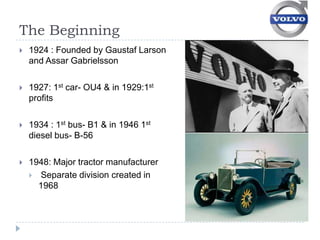
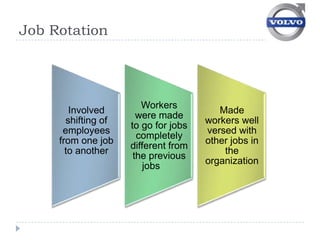
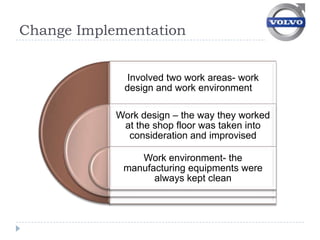
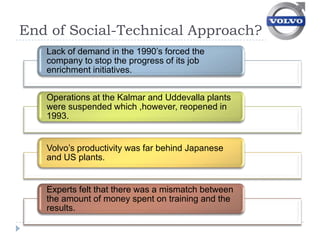
Volvo implemented job enrichment programs in the 1970s to address high employee turnover and absenteeism. This included (1) job rotation to expose workers to different roles, (2) small self-managed work groups, and (3) management-employee councils to improve communication and involvement in decision-making. While these programs improved conditions initially, Volvo struggled with productivity and had to revert to traditional assembly lines by the 1990s due to market pressures.