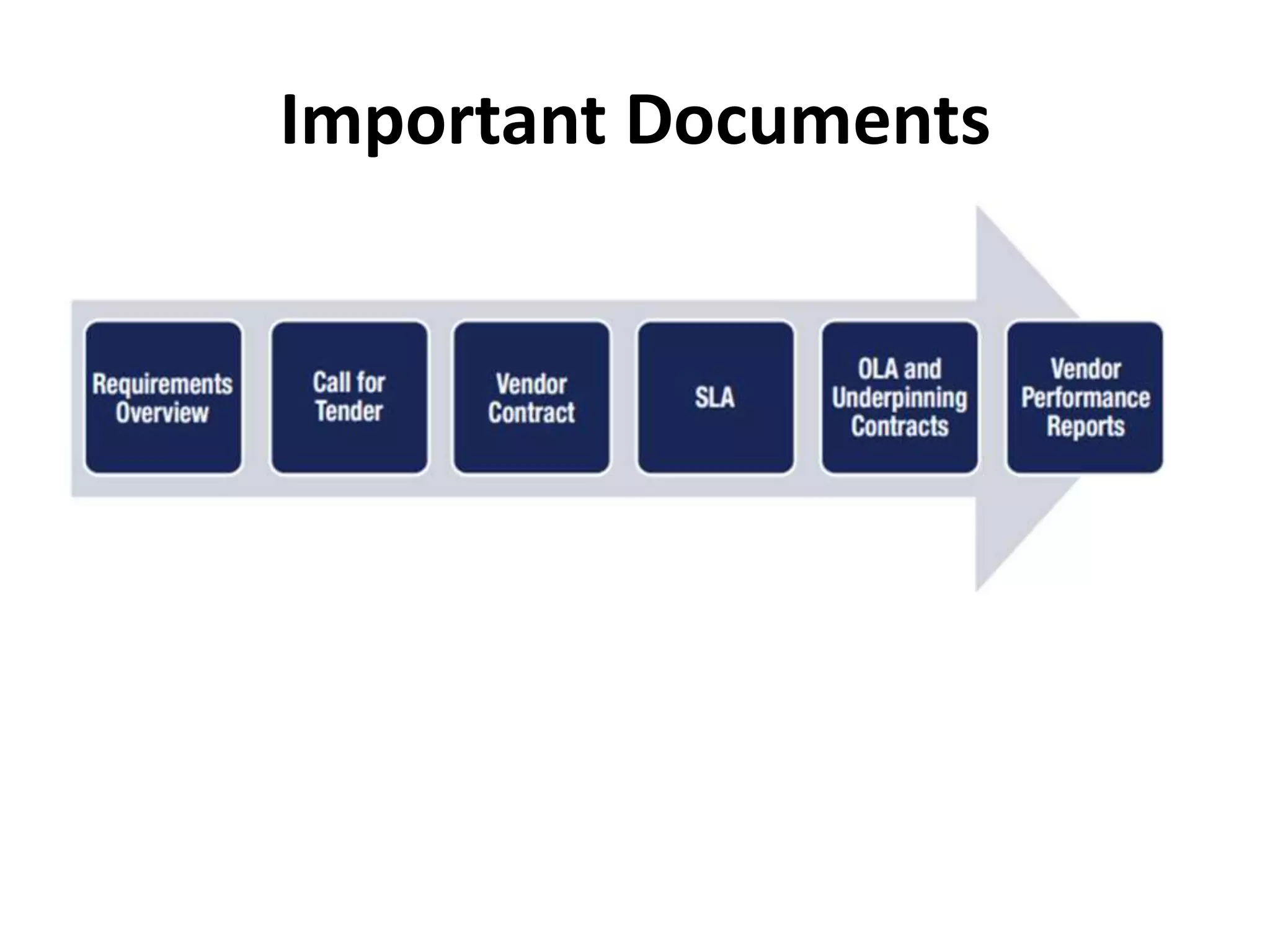
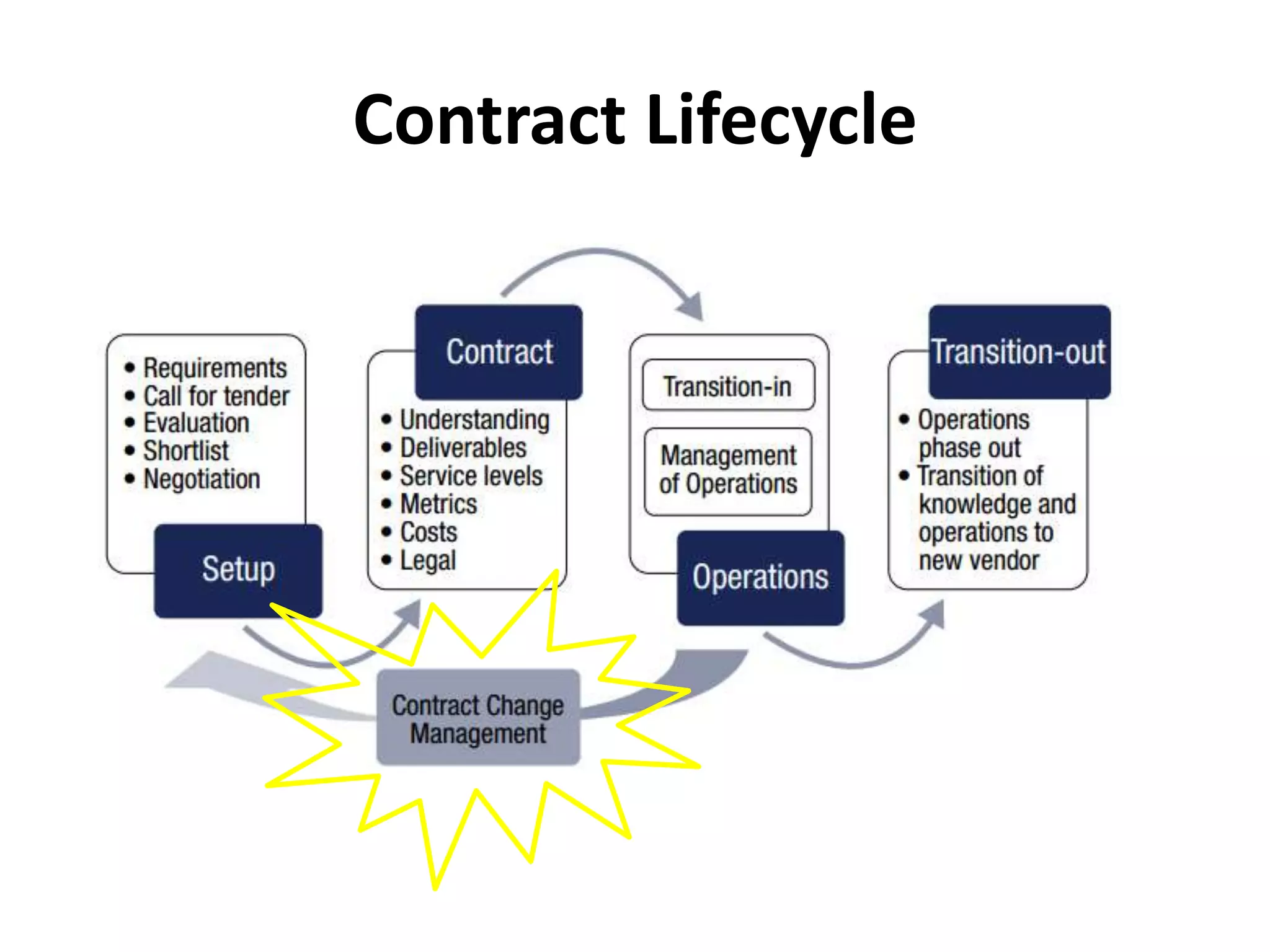
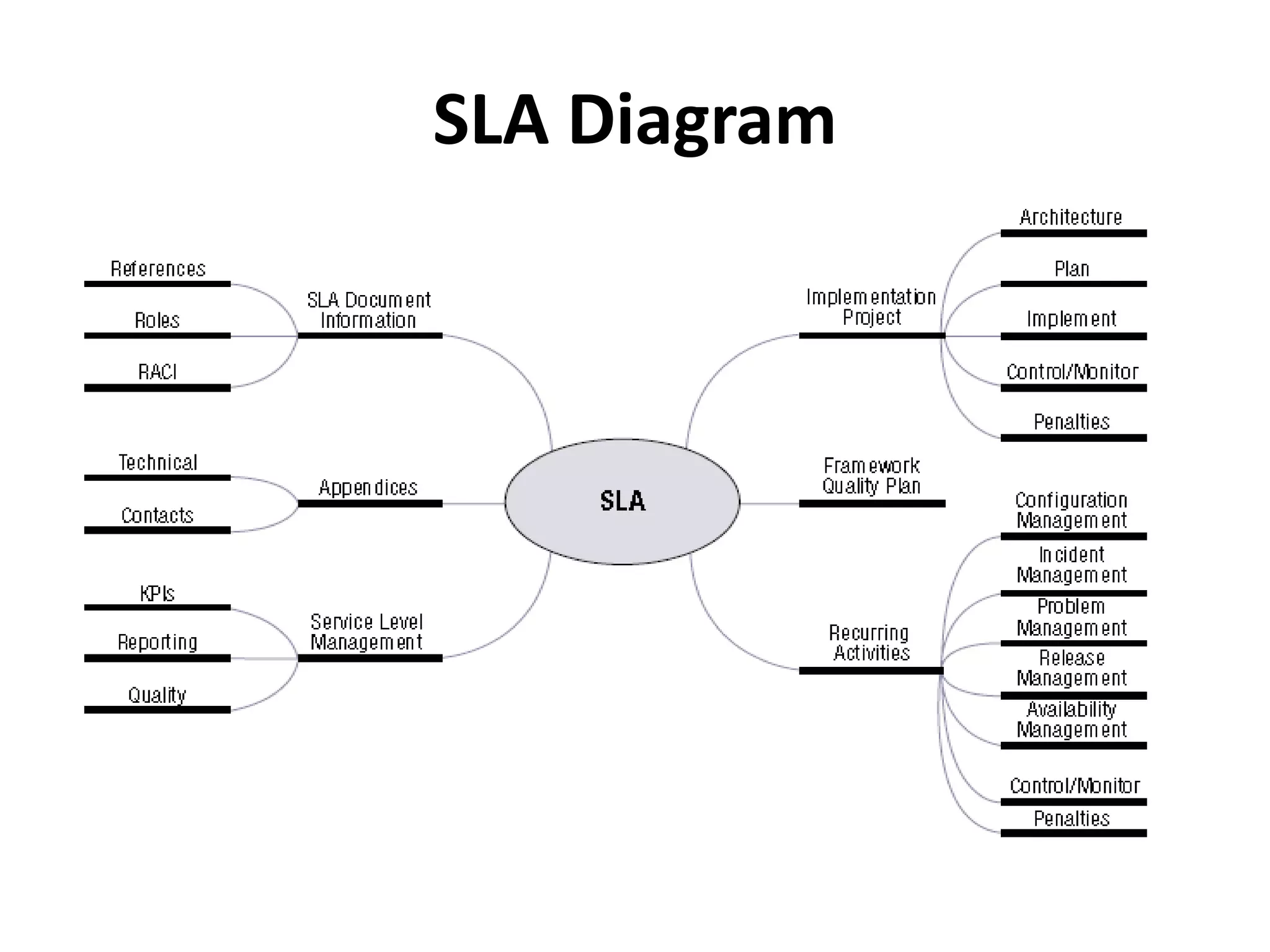
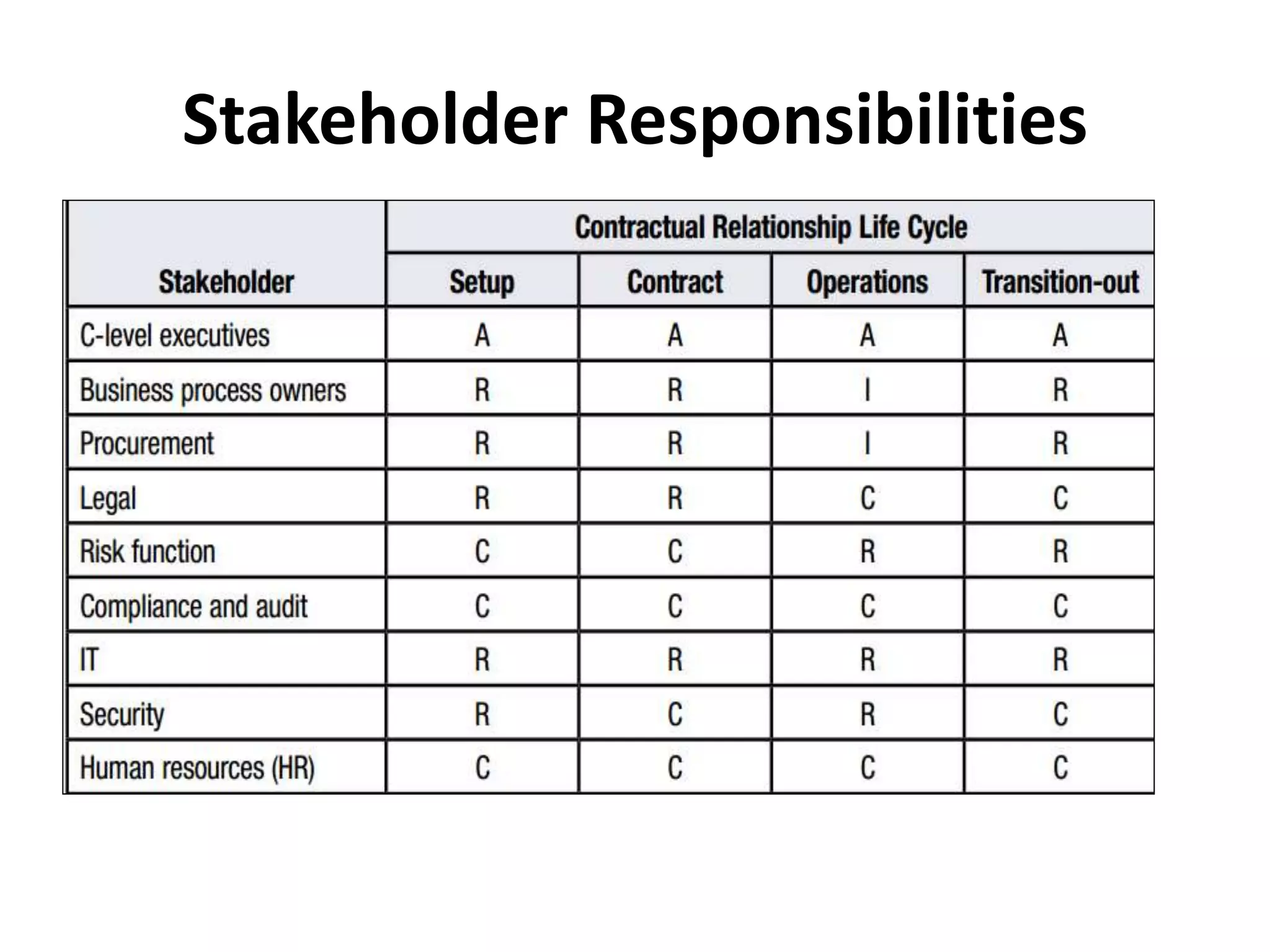
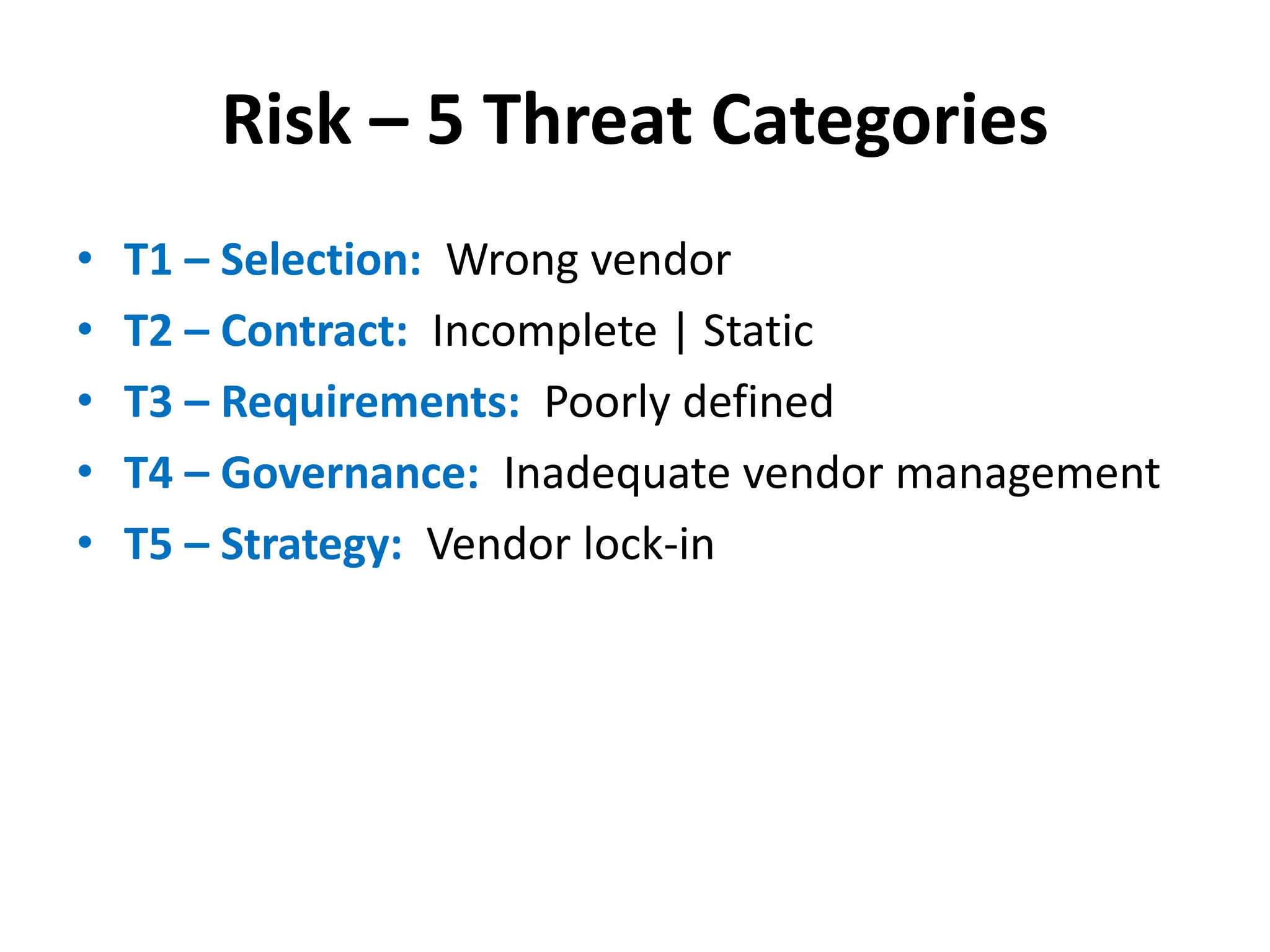
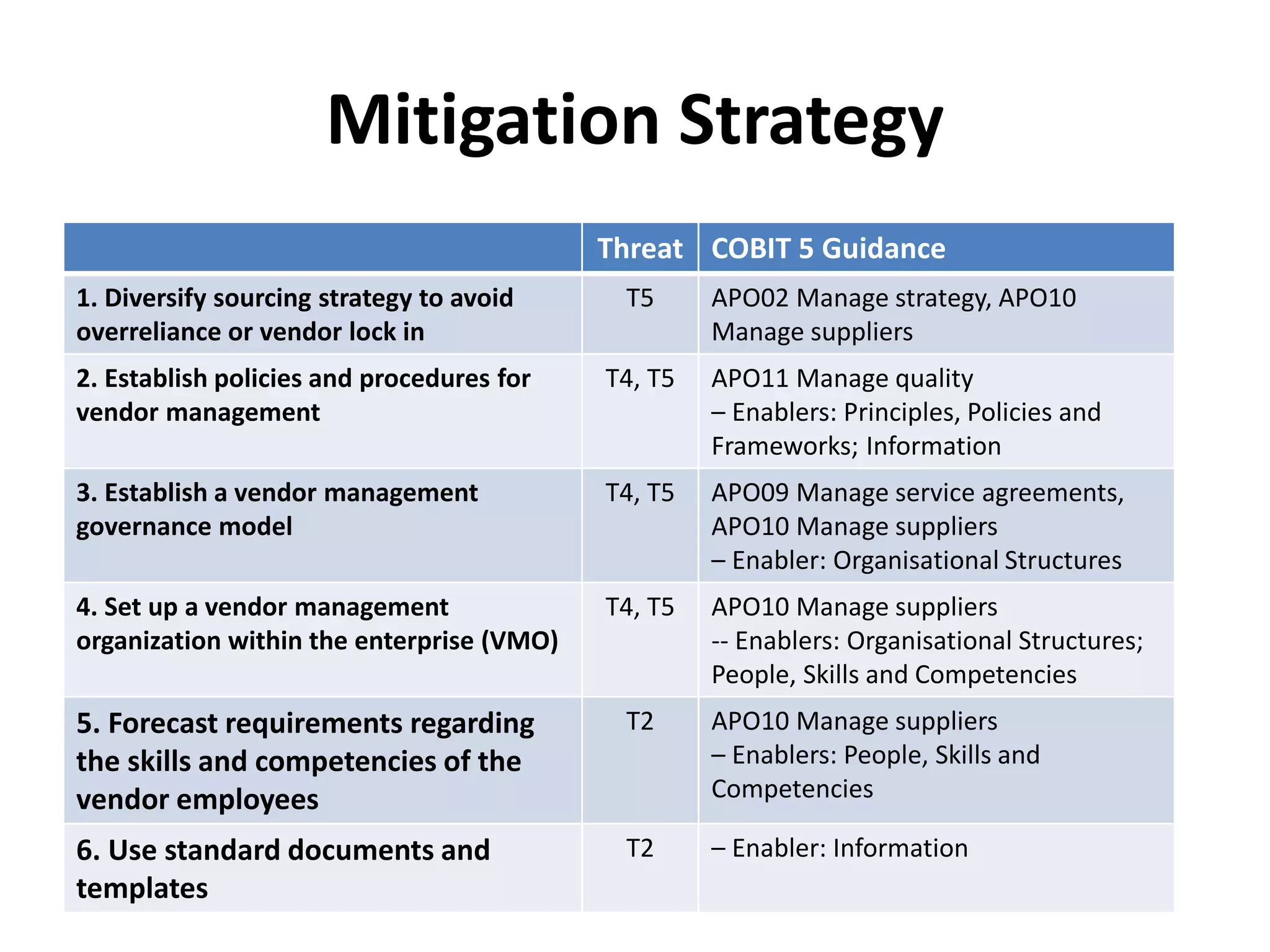
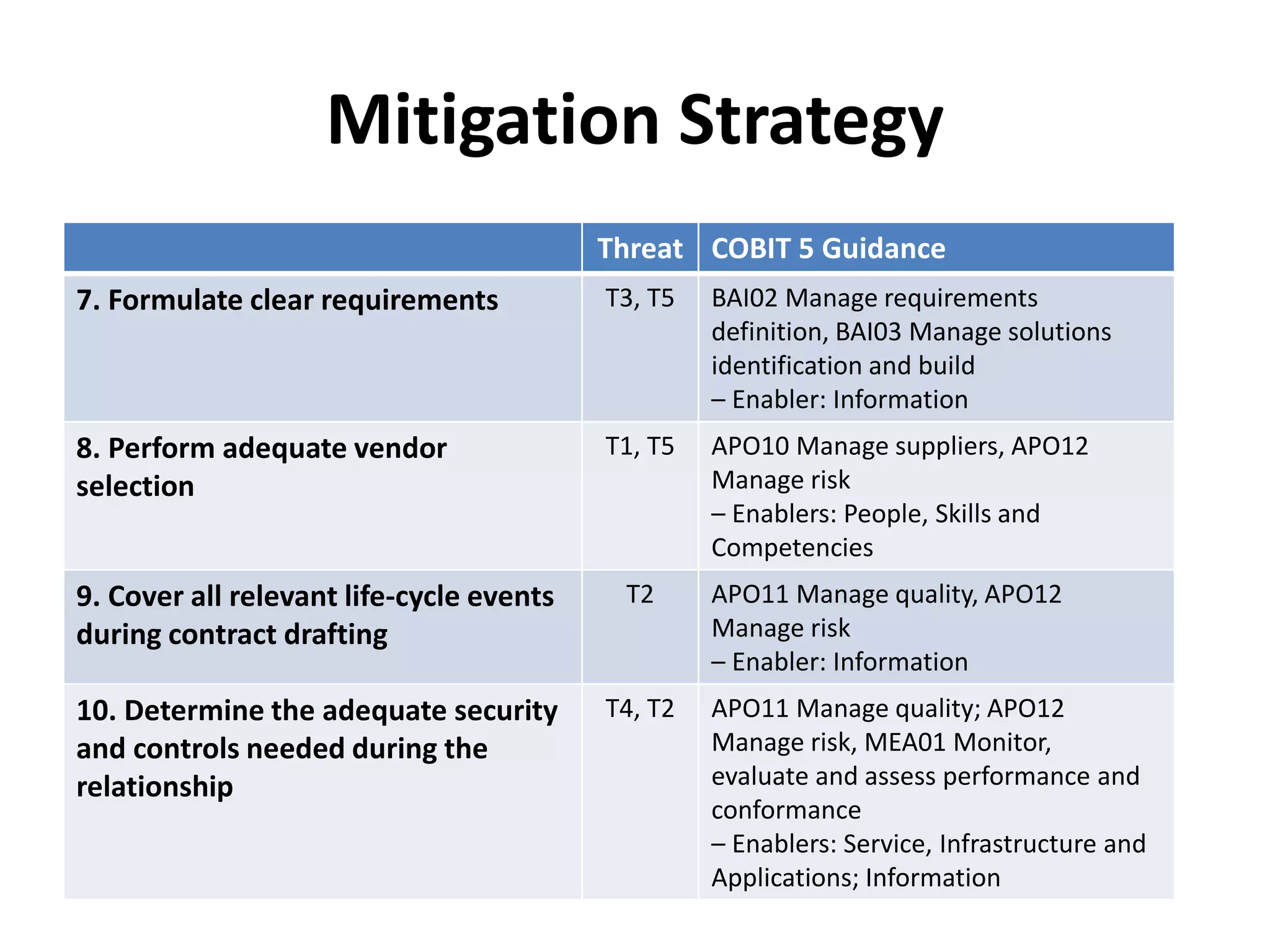
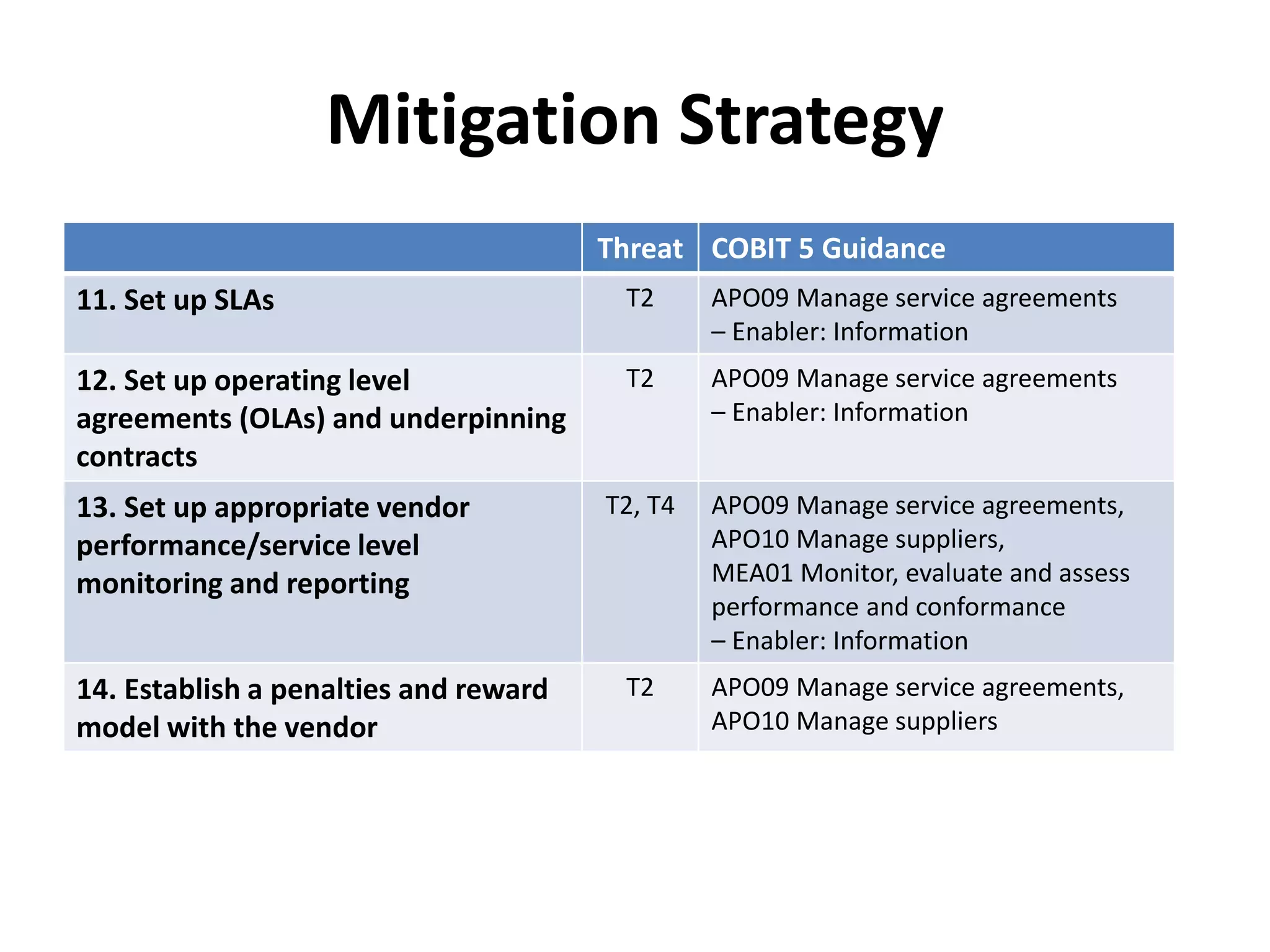
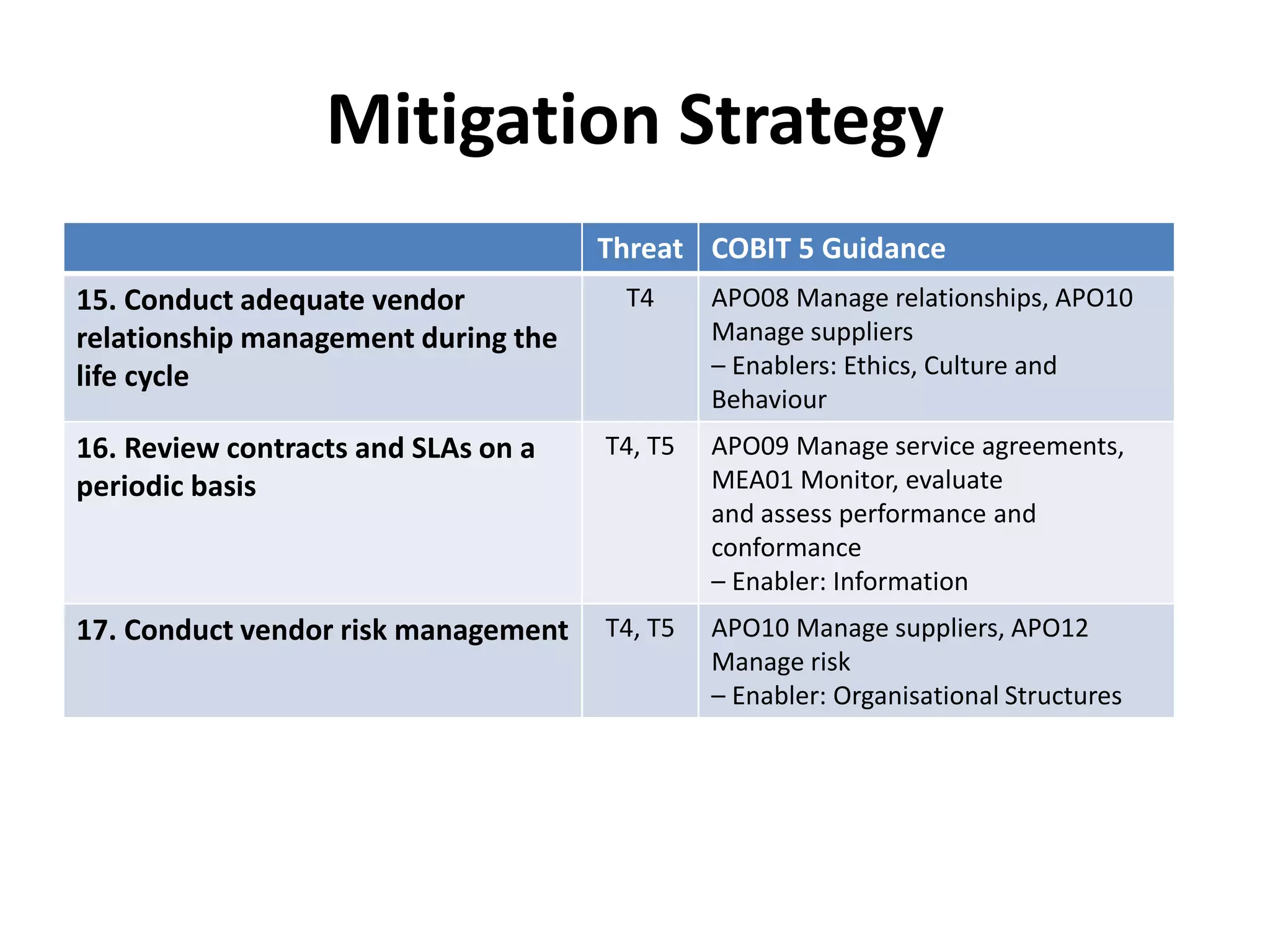
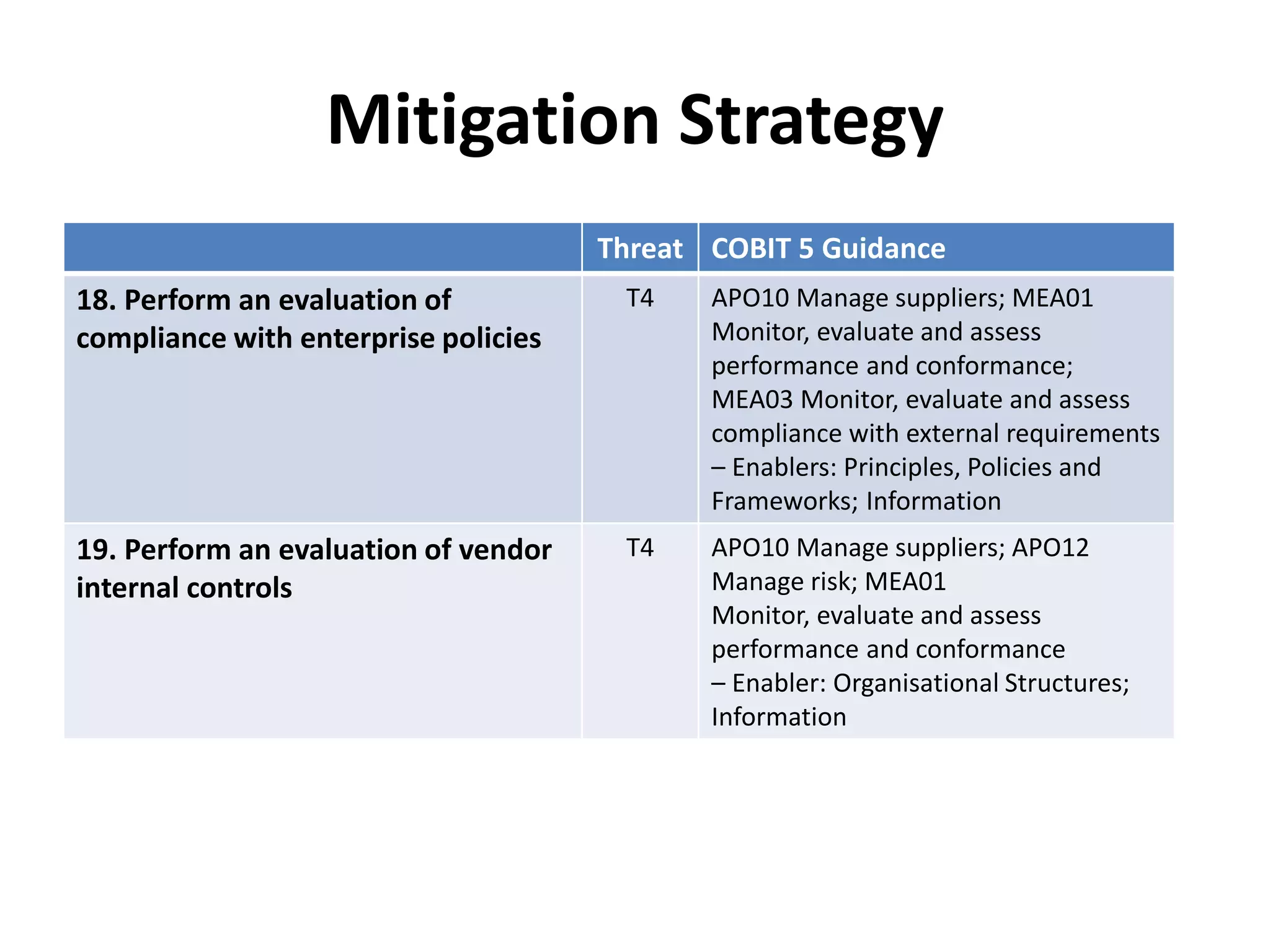
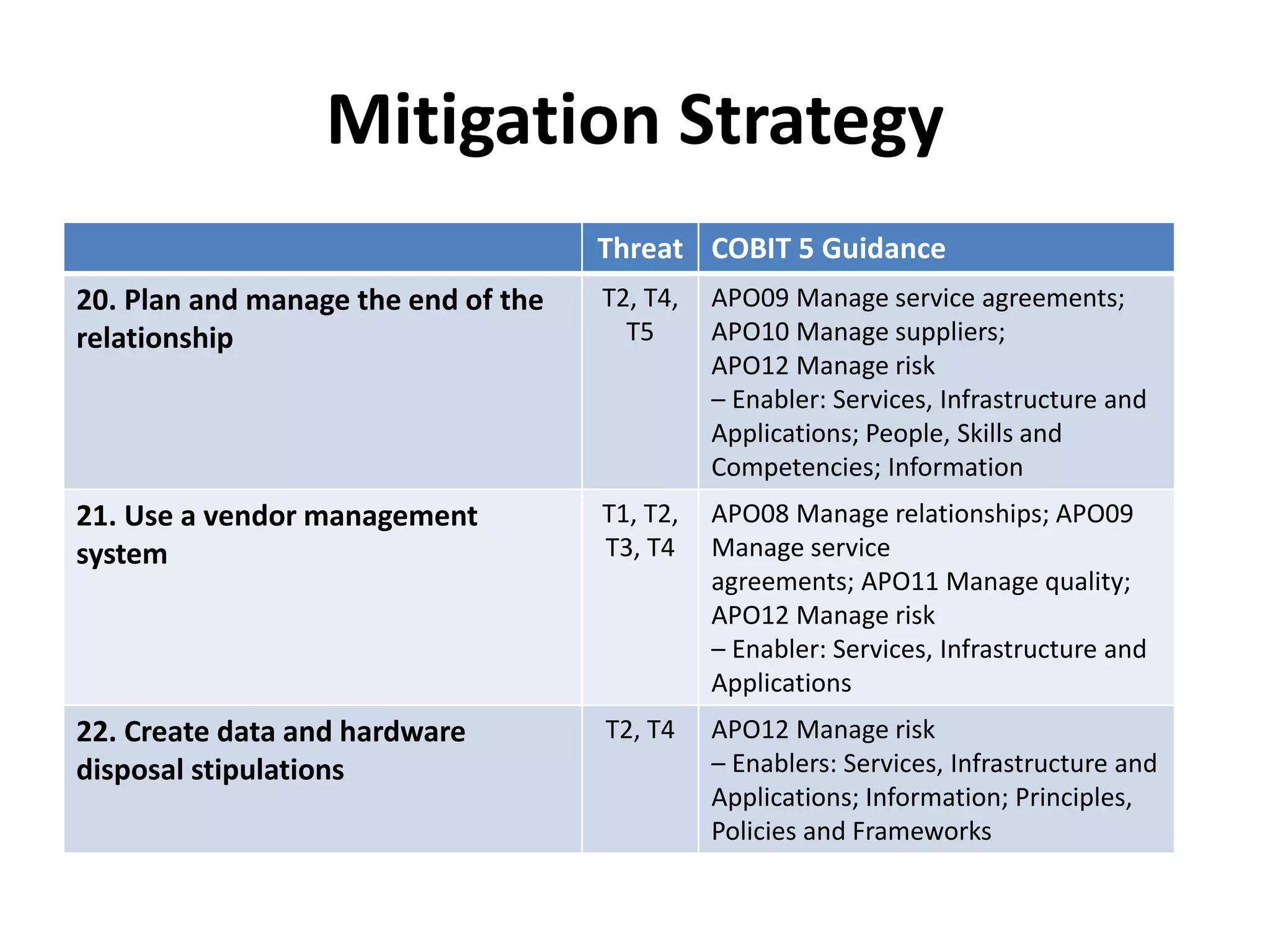
The document outlines best practices for vendor management using COBIT 5, emphasizing the strategic importance of building and maintaining effective vendor relationships. It highlights objectives such as value creation, risk minimization, and the enhancement of service delivery through well-defined contracts and Service Level Agreements (SLAs). The guidance provided includes risk management strategies and recommendations for establishing a governance model to improve vendor selection, communication, and performance monitoring.