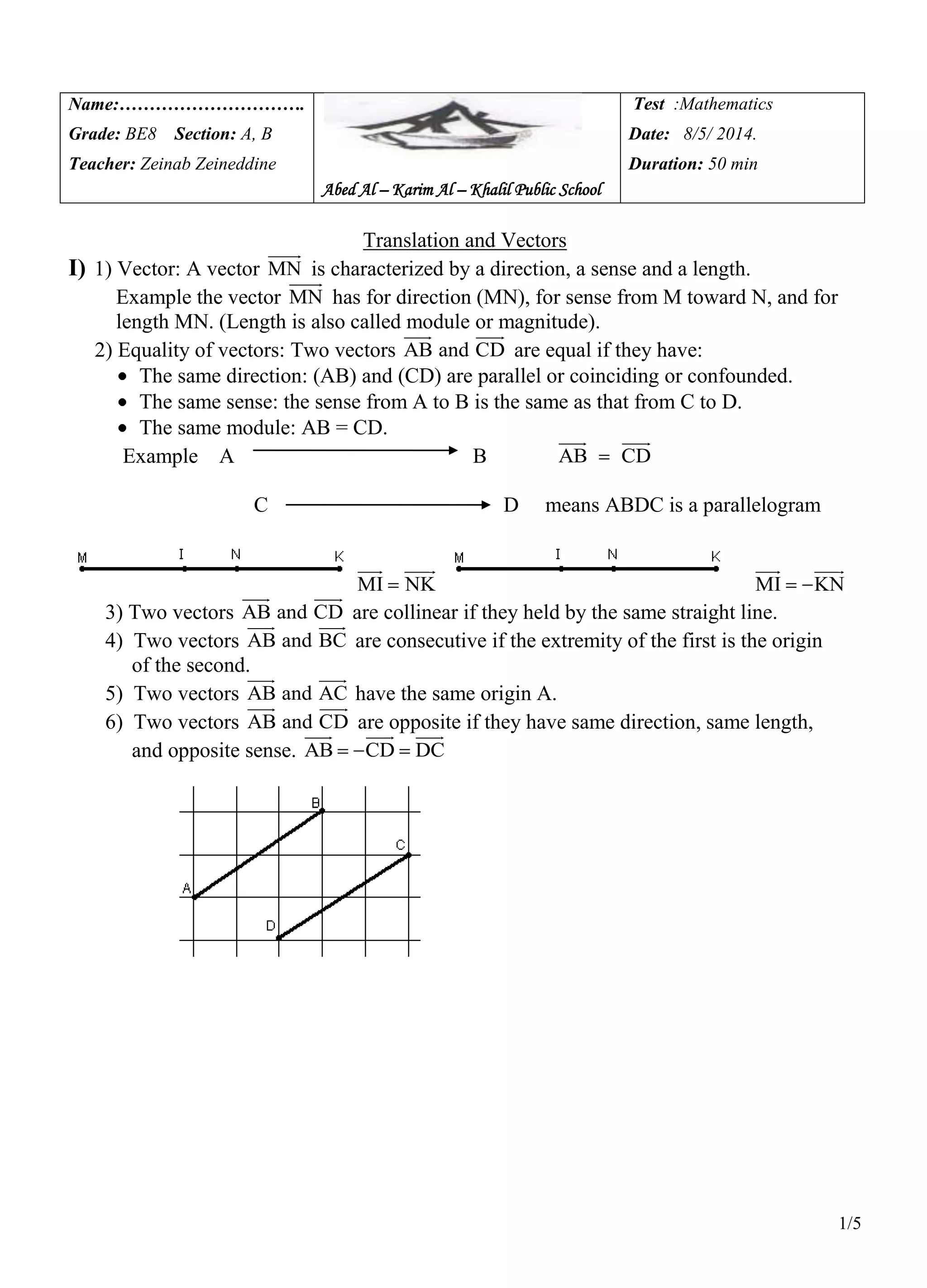
1. The document discusses vectors and their properties including direction, sense, length, equality of vectors, collinear vectors, consecutive vectors, opposite vectors, and translation.
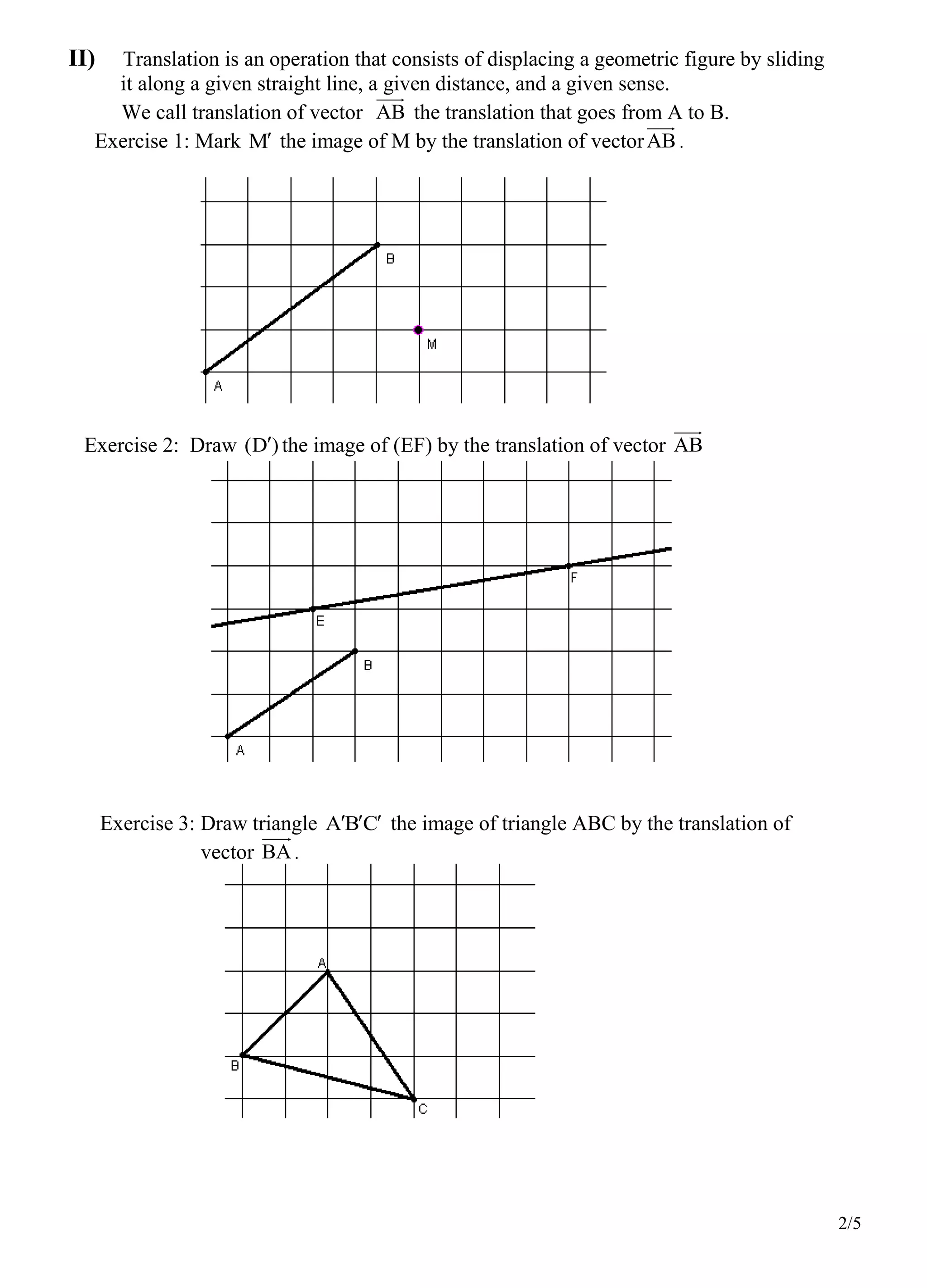
2. Translation is defined as displacing a geometric figure along a given straight line a given distance and direction. The translation of a vector AB moves from point A to B.
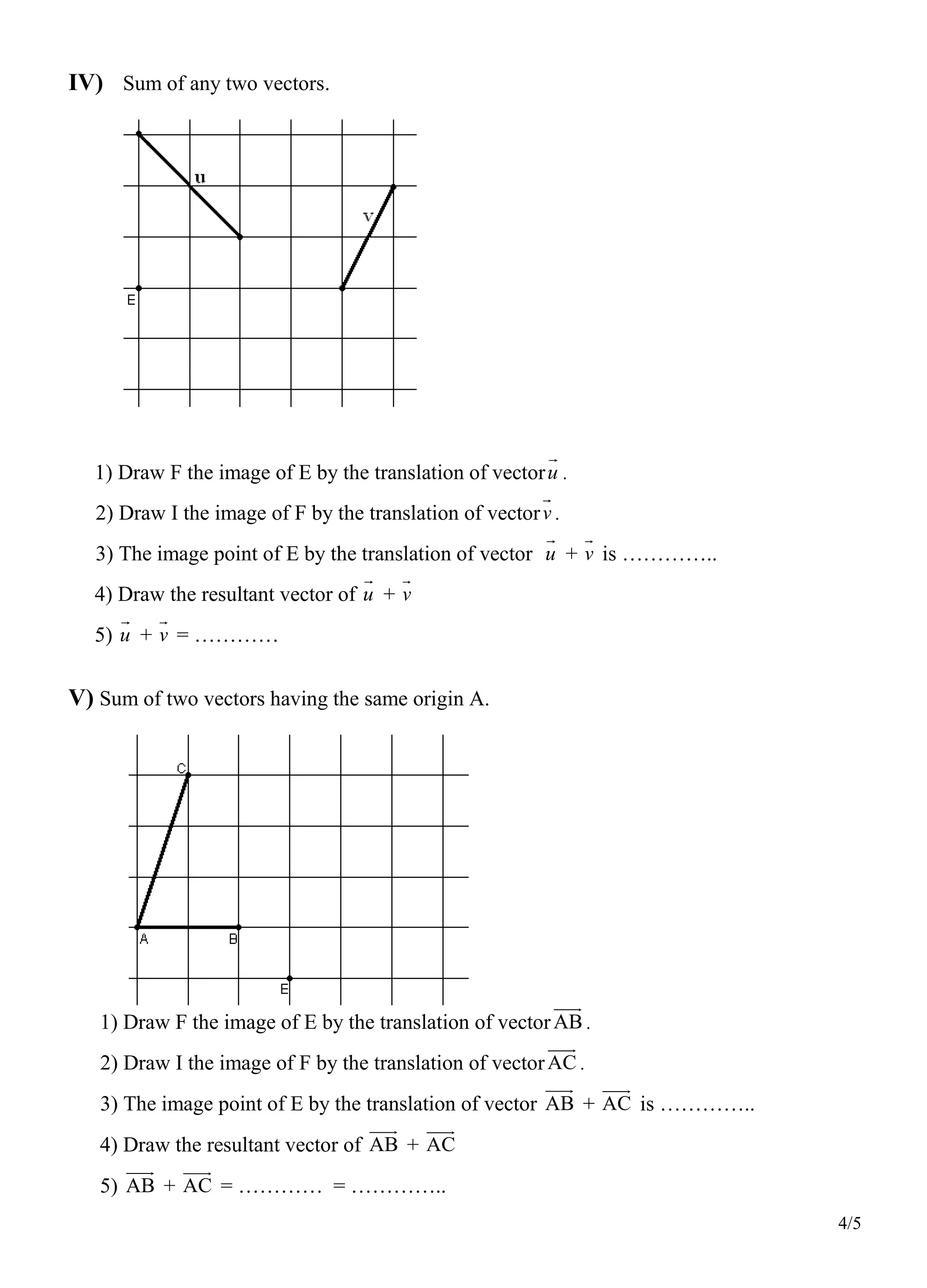
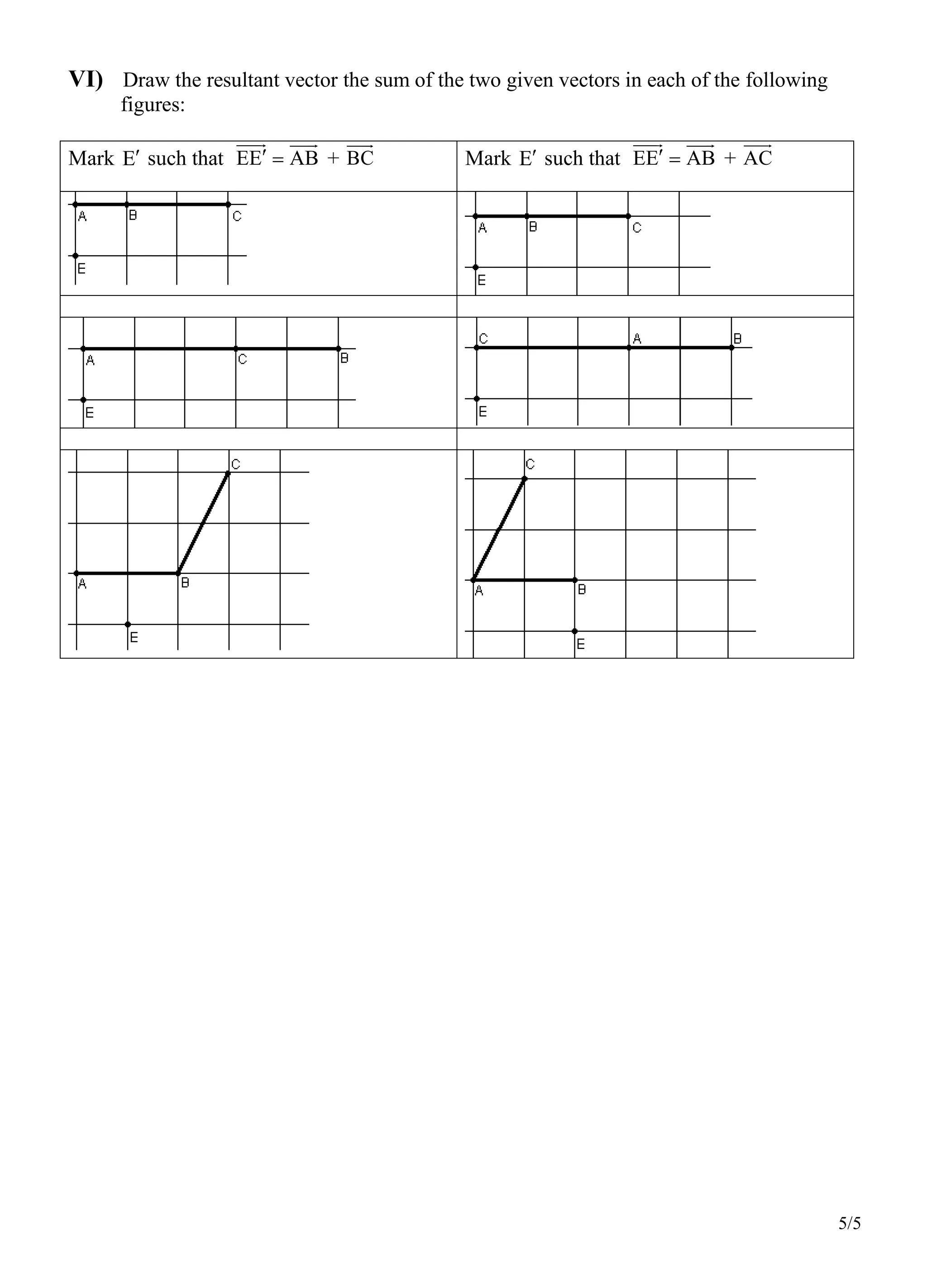
3. Sections discuss summing consecutive vectors, any two vectors, and vectors with the same origin by translating points using the vectors. Exercises involve drawing images of figures under translations and finding resultant vectors.