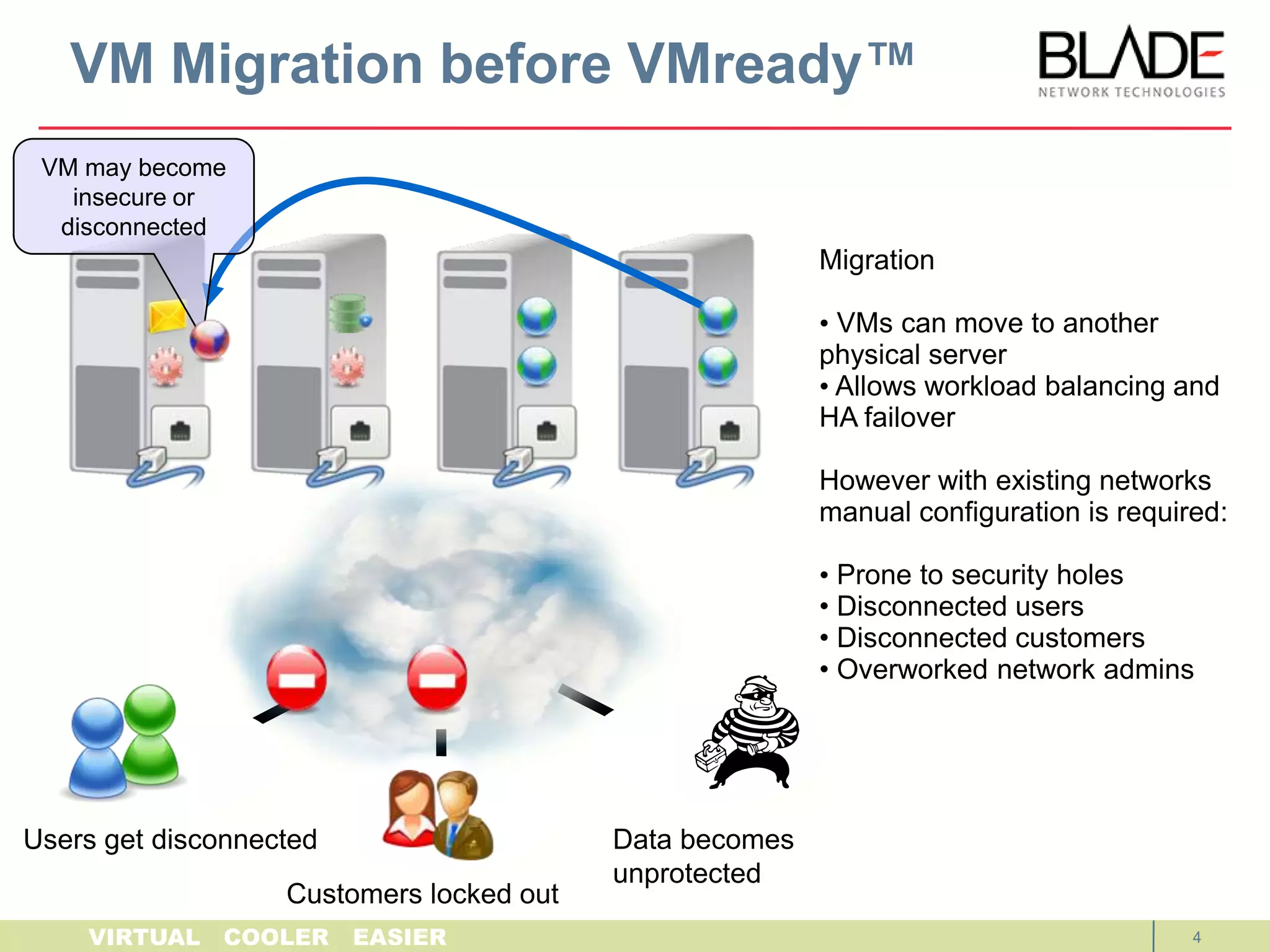
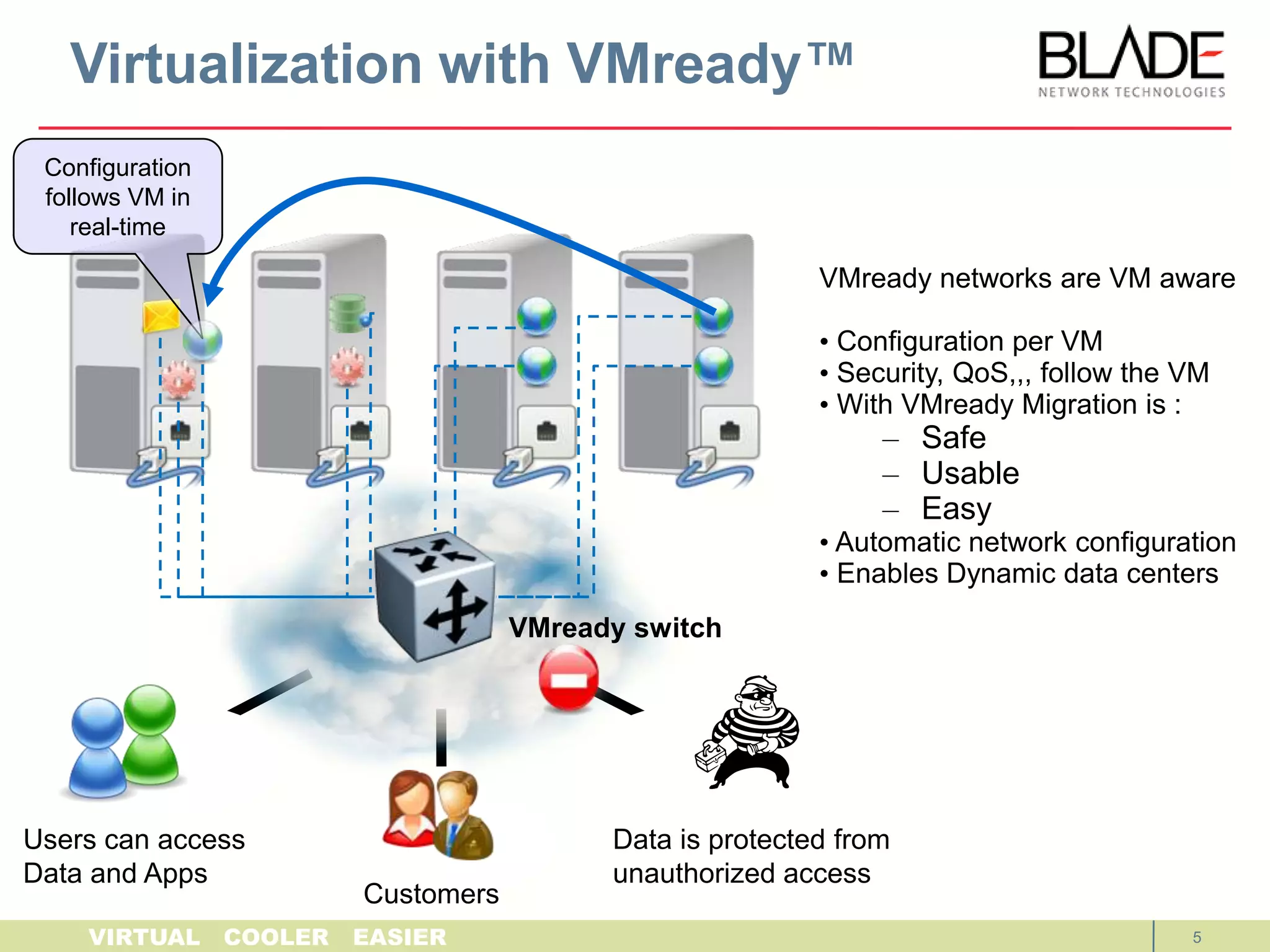
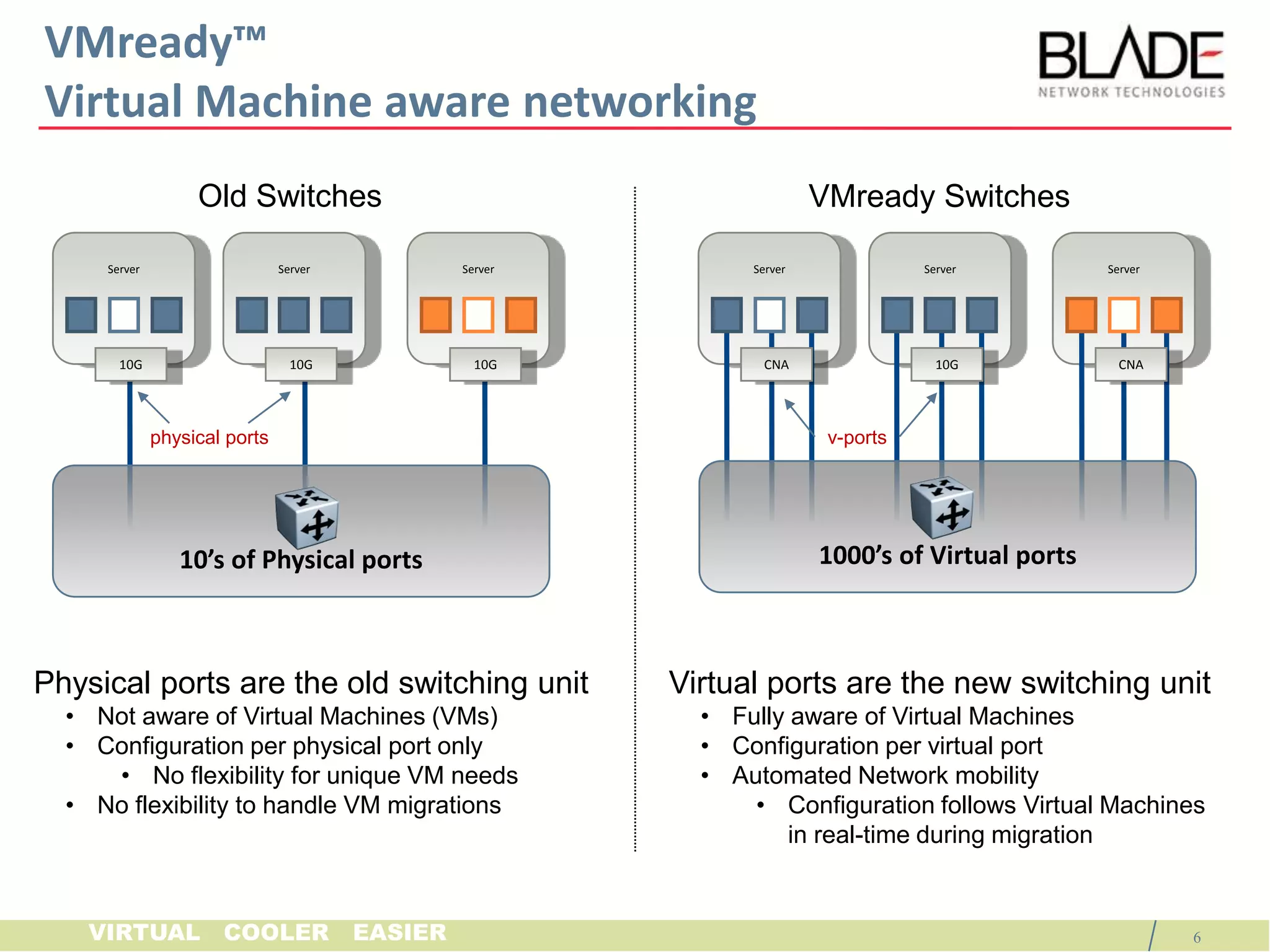
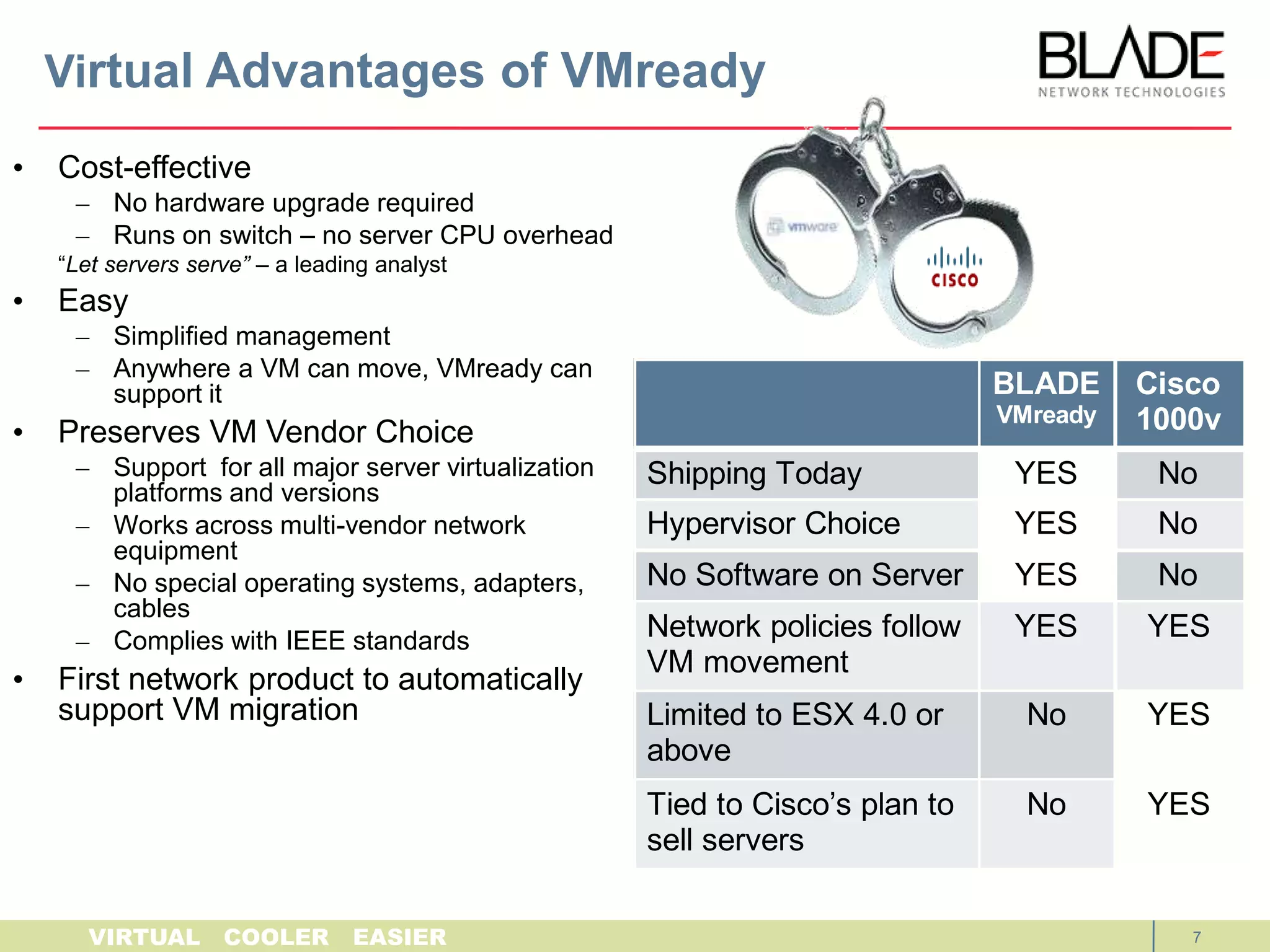
The document discusses BLADE Network Technologies' VMready product, which provides virtual machine aware networking capabilities that allow network administrators to configure and manage virtual machine network traffic, ensuring network connectivity and security when virtual machines migrate between physical servers. VMready integrates with VMware vCenter to automate configuration of virtual switches and provide visibility of virtual machine information. The VMready switch module from BLADE Network Technologies brings these virtualization-aware networking features to the HP BladeSystem through firmware upgrades.

![Current Virtualization market playersVMware™ VMware is the current market leader in server virtualization. Their flagship product vSphere provides the infrastructure and management solutions for large enterprise level virtual environmentsXen Xen is an open-source hypervisor that is available for Linux and Solaris operating systems. Citrix XenServer™ is a commercial and fully supported Xen hypervisor Microsoft Microsoft’s Hyper-V™ (hypervisor) product runs on Windows 2008 Server™ and is provided with the server software. It supports Microsoft guest virtual machines and some non-Microsoft [Linux] guest operating systems. KVM Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is a hypervisor that is rapidly gaining interest. KVM is part of the Linux kernel since 2.6.20 and provides native virtualization on Intel VT and AMD-V CPUs Oracle VM Oracle VM is a Xen based hypervisor that is fully supported by Oracle2/2/2010BLADE Network Technologies Confidential4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vmready-hp-090826173553-phpapp02/75/VMready-Virtual-Machine-aware-Networking-for-HP-8-2048.jpg)