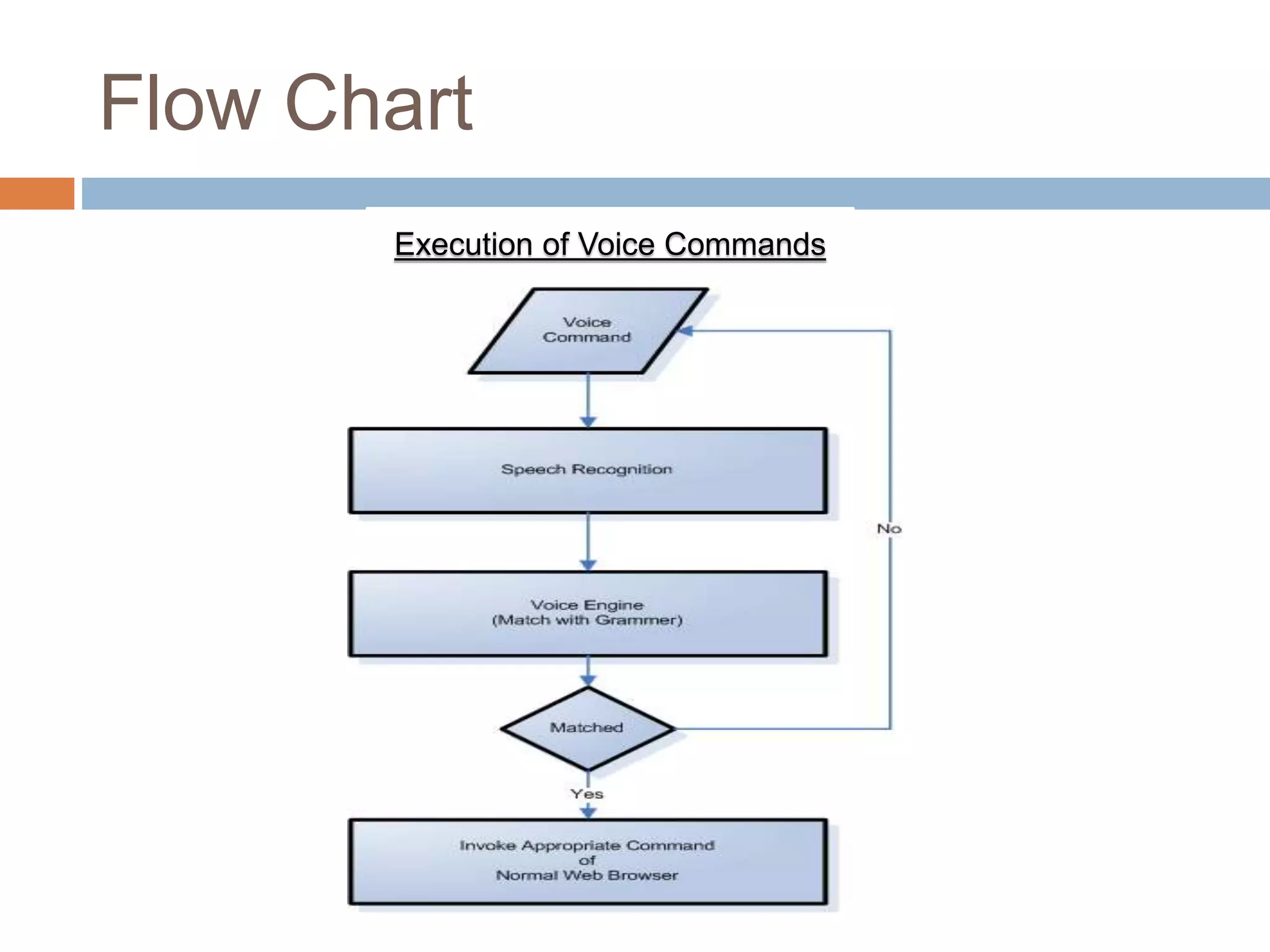
This document presents a voice operated web browser called Smowser. Smowser uses Microsoft Speech SDK for voice control integration to allow users to operate a web browser using voice commands. The voice commands are converted to text and matched to a set of predefined commands to execute browser functions like opening bookmarks, refreshing pages, scrolling, and tab operations. The presentation concludes that voice-based browsers allow for more interactive browsing and that greater accuracy is still needed for speech recognition, especially for accent recognition.