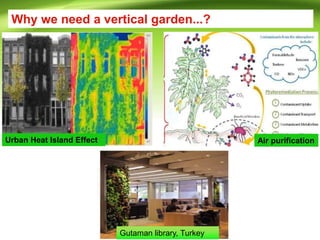
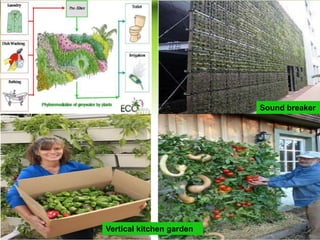
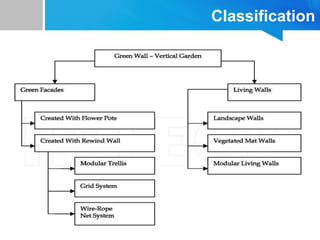
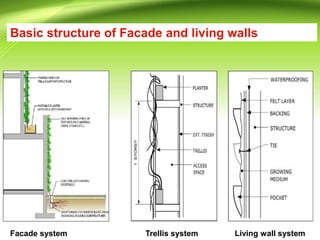
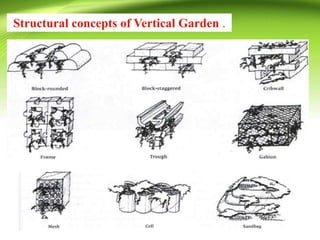
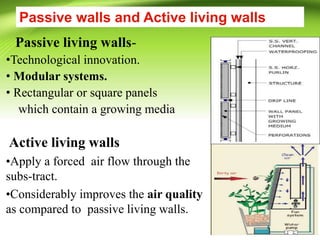
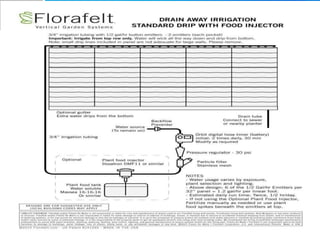
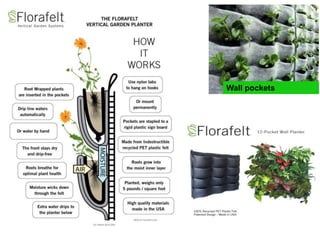
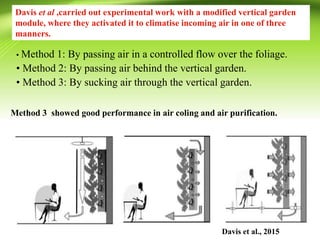
Vertical gardens, also known as green walls, involve growing plants on trellises or other structures in an upright direction. They provide several benefits such as improving air quality by removing pollutants, reducing urban heat through shading and evapotranspiration, and making efficient use of limited space. Different types of vertical garden systems include living walls with pre-vegetated panels, modular trellis systems, and wire-rope net walls. Proper selection of plant species that tolerate vertical growth and local climate is important. While initial costs are high, vertical gardens can help beautify buildings and environments if maintained properly over time.