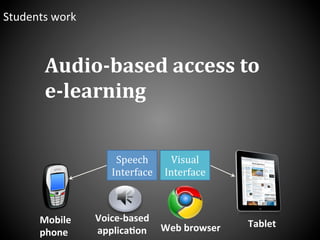
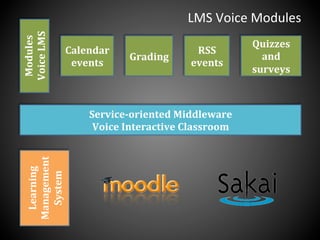
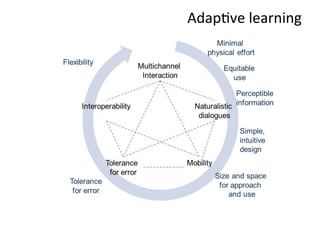
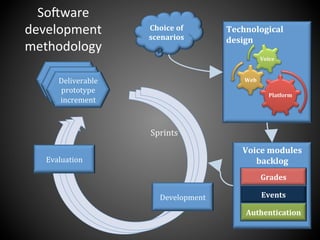
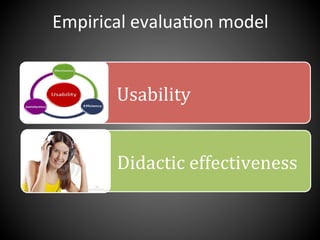
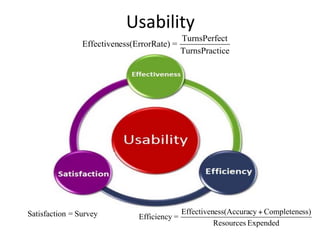
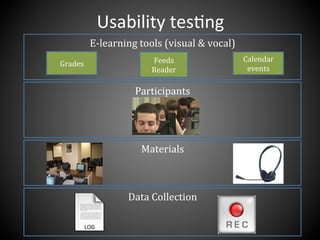
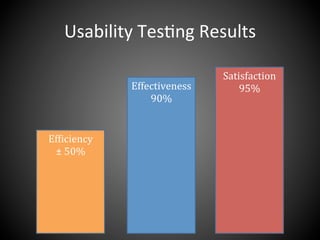
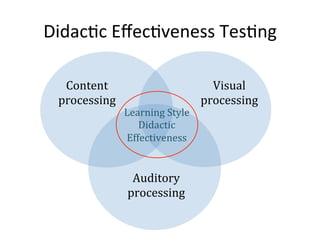
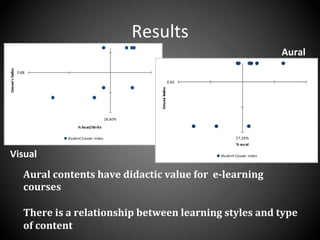
This document presents a framework for voice interactive learning and its evaluation. The framework was developed by researchers in Spain to integrate audio features into e-learning using a service-oriented middleware and voice modules. They developed an empirical evaluation model to assess usability and didactic effectiveness. Testing showed the voice interactive classroom had high usability ratings and auditory content was educationally valuable for different learning styles. The researchers concluded their evaluation method should be expanded and applied to further analyze memorability and learnability.