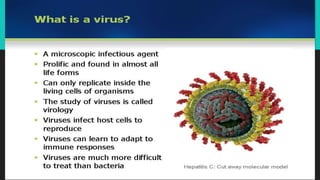
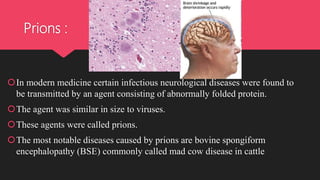
Viruses are obligate parasites that contain genetic material of either RNA or DNA. They cause diseases in animals and plants by infecting host cells. Viruses that infect plants typically contain single-stranded RNA, while those that infect animals can contain single or double-stranded RNA or double-stranded DNA. Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria and contain double-stranded DNA. Viroids are infectious agents smaller than viruses that consist only of free RNA and lack a protein coat. Prions are infectious agents similar in size to viruses that are composed of abnormally folded protein and cause neurological diseases like mad cow disease. Lichens represent a symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria