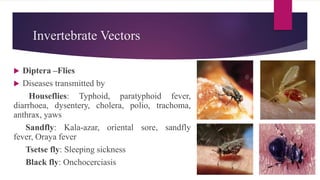
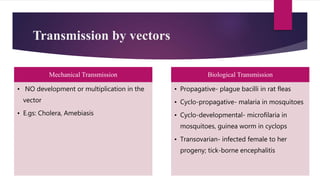
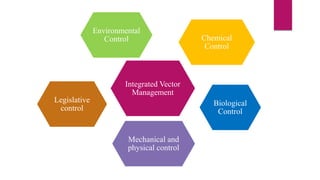
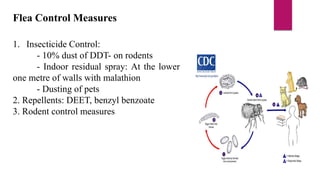
This document discusses vector control measures for various disease-carrying insects and animals. It begins by defining vectors as living organisms that can transmit infectious diseases between hosts. It then categorizes common invertebrate vectors like mosquitoes, flies, ticks, mites, and fleas, as well as vertebrate vectors like mice and rats. The document outlines integrated vector management strategies, including environmental control, chemical treatments, biological control, and legislative measures. It provides specific control recommendations for major vector types like larval source reduction, residual sprays, genetic techniques, and personal protection measures.