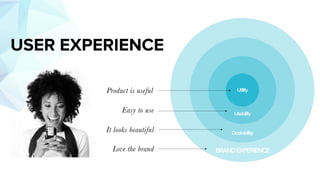
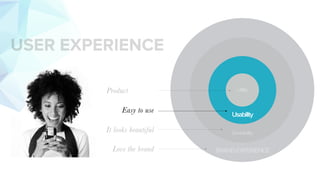
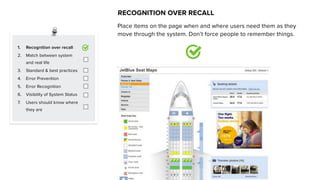
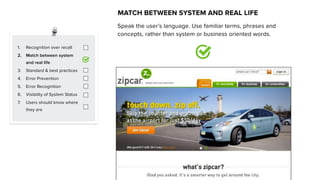
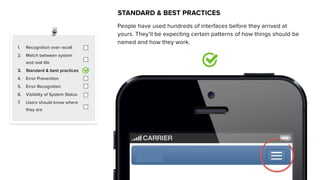
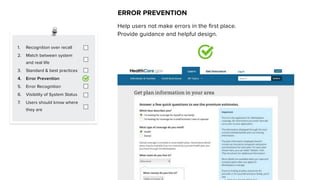
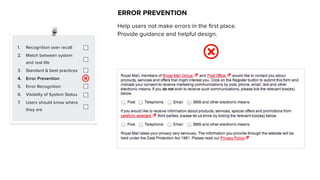
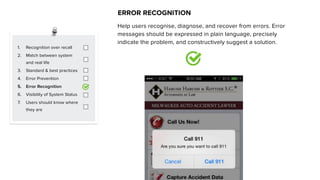
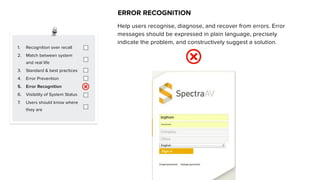
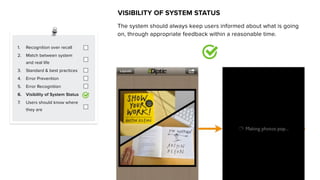
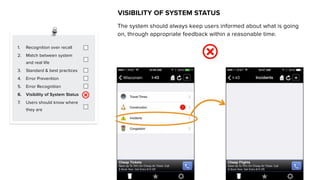
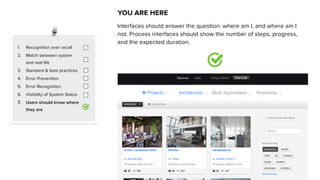
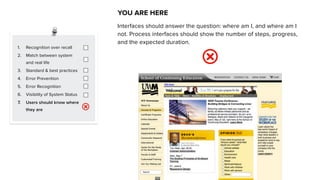
This document discusses usability and user experience. It defines usability as how intuitive and easy a product is to use, and how it can increase efficiency and remove obstacles. The document then lists several aspects of usability - intuitive design, learnability, efficiency of use, memorability, and error frequency. It provides a usability checklist with seven guidelines: recognition over recall, matching the system to real life, following standards and best practices, preventing errors, recognizing errors, visibility of system status, and informing users of their location. Examples are given for each guideline.