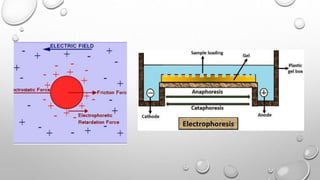
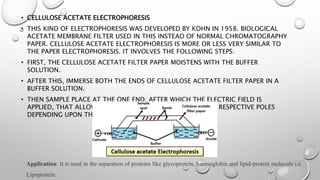
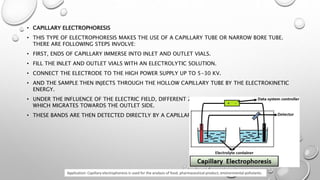
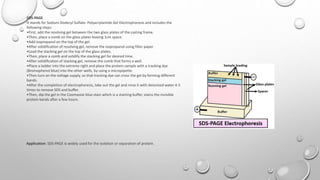
Electrophoresis is a technique that uses an electric field to separate biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and amino acids based on their size, charge, and shape. During electrophoresis, molecules move through a substrate or matrix toward the electrode of opposite charge - positively charged molecules move toward the negative electrode (anode) and negatively charged molecules move toward the positive electrode (cathode). Common electrophoresis methods include paper, cellulose acetate, capillary, and gel electrophoresis, with gel electrophoresis being the most widely used. Gel electrophoresis separates molecules based on their size as they migrate through a gel matrix under an applied electric field.