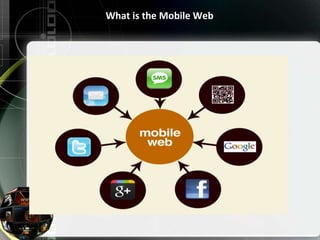
This document discusses using mobile technologies to develop new ways for libraries and information centers to provide services. It describes the evolution of mobile devices and high-speed wireless networks that allow for mobile internet browsing. Libraries can offer mobile services like e-books, mobile versions of their online catalogs, mobile applications, and mobile databases. Effective library mobile sites provide features like the mobile catalog, loan services, contact information, links to databases and social media, and information about the library. The document concludes that mobile technology holds promise for enhanced library services, but libraries will need to address issues, support staff, and explore new funding models to fully realize this potential.