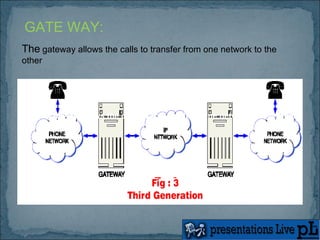
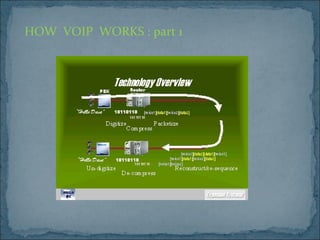
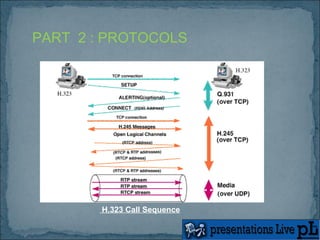
The document presents an overview of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology. It discusses how gateways allow calls to transfer between networks, and covers protocols like H.323 and encoding standards like G.723.1 that are used for VoIP calls. Benefits of VoIP include using a single network infrastructure and simple upgrades. Challenges can include latency, jitter and packet loss. The conclusion is that VoIP will continue growing as more voice traffic moves to data networks.