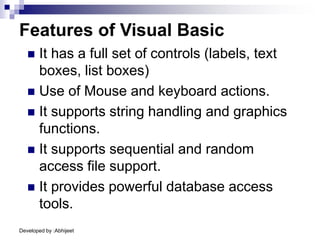
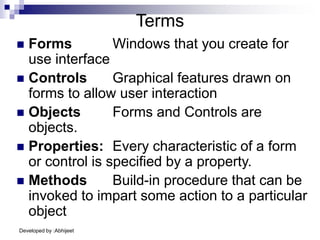
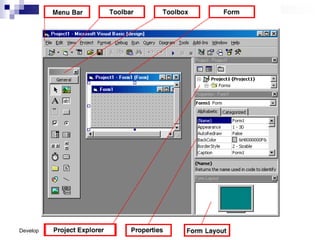
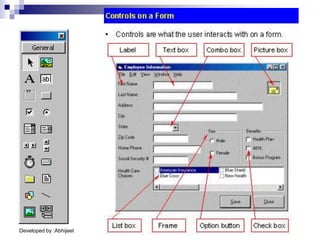
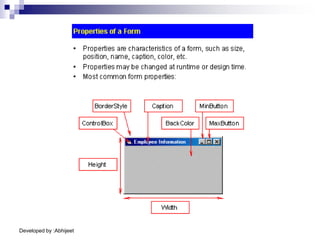
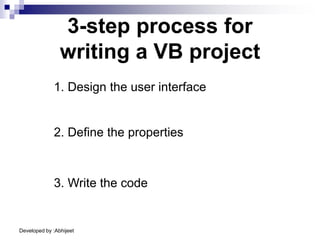
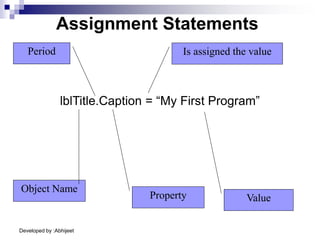
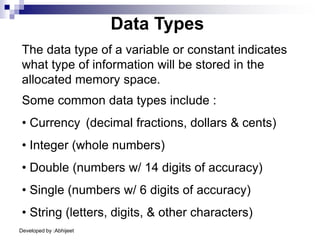
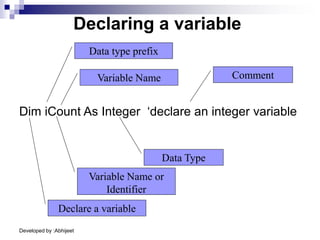
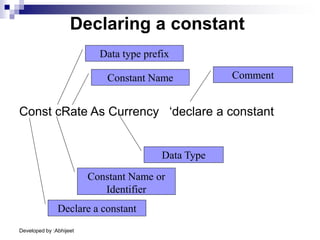
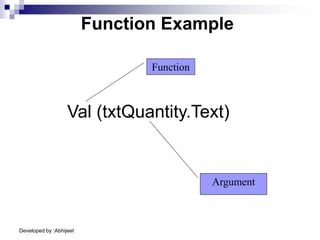
Visual Basic is an event-driven programming language. It was created by Microsoft to develop applications for Windows. Visual Basic has an integrated development environment that allows programmers to design graphical user interfaces using controls and write code. The code is executed in response to events like button clicks. Visual Basic uses forms for the user interface and objects like controls that have properties and methods. Programmers declare variables and constants, write code using statements and functions, and develop projects using a three-step process of designing the interface, defining properties, and writing code.
























![Developed by :Abhijeet
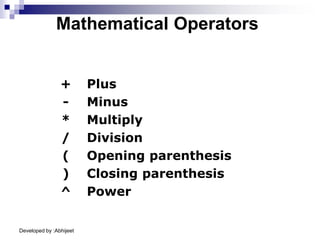
Format Function
The Format function controls the way output is
displayed
lblGst.Caption = Format$(cGst, "Currency")
Format[$] (ExpressionToFormat [, “Description”])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtovb-220805064254-74d70725/85/Intro_to_VB-PPT-37-320.jpg)