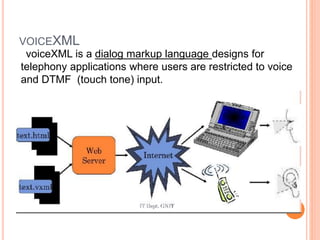
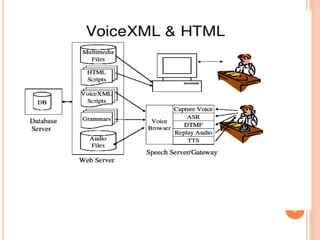
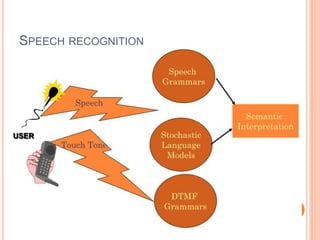
Voice browser is a device that interprets voice input and generates voice output. It interprets scripts specifying what verbal information to present to users and when. Voice browsers were motivated by the fact that there are more phones than computers globally, phone usage is growing, and speaking is natural for phones. Key technologies include speech recognition to convert voice to text, speech synthesis to convert text to voice output, and VoiceXML for building voice applications. Voice browsers allow accessing information and services by voice on mobile devices.