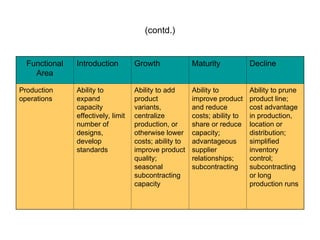
Value chain analysis examines how a business creates customer value by assessing its internal activities from input to product delivery and after-sales service. It allows firms to identify strengths and weaknesses through internal resources while integrating SWOT analysis to evaluate both environmental opportunities and threats. The document also discusses various perspectives for internal analysis, including past performance comparisons, industry benchmarks, and distinctive competencies across functional areas throughout different stages of industry evolution.