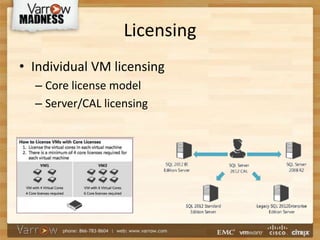
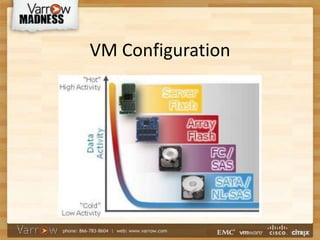
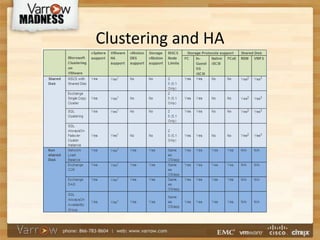
This document discusses best practices for virtualizing SQL Server. It outlines the advantages of virtualization like high availability and flexibility. It covers licensing considerations for virtual SQL, as well as VM configuration guidelines for optimizing performance. Backup strategies that support full recovery are recommended. The document also discusses clustering and high availability options like vSphere HA and SQL AlwaysOn clustering to provide redundancy. Key takeaways are to use templates for VM configuration, obtain vCenter access, and to scale resources as needed rather than overprovisioning.