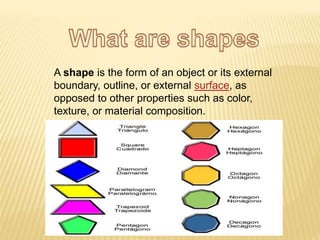
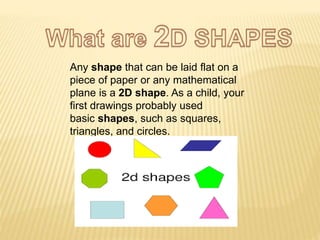
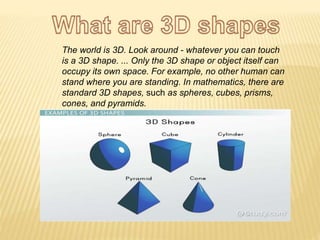
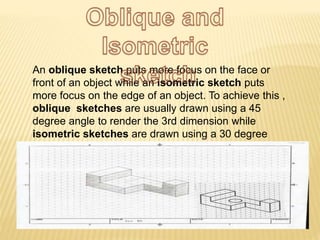
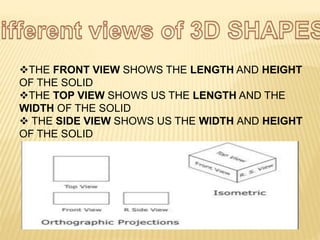
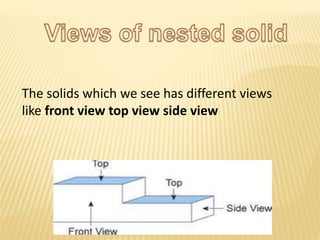
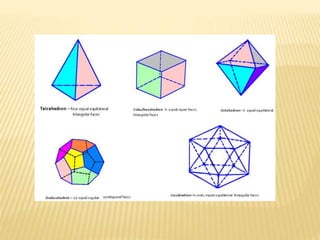
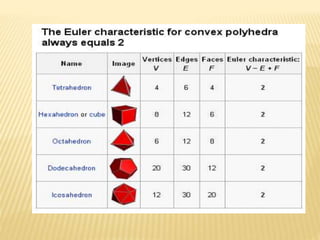
A shape is defined by its external boundary or outline rather than other properties. 2D shapes can be laid flat while 3D shapes occupy their own space. There are standard 3D shapes like spheres, cubes, cones and pyramids. Solids have different views - the front view shows length and height, the top view length and width, and the side view width and height. A solid is a 3D object with length, breadth and thickness bounded by surfaces, and can be classified as polyhedrons or solids of revolution. Regular polyhedra are the most symmetrical shapes and include the five Platonic solids.