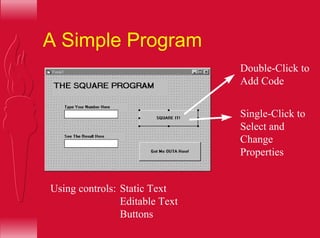
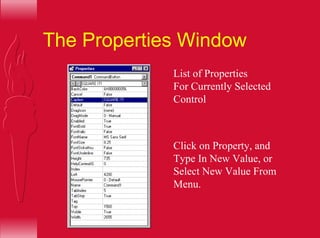
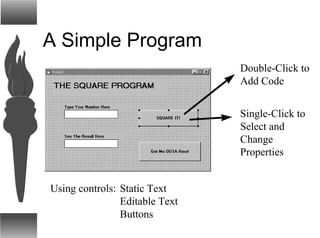
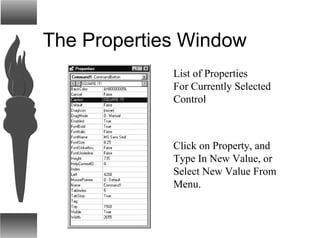
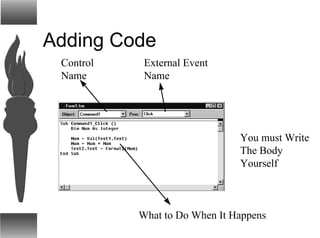
Visual Basic provides a convenient method for building user interfaces compared to other programming languages. It allows drawing buttons, text boxes and other controls onto a form and adding code to handle user interaction. More complex controls can execute commands, have active properties, and support many event types. Visual Basic can also interface with code written in C for efficiency.


















![VB For Statements
For <Variable> = <start> to <finish>
<List of Statements>
Next <Variable>
For <Variable> = <start> to <finish> Step <increment>
<List of Statements>
Next <Variable>
Example:
For I = 1 to 10 do
A[I] = A[I] + 1
Next I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbasic-150803042614-lva1-app6891/85/Vbasic-21-320.jpg)
![VB Arrays
H Indices Always Start With Zero
H Dim A[10] As Integer Declares 11 elements,
indexed from 0 through 10.
H Multi-Dimensional Arrays are Permitted.
H Arrays can be resized at run time (See VB
Help File for ReDim)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbasic-150803042614-lva1-app6891/85/Vbasic-22-320.jpg)


















![VB For Statements
For <Variable> = <start> to <finish>
<List of Statements>
Next <Variable>
For <Variable> = <start> to <finish> Step <increment>
<List of Statements>
Next <Variable>
Example:
For I = 1 to 10 do
A[I] = A[I] + 1
Next I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbasic-150803042614-lva1-app6891/85/Vbasic-45-320.jpg)
![VB Arrays
H Indices Always Start With Zero
H Dim A[10] As Integer Declares 11 elements,
indexed from 0 through 10.
H Multi-Dimensional Arrays are Permitted.
H Arrays can be resized at run time (See VB
Help File for ReDim)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbasic-150803042614-lva1-app6891/85/Vbasic-46-320.jpg)

