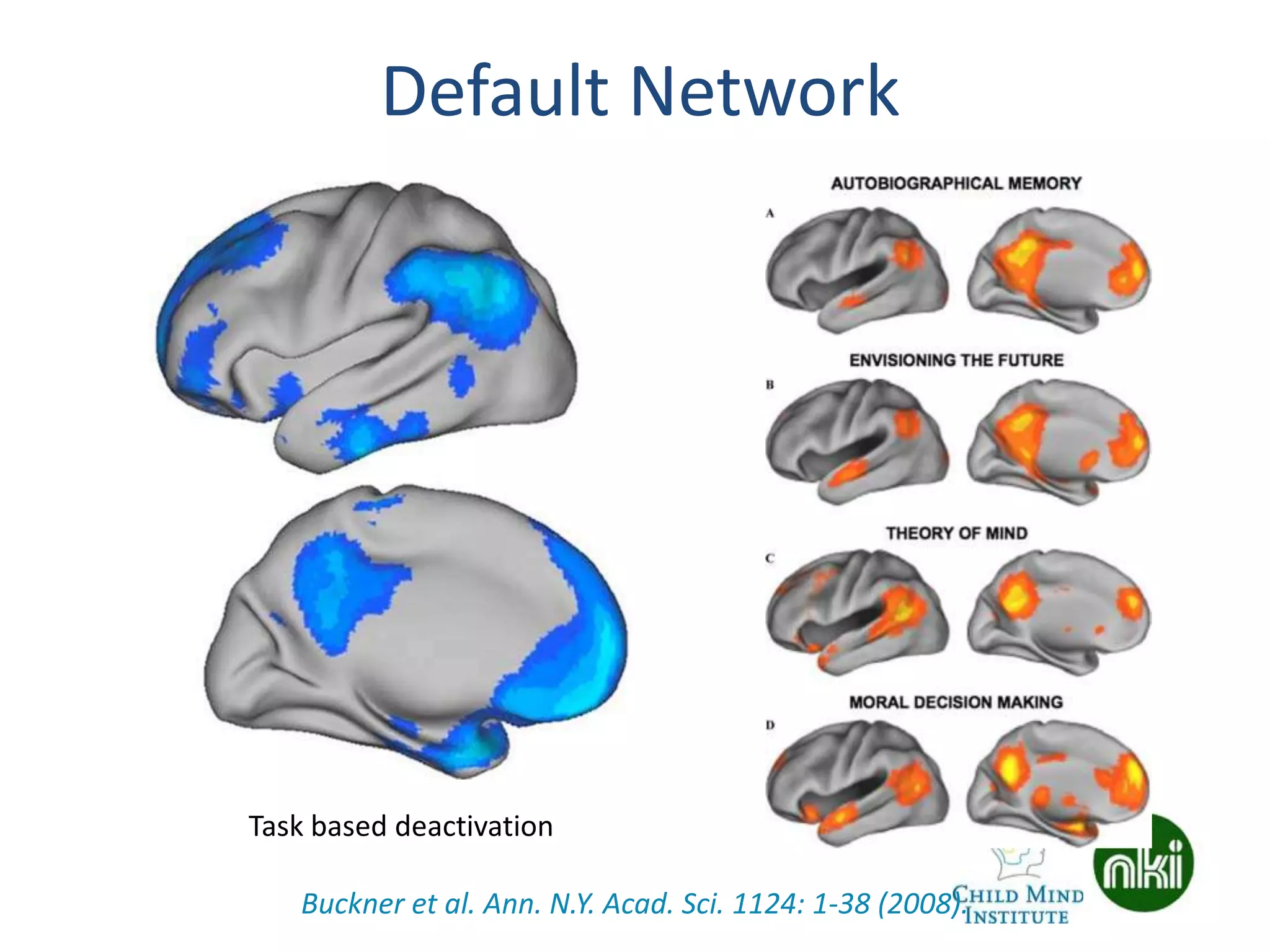
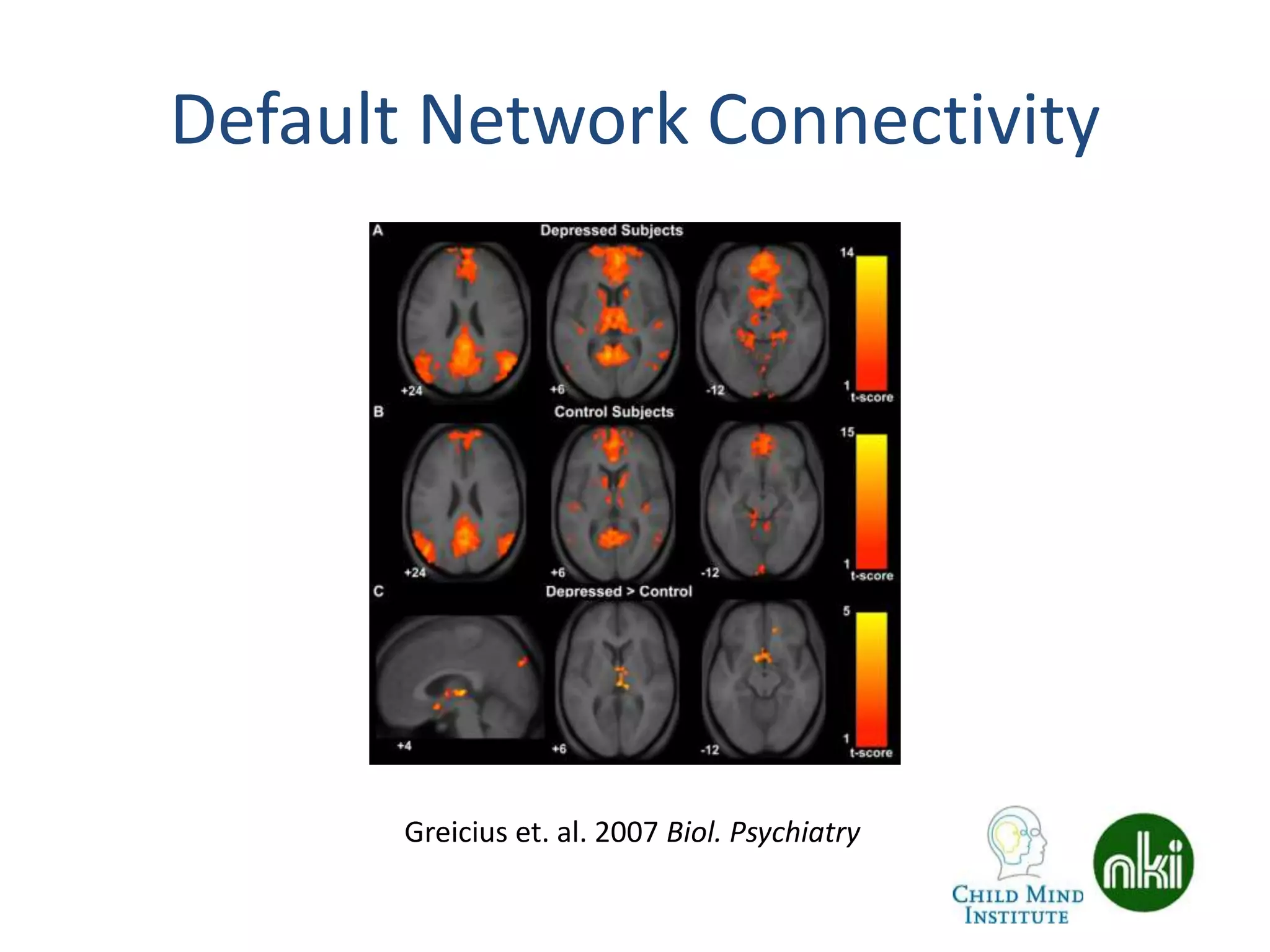
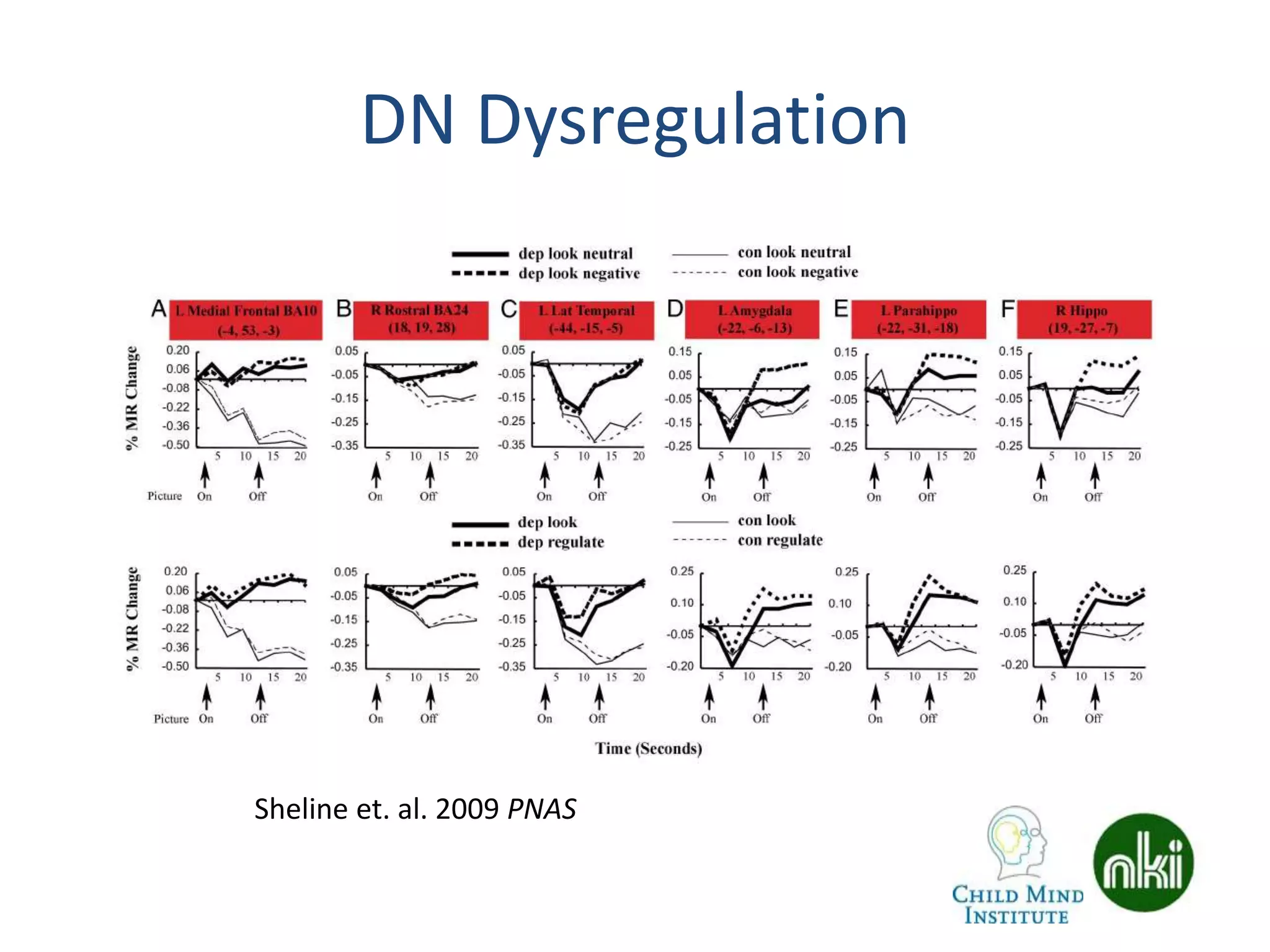
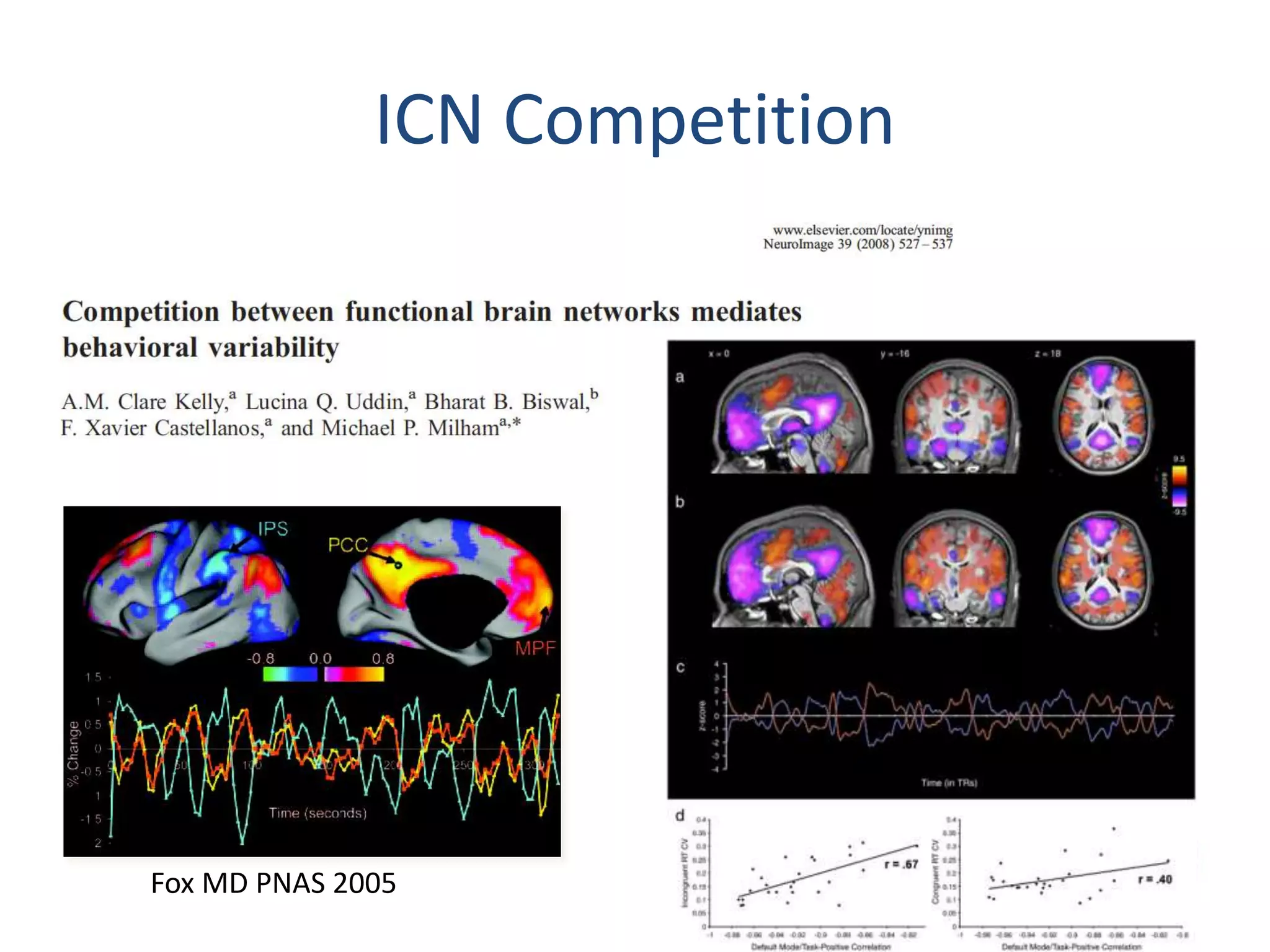
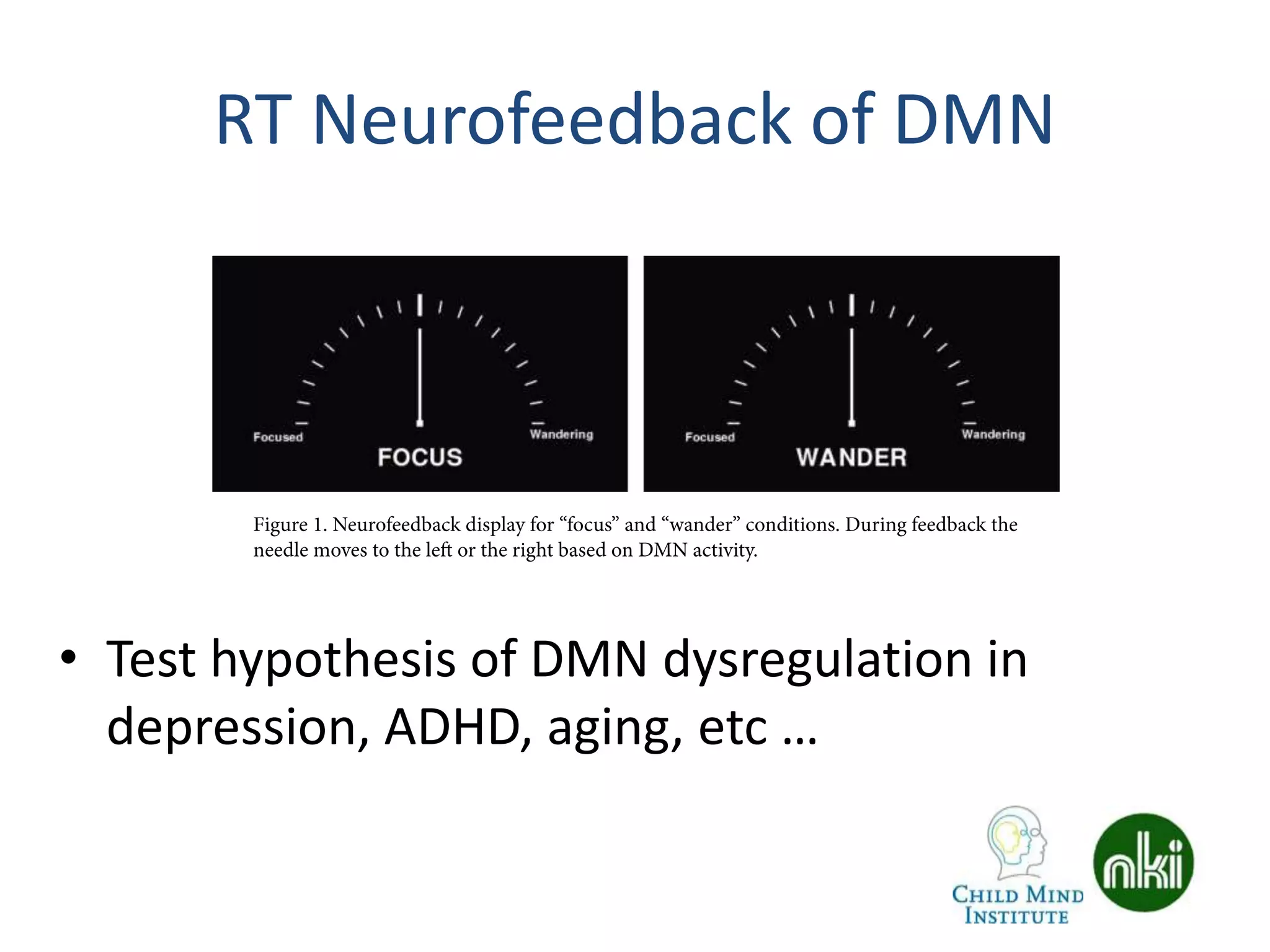
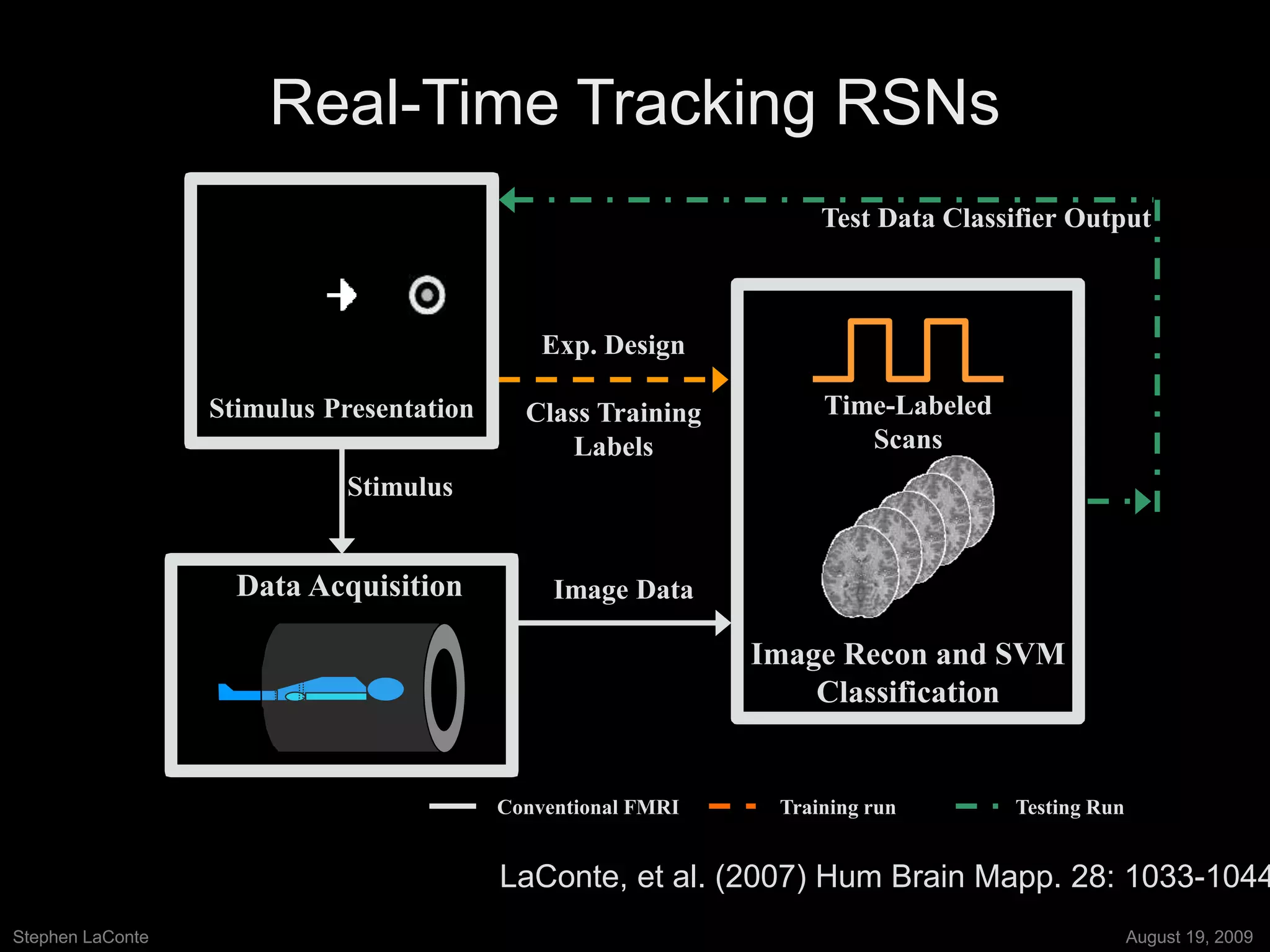
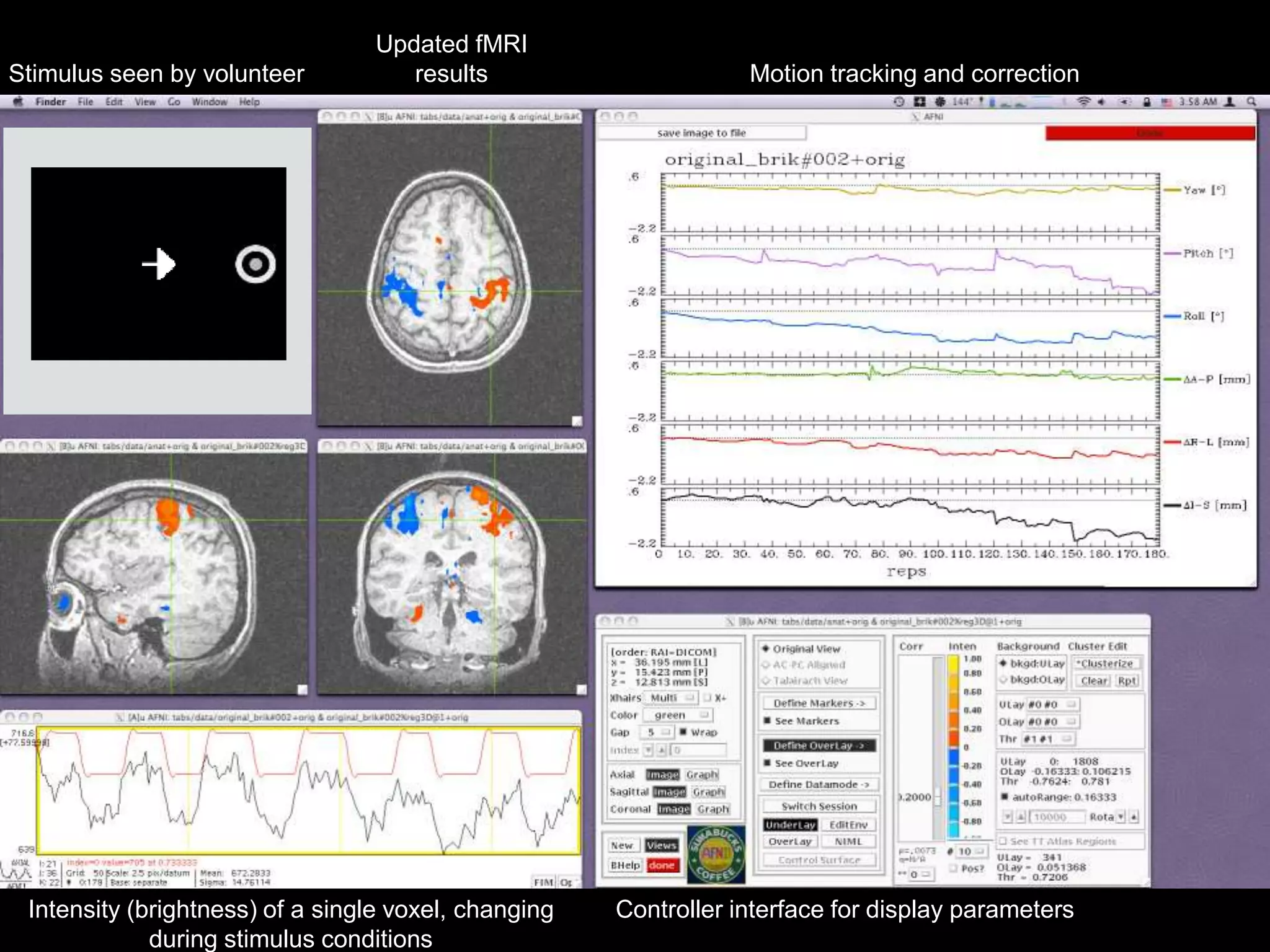
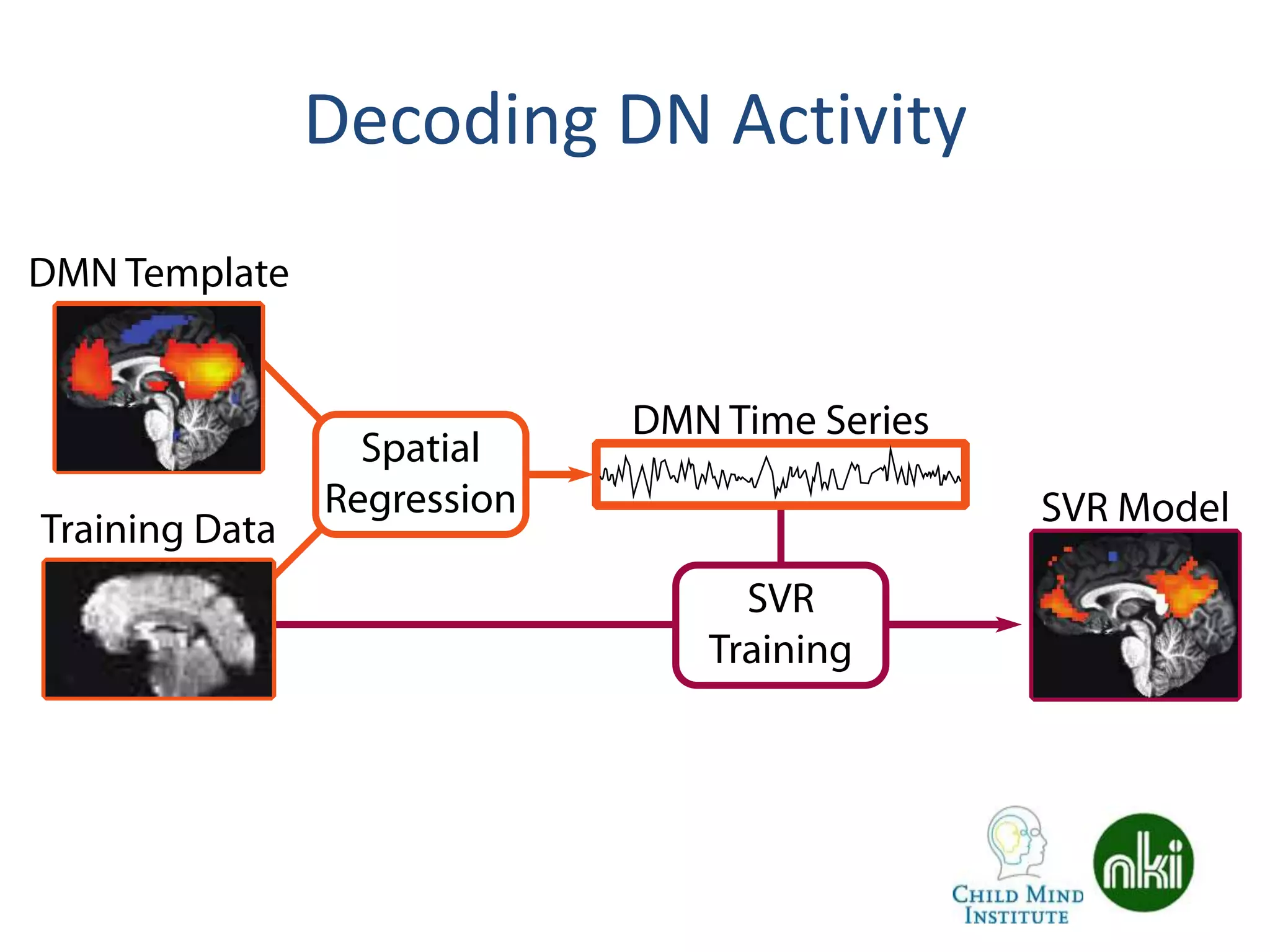
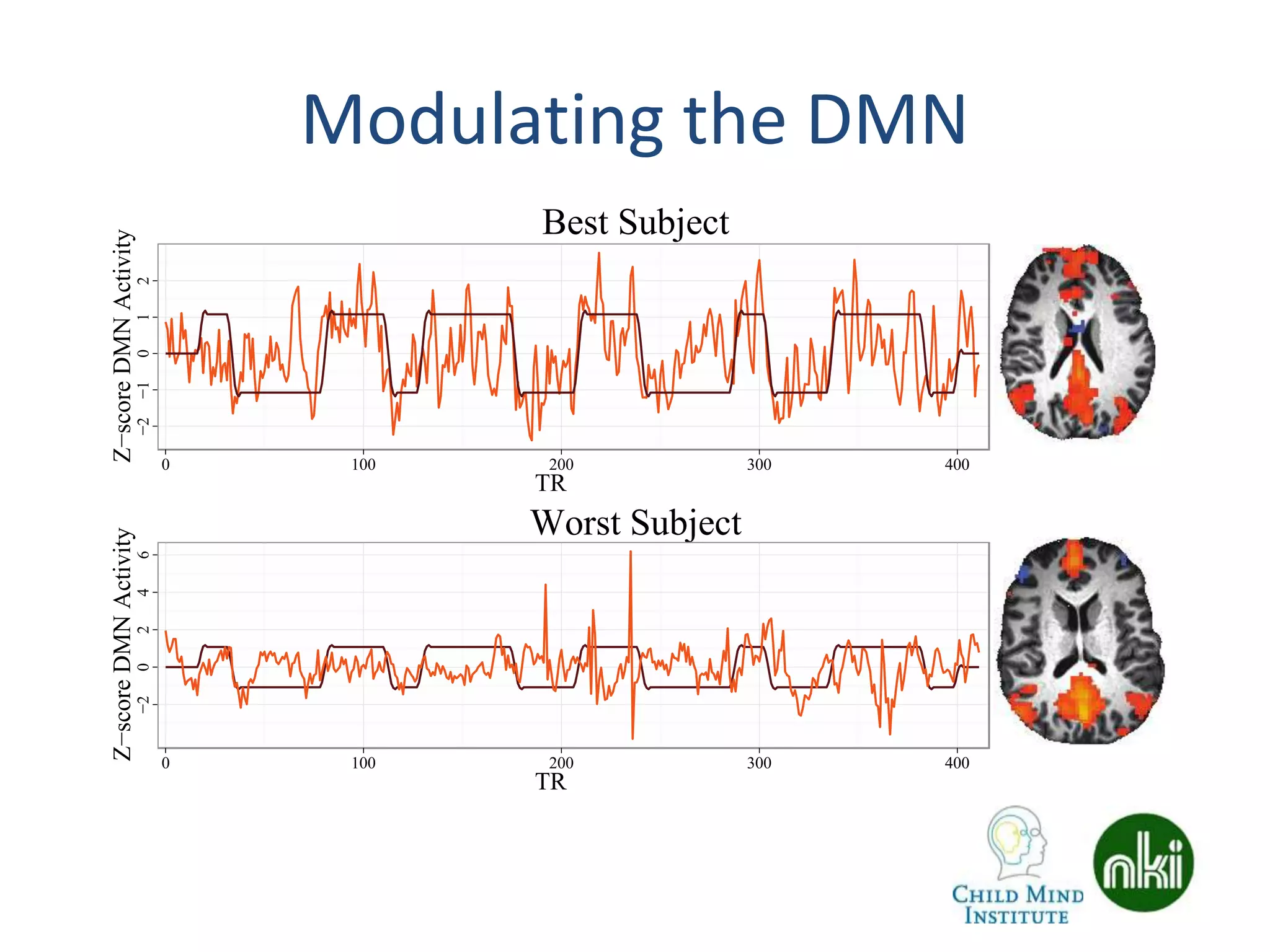
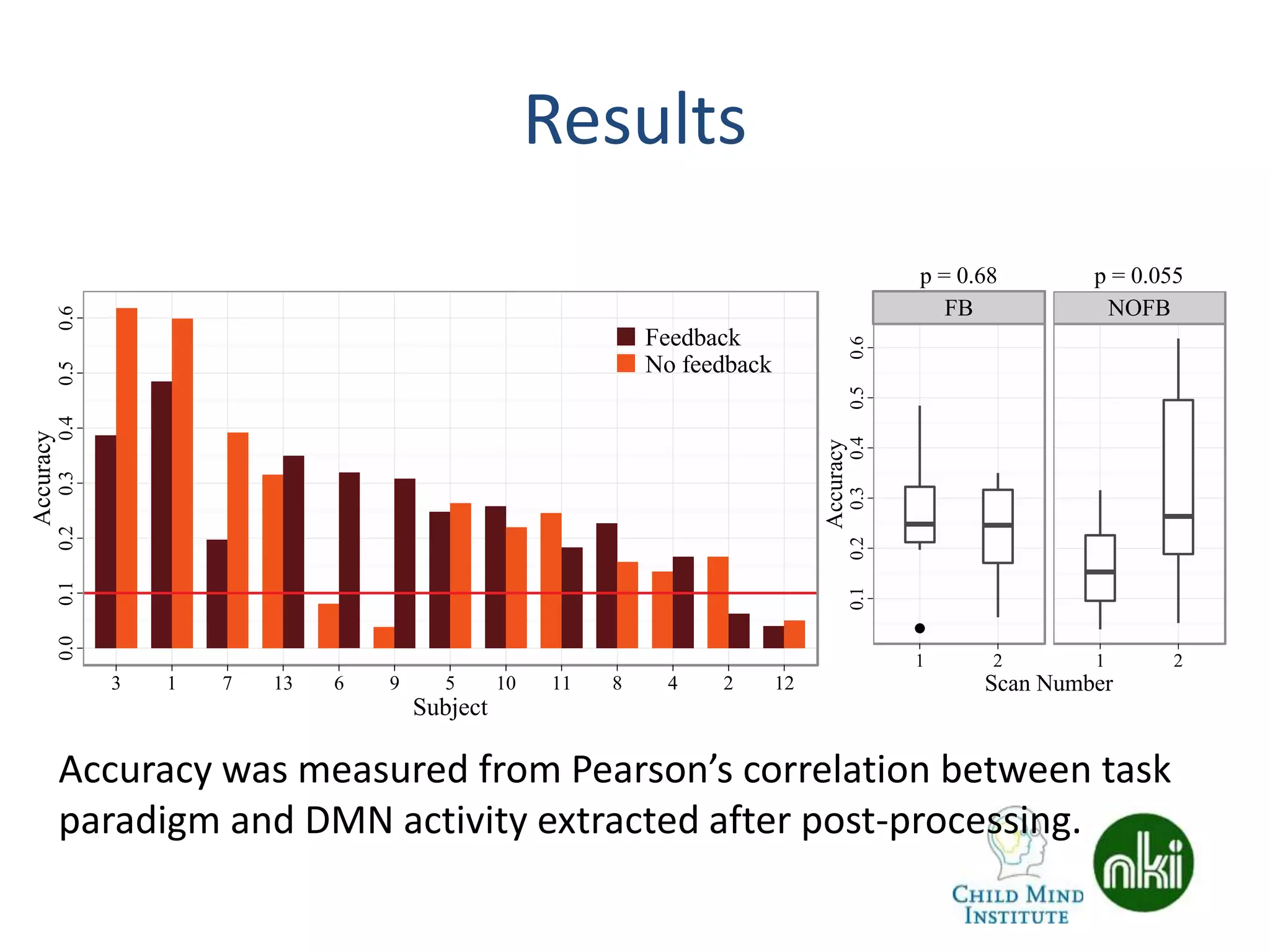
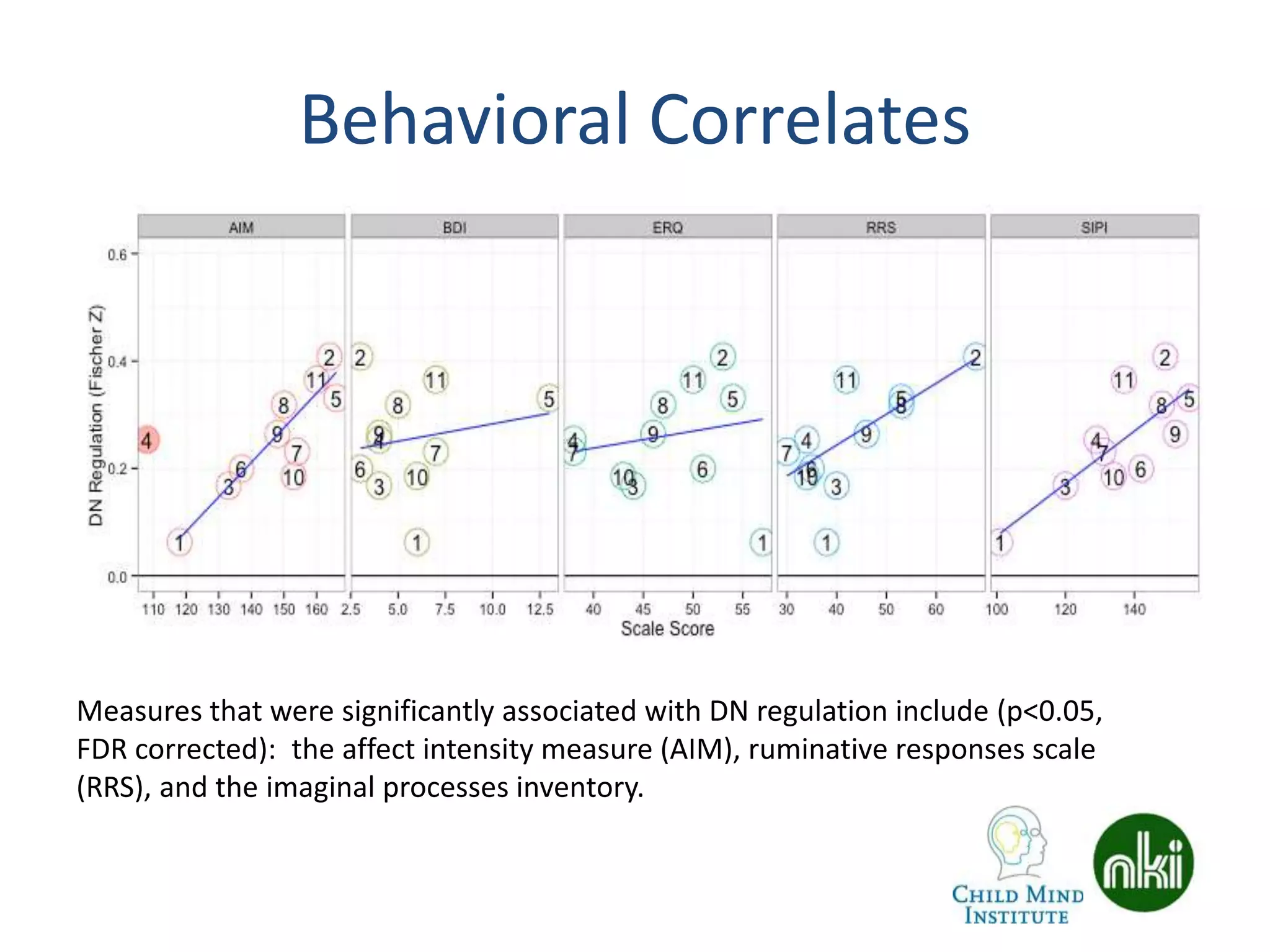
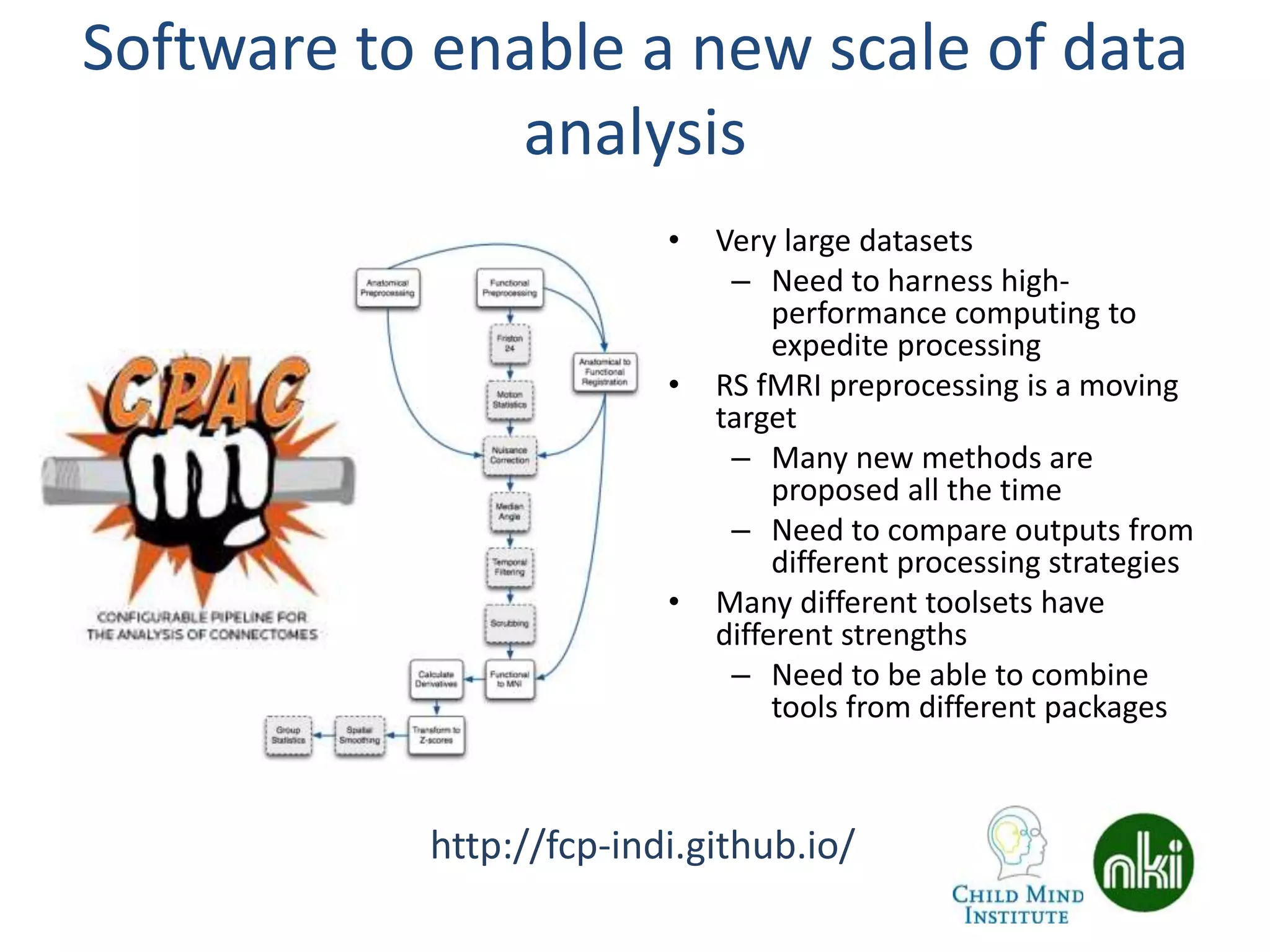
The document discusses the use of real-time fMRI-based neurofeedback to study the regulation of the default network (DN), particularly in relation to disorders like depression and ADHD. It details experimental designs, data acquisition methods, and training protocols, as well as behavioral correlates associated with DN regulation. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of sharing neuroimaging data and tools to enhance reproducibility and collaboration within the research community.