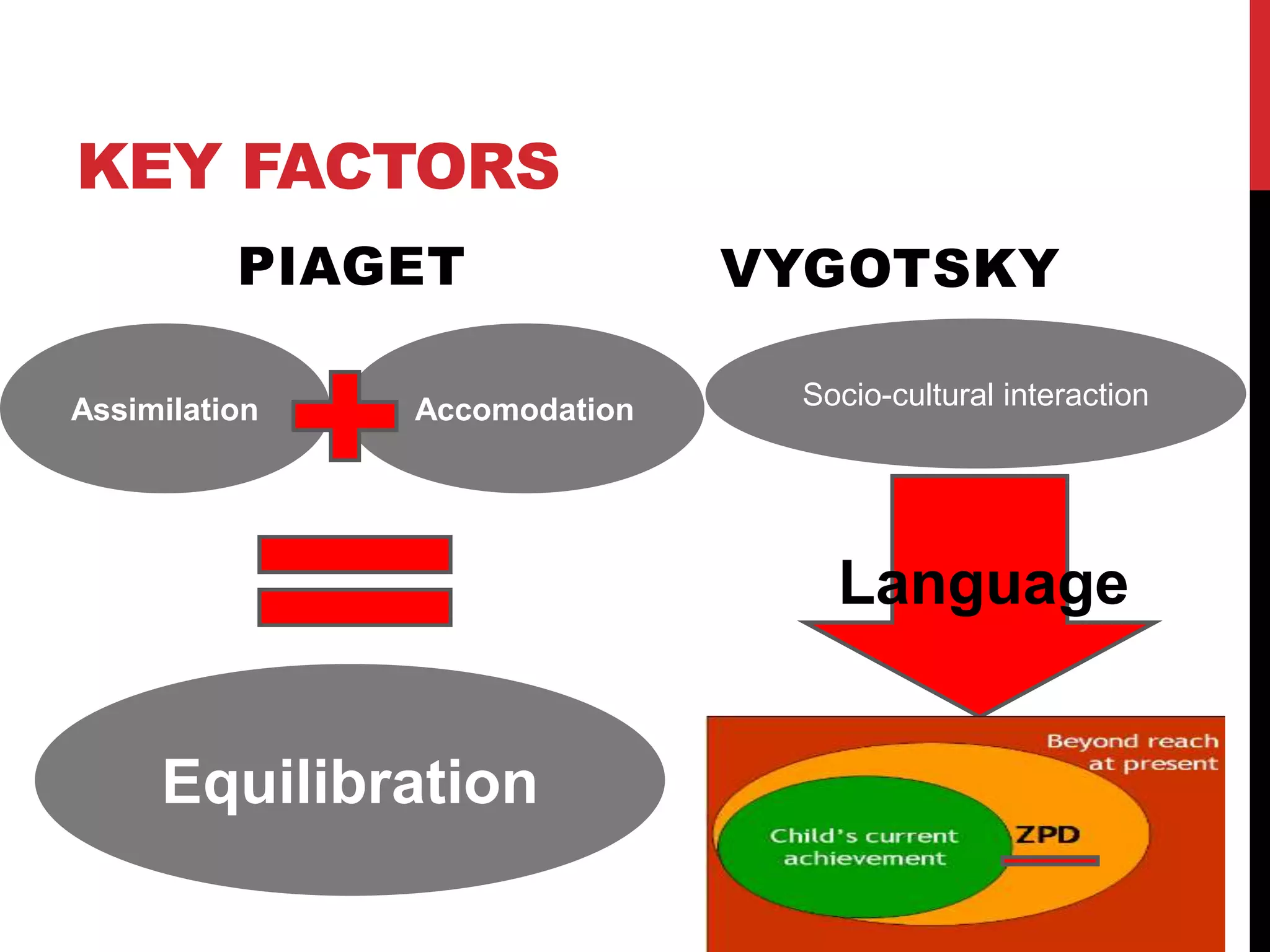
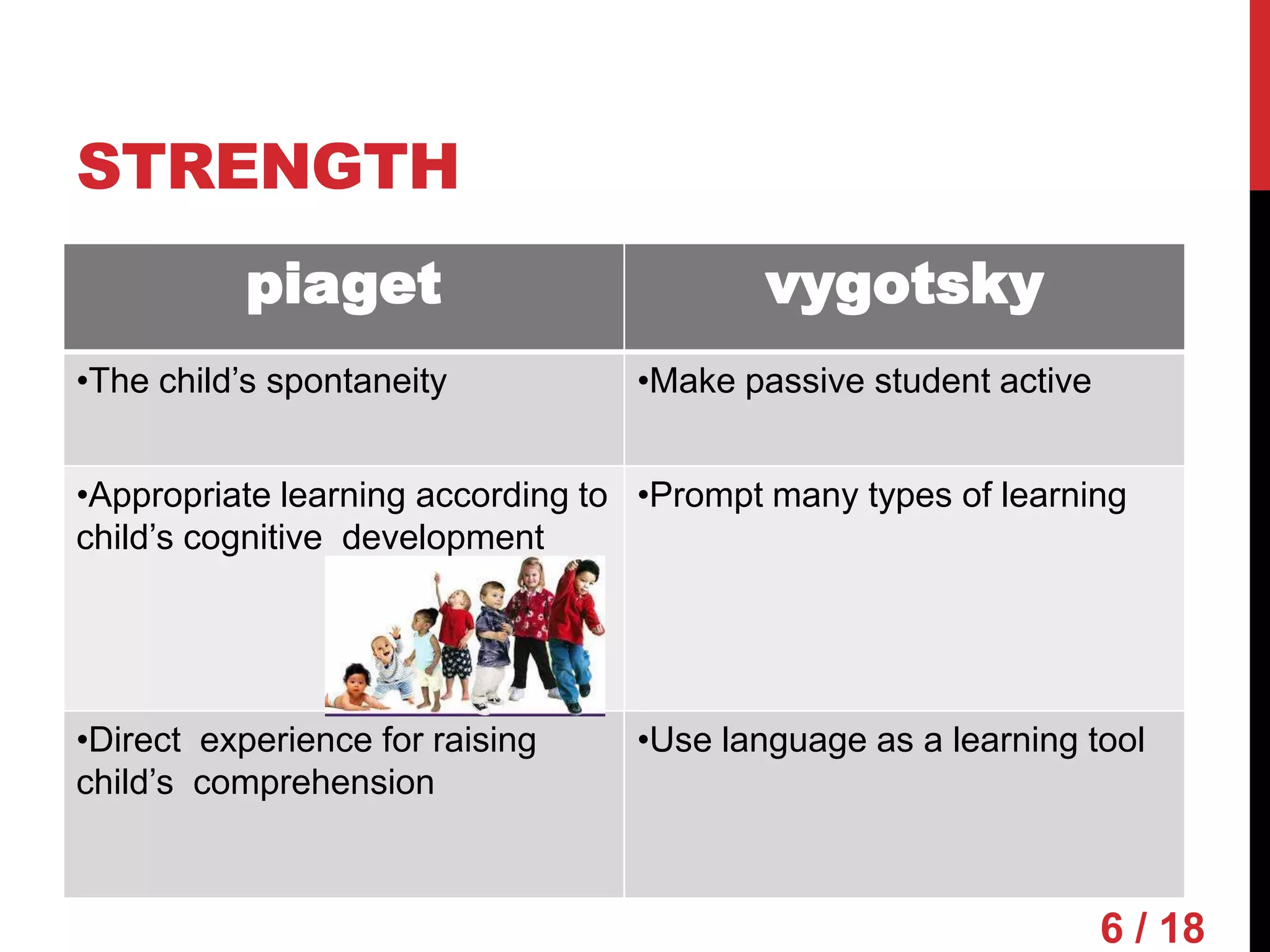
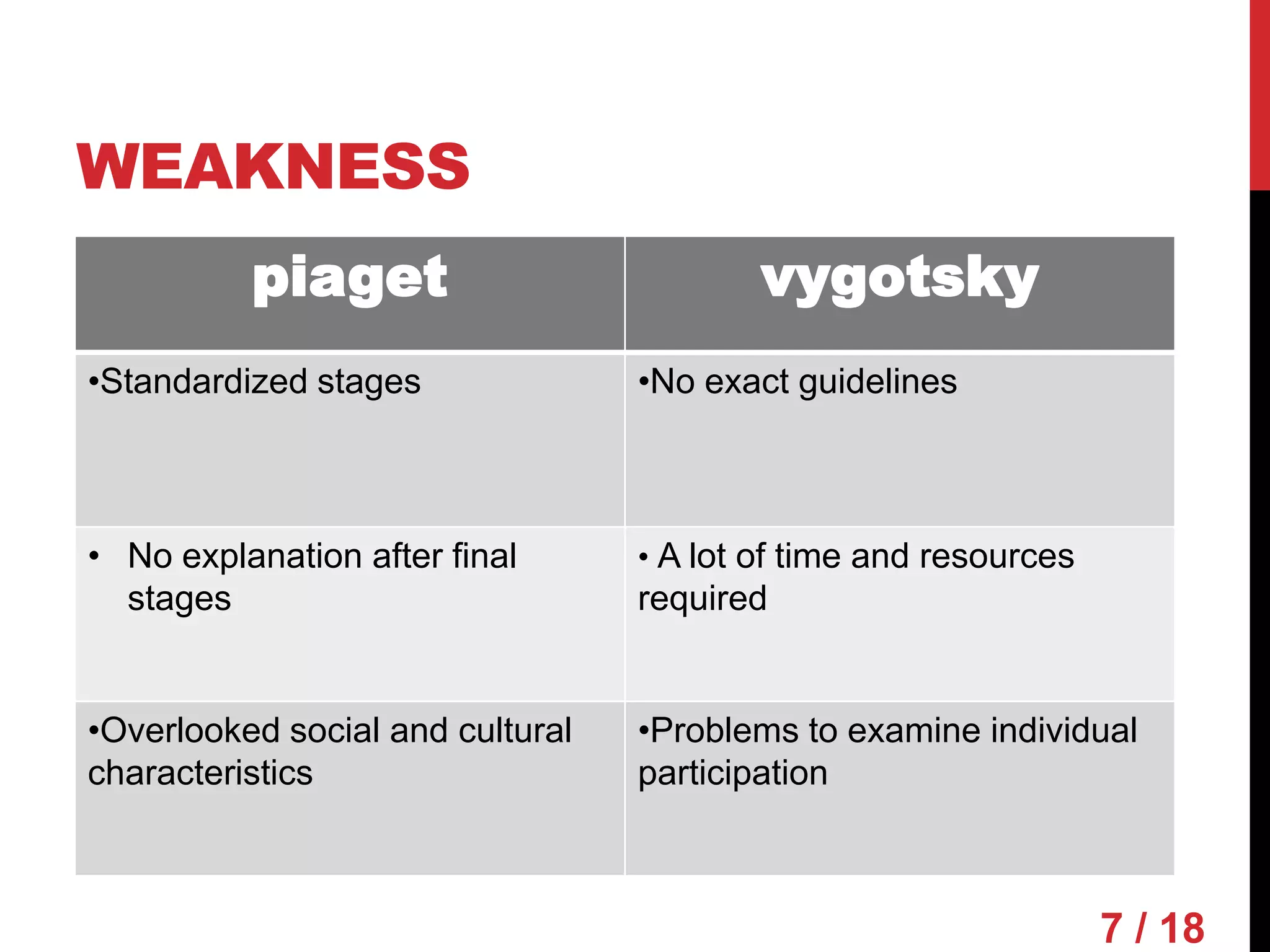
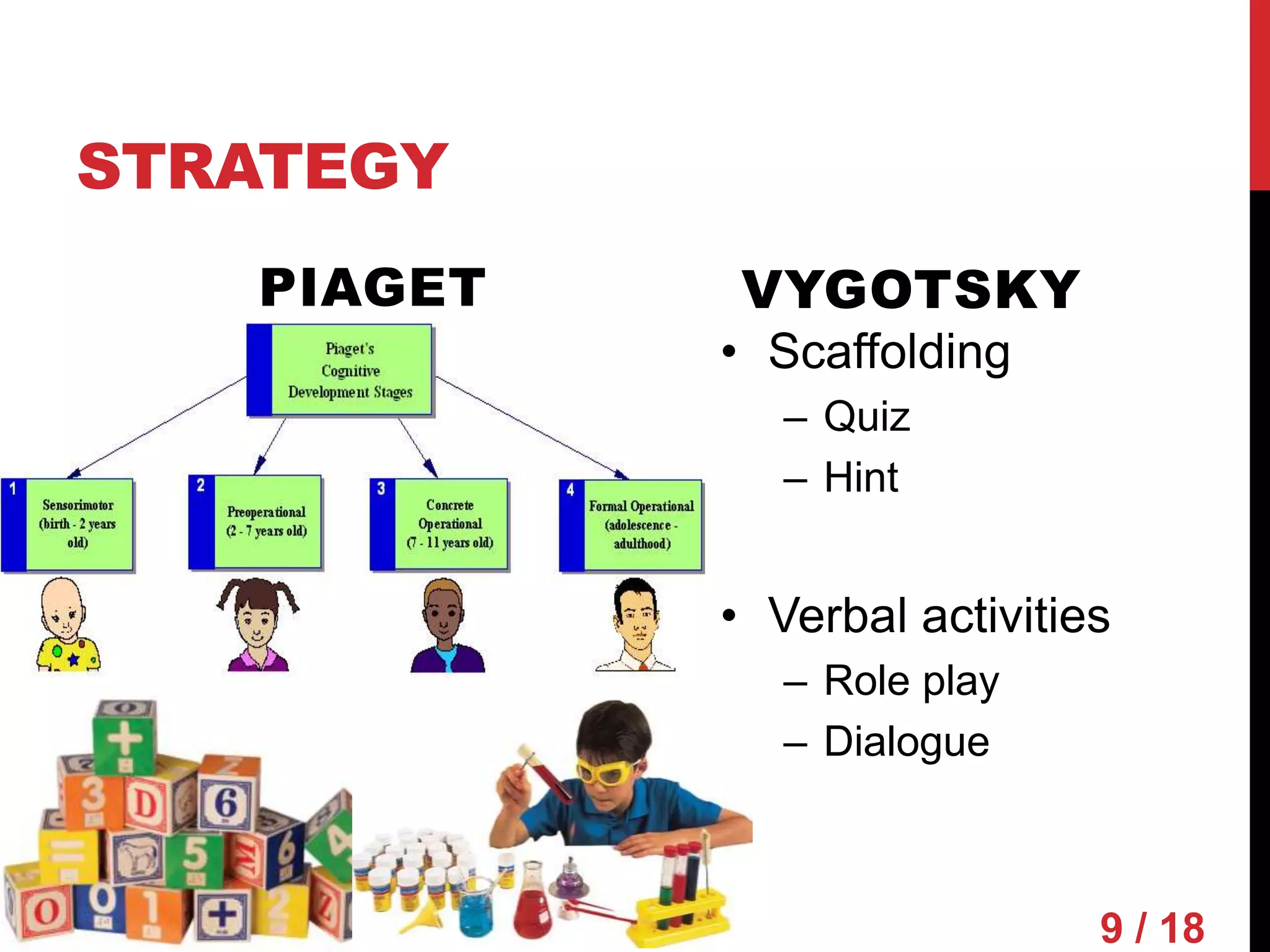
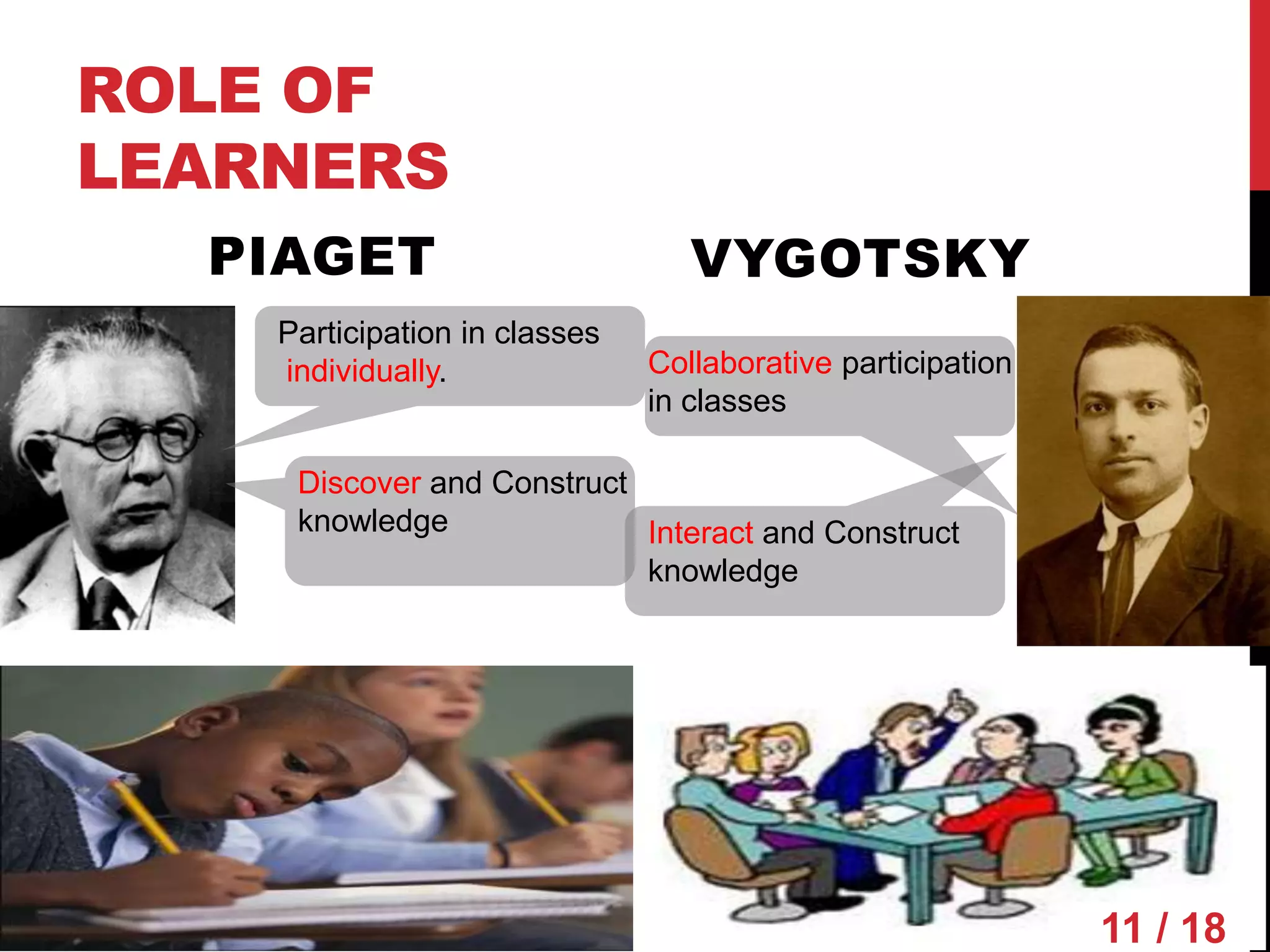
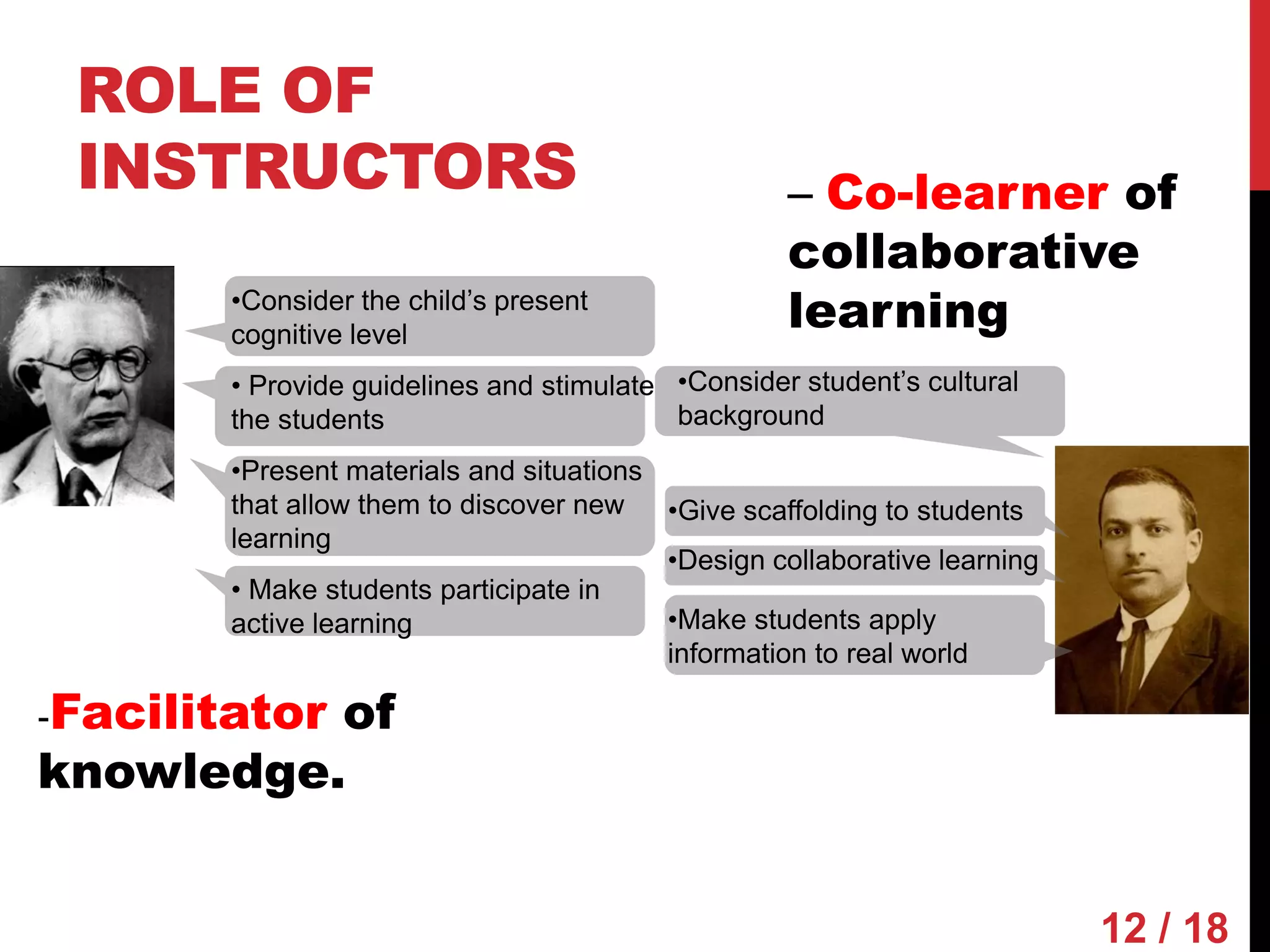
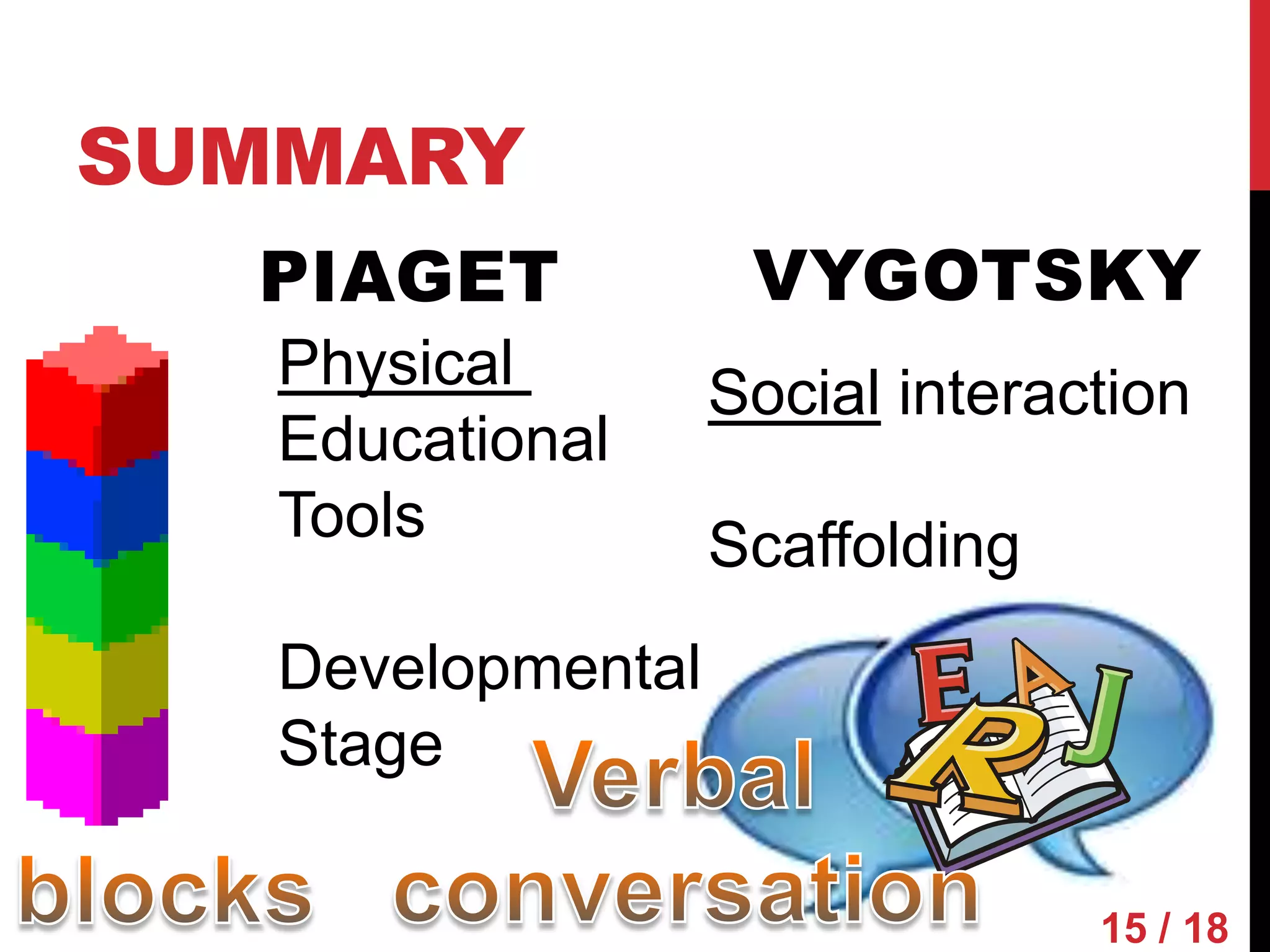
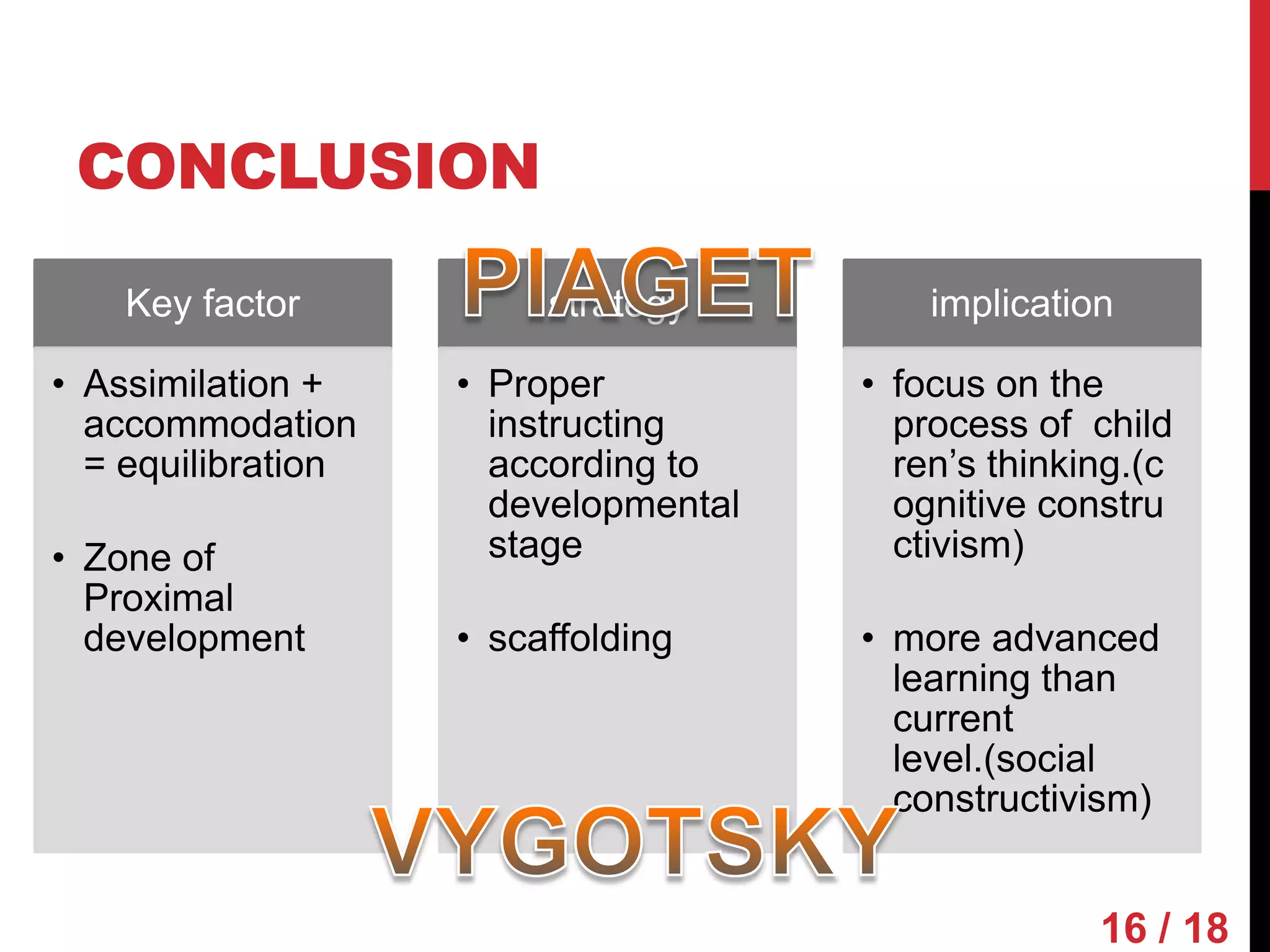
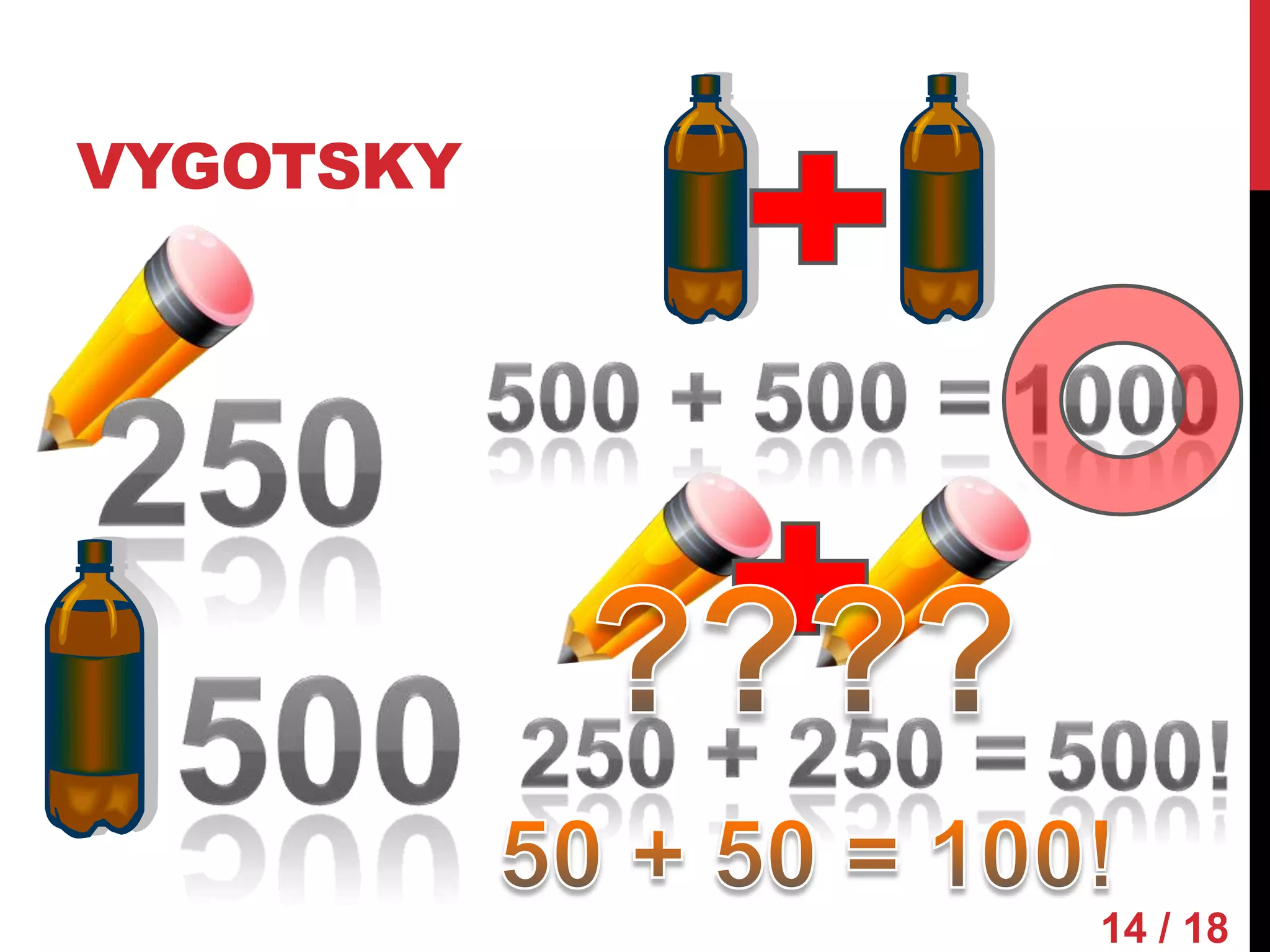Piaget and Vygotsky were both influential developmental psychologists who studied how children learn and develop. While they agreed that children are active participants in their own learning, they differed on some key factors. Piaget focused on physical development and interactions, emphasizing assimilation and accommodation. Vygotsky emphasized social interactions and language, seeing learning as occurring through scaffolding within a child's zone of proximal development.