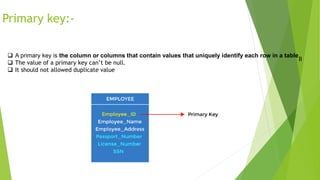
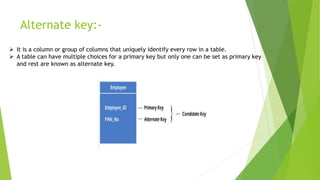
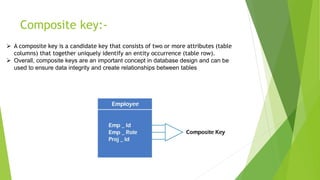
The document defines and describes different types of keys used in database management systems. It explains that a primary key uniquely identifies each row in a table and cannot contain null values or duplicate values. A candidate key can also uniquely identify rows but other attributes can also qualify. An alternate key is like a primary key but a table can only have one primary key while other candidate keys are alternate keys. A composite key contains two or more columns that together uniquely identify each row. A super key can identify rows but may contain extra attributes, allowing null values. A foreign key points to the primary key in another table to link the tables.