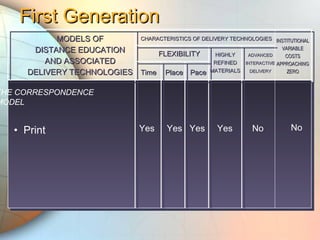
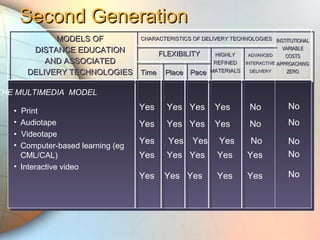
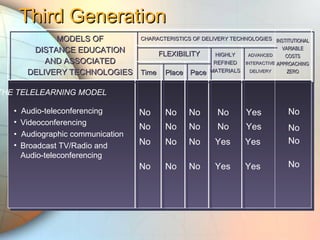
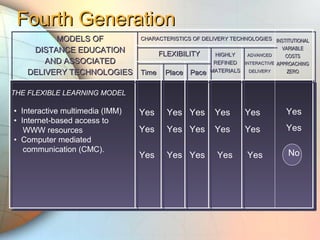
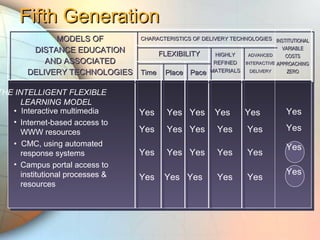
E-learning utilizes electronic technologies to provide educational content outside of a traditional classroom. It includes various formats from knowledge databases and online support to synchronous training, asynchronous self-study, and instructor-led methods. Keys to effective e-learning include varying content types, interactive elements like quizzes, and encouraging interaction. Models of distance education have evolved from early print-based correspondence to today's intelligent flexible learning using interactive multimedia, internet access, and automated response systems. Benefits of e-learning include lower costs, flexibility of location and scheduling, ease of updating, and consistent standardized content.