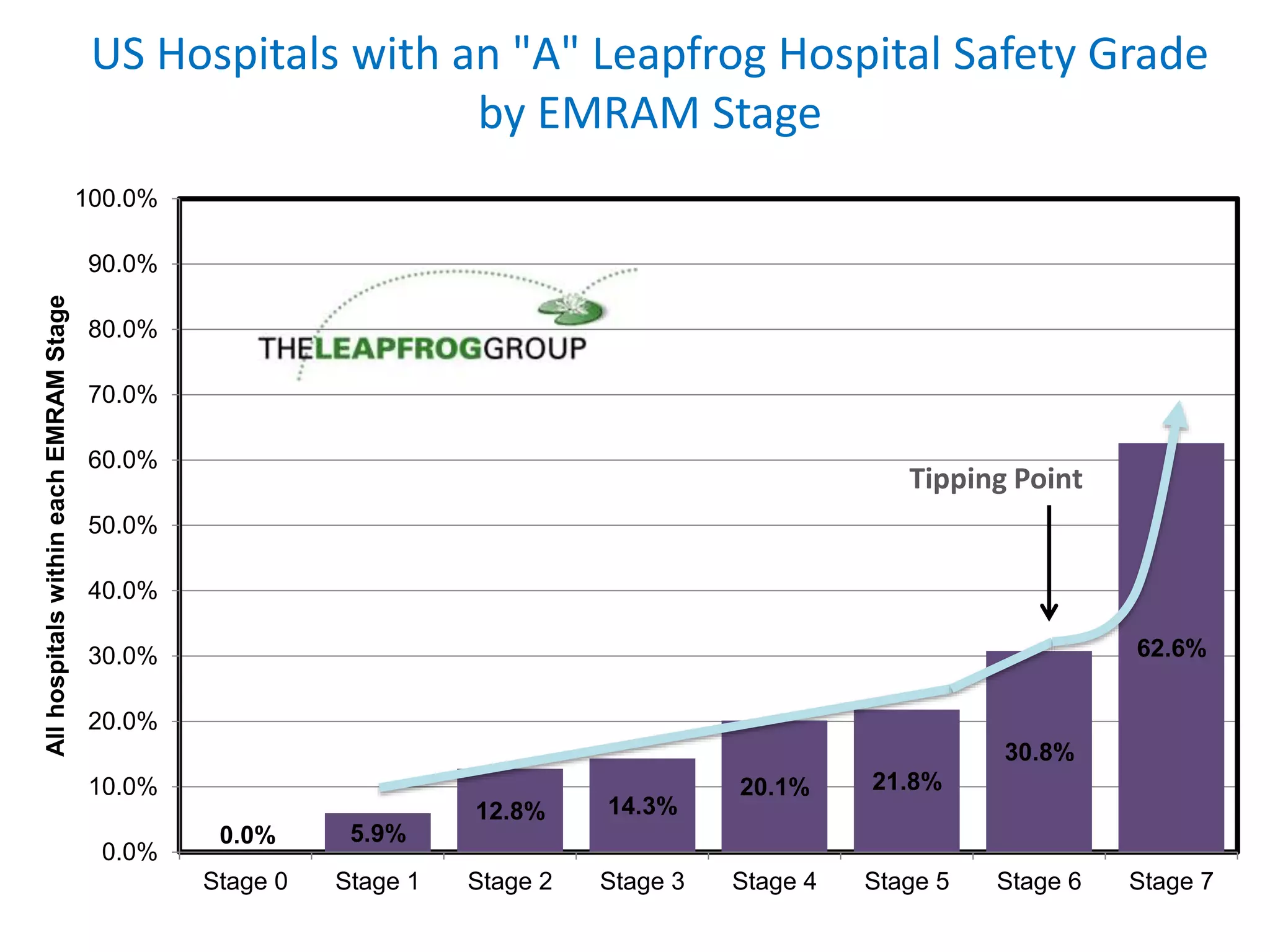
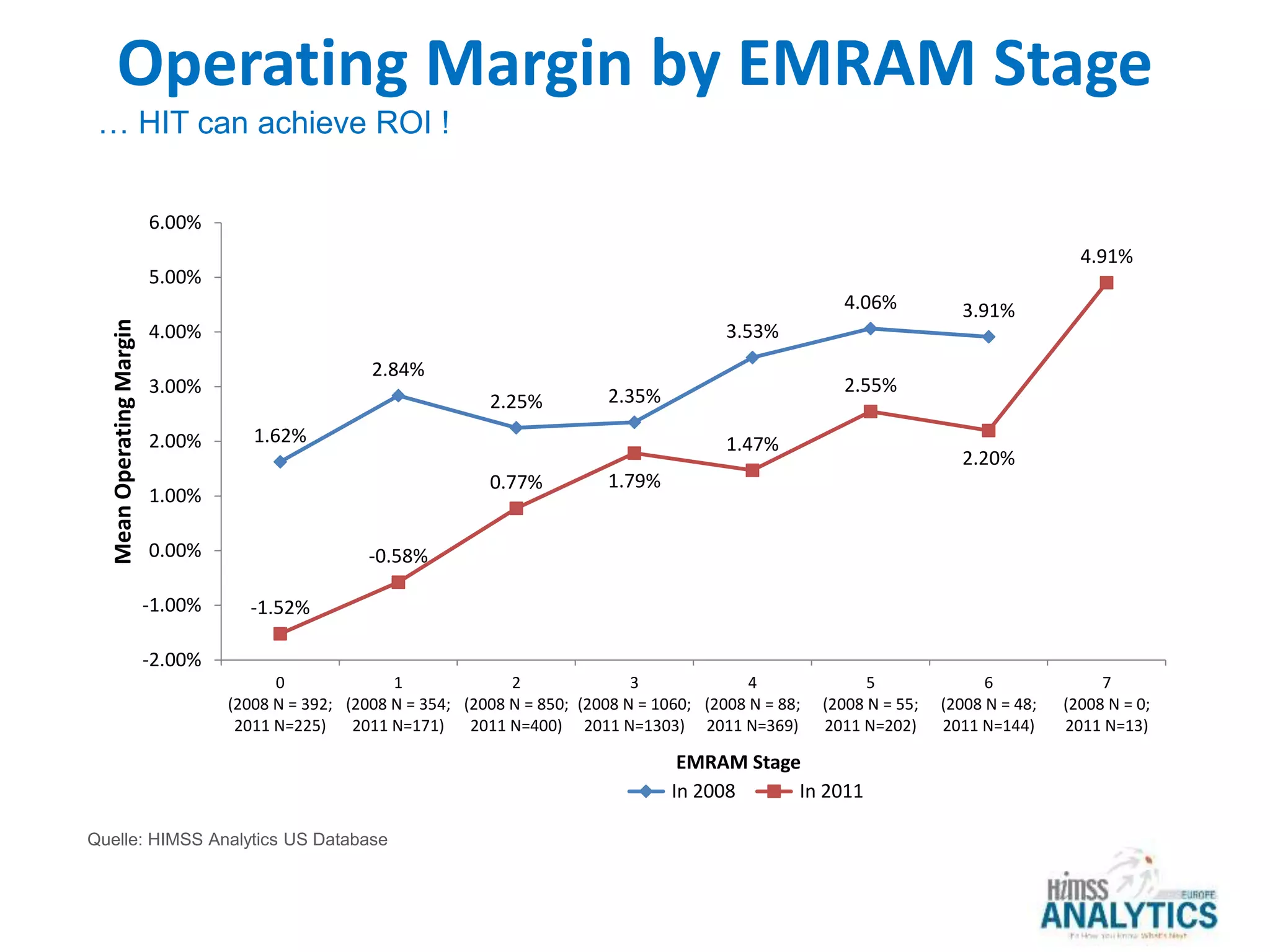
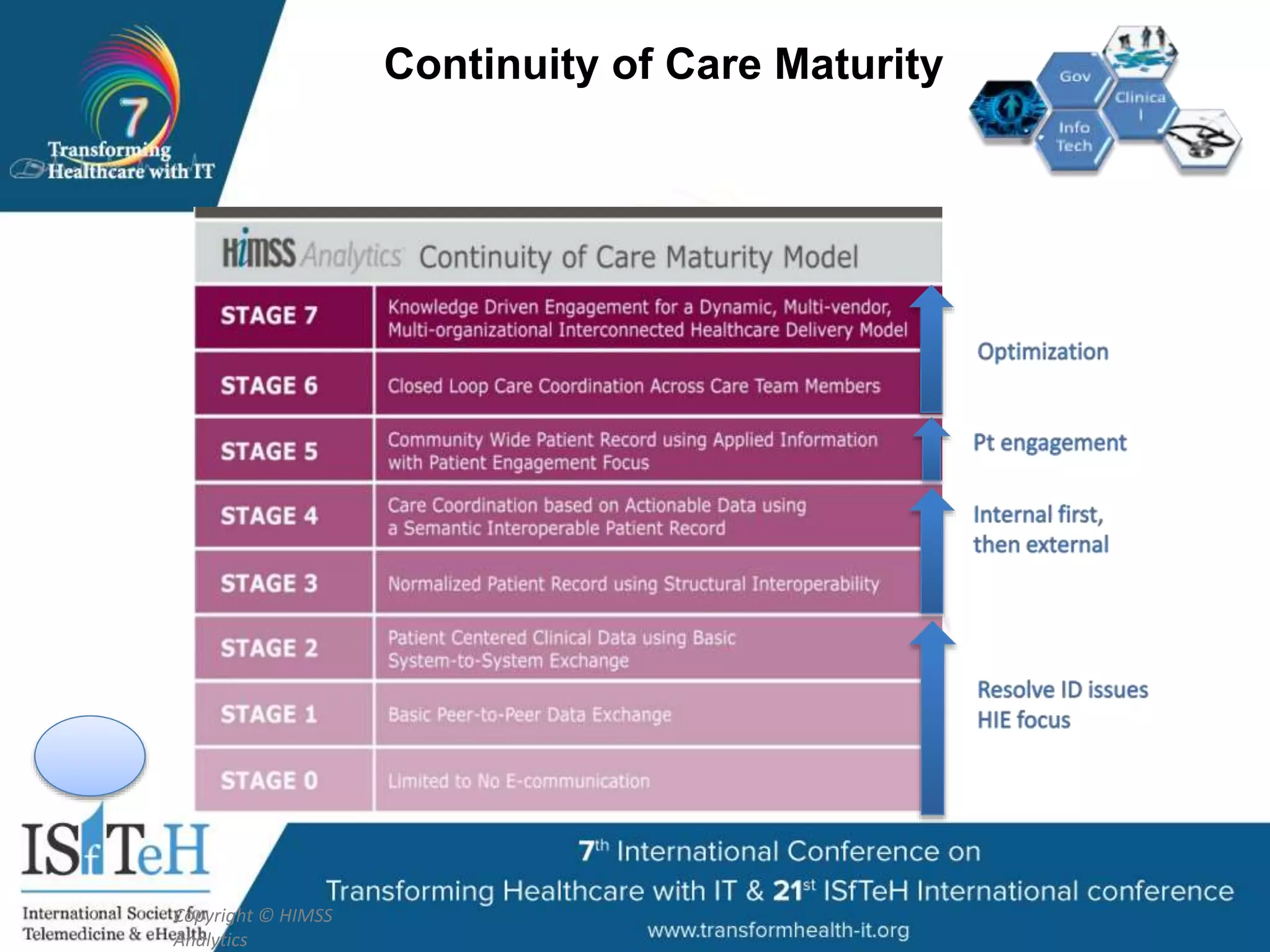
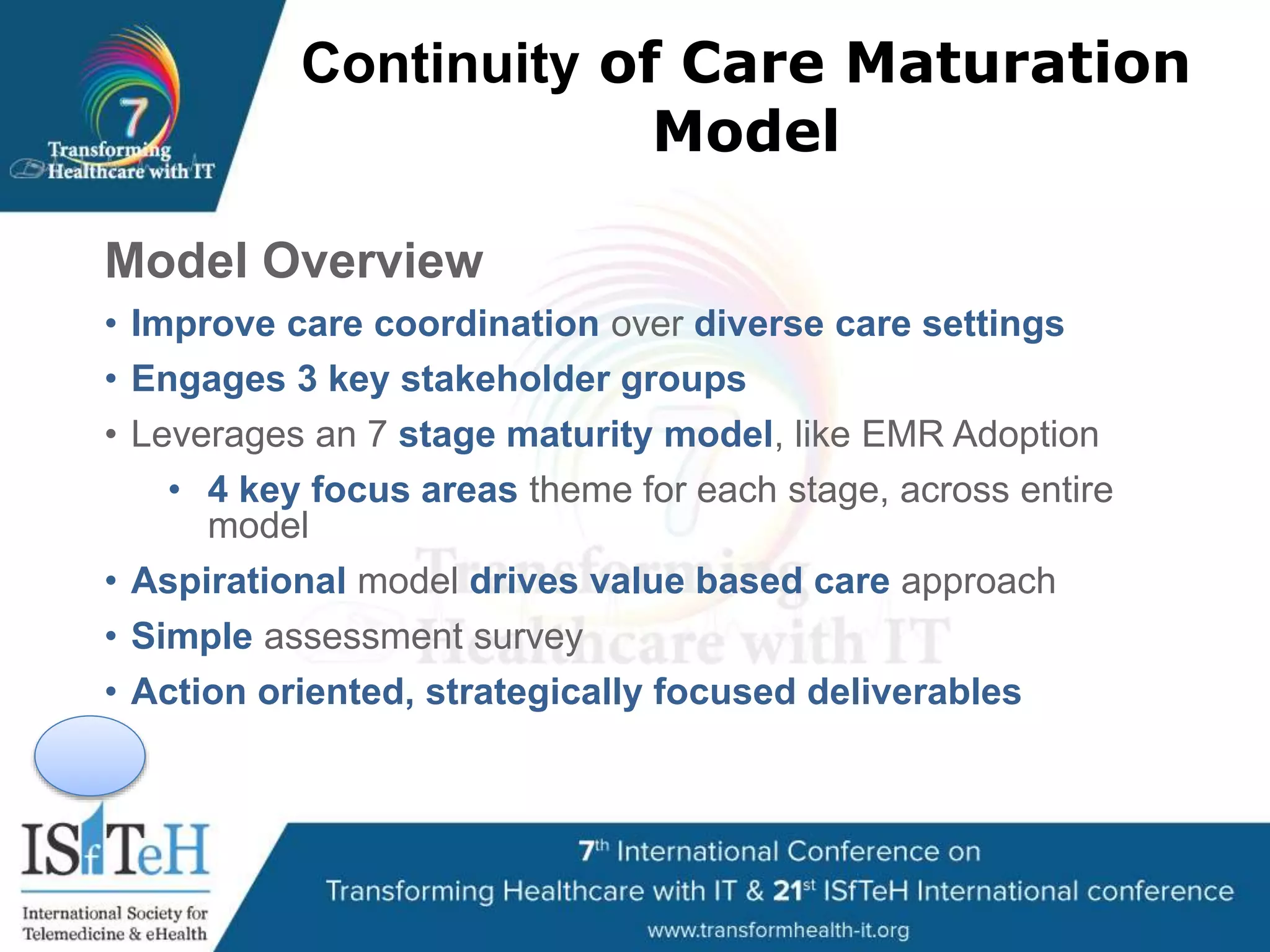
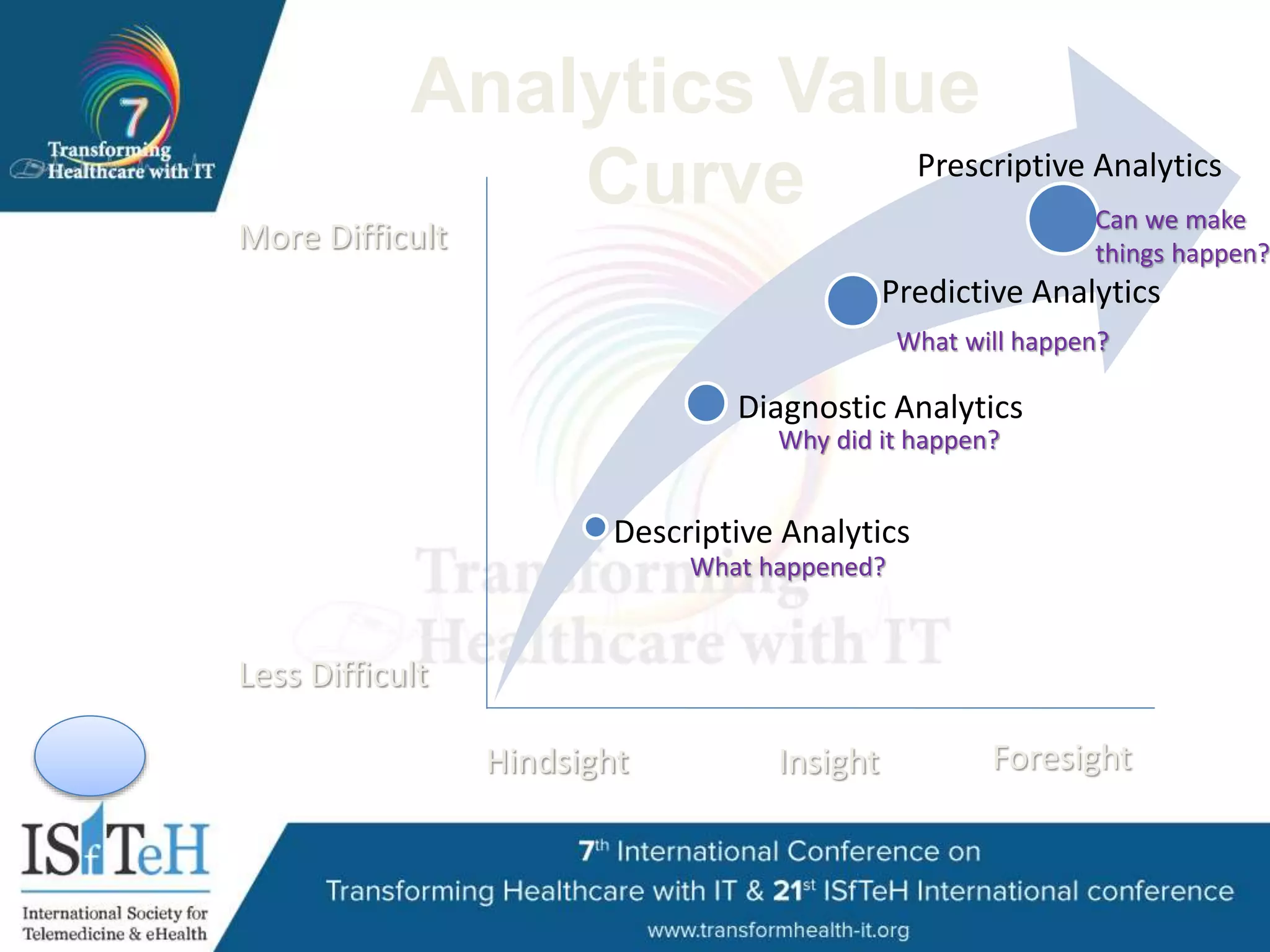
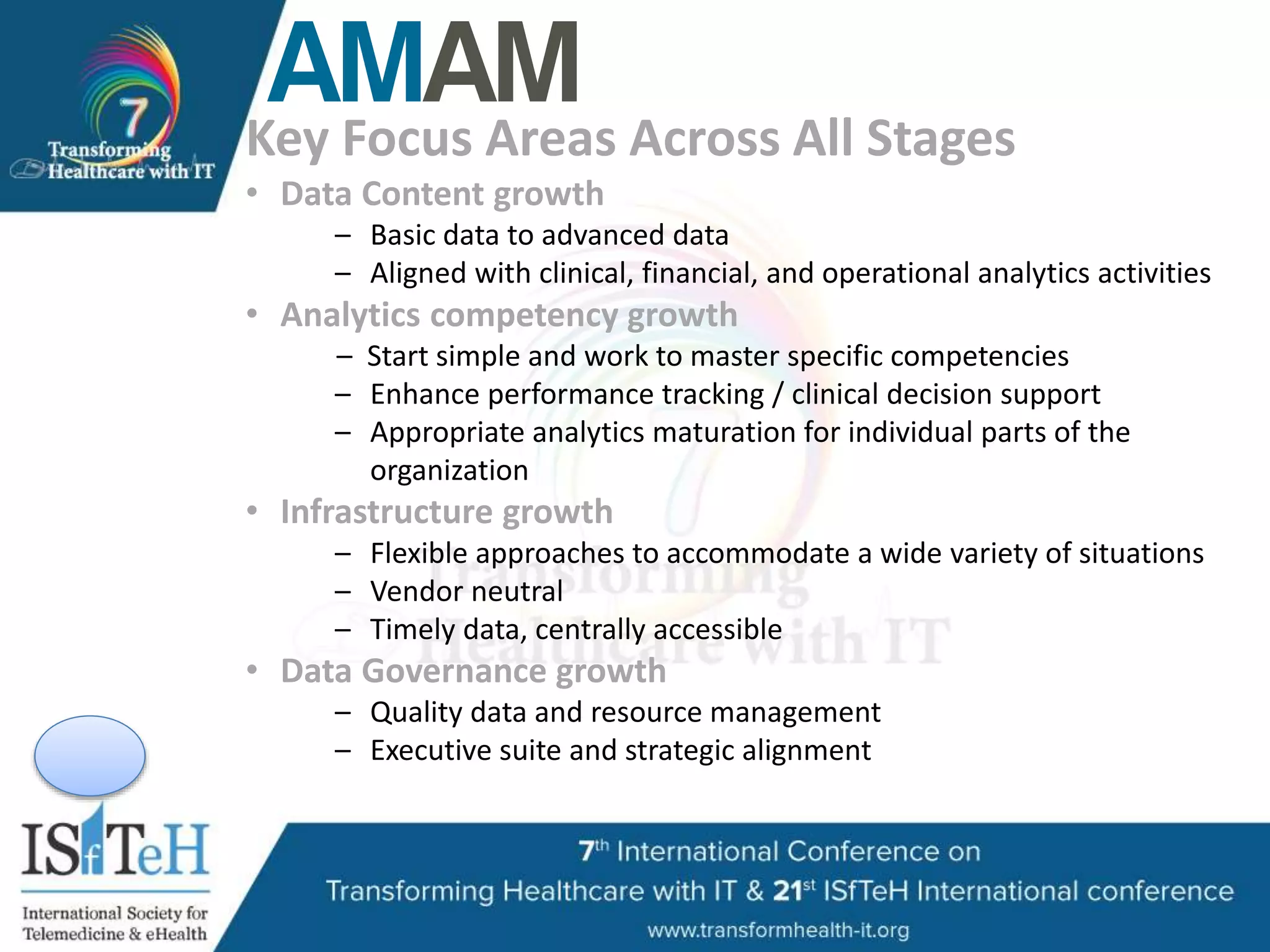
The document outlines HIMSS's role as a global organization focused on improving health care through the use of technology and data. It emphasizes the significant correlation between advanced EMR capabilities and improved patient outcomes, highlighting a structured model for healthcare providers to enhance care quality. HIMSS collaborates with various stakeholders to address common global health issues and promote better care delivery through data-driven approaches.