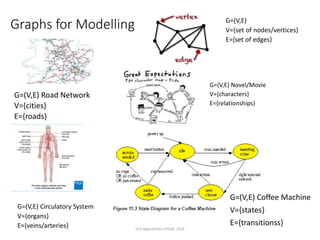
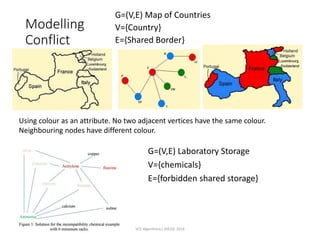
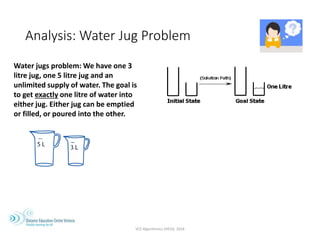
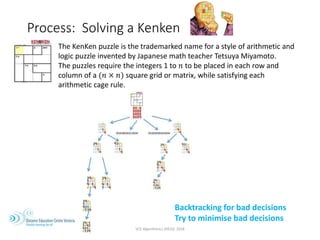
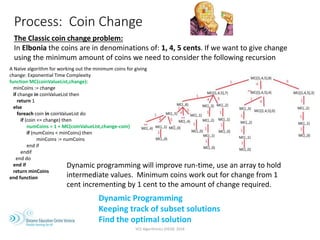
The document outlines the VCE Algorithmics program offered by the Distance Education Centre Victoria (DECV) in 2018, emphasizing online delivery and live lessons. It covers key concepts such as problem-solving, modeling, and algorithm development, with practical examples like the water jug problem and coin change problem. The document also provides details on enrollment eligibility and encourages the importance of problem-solving skills in society.