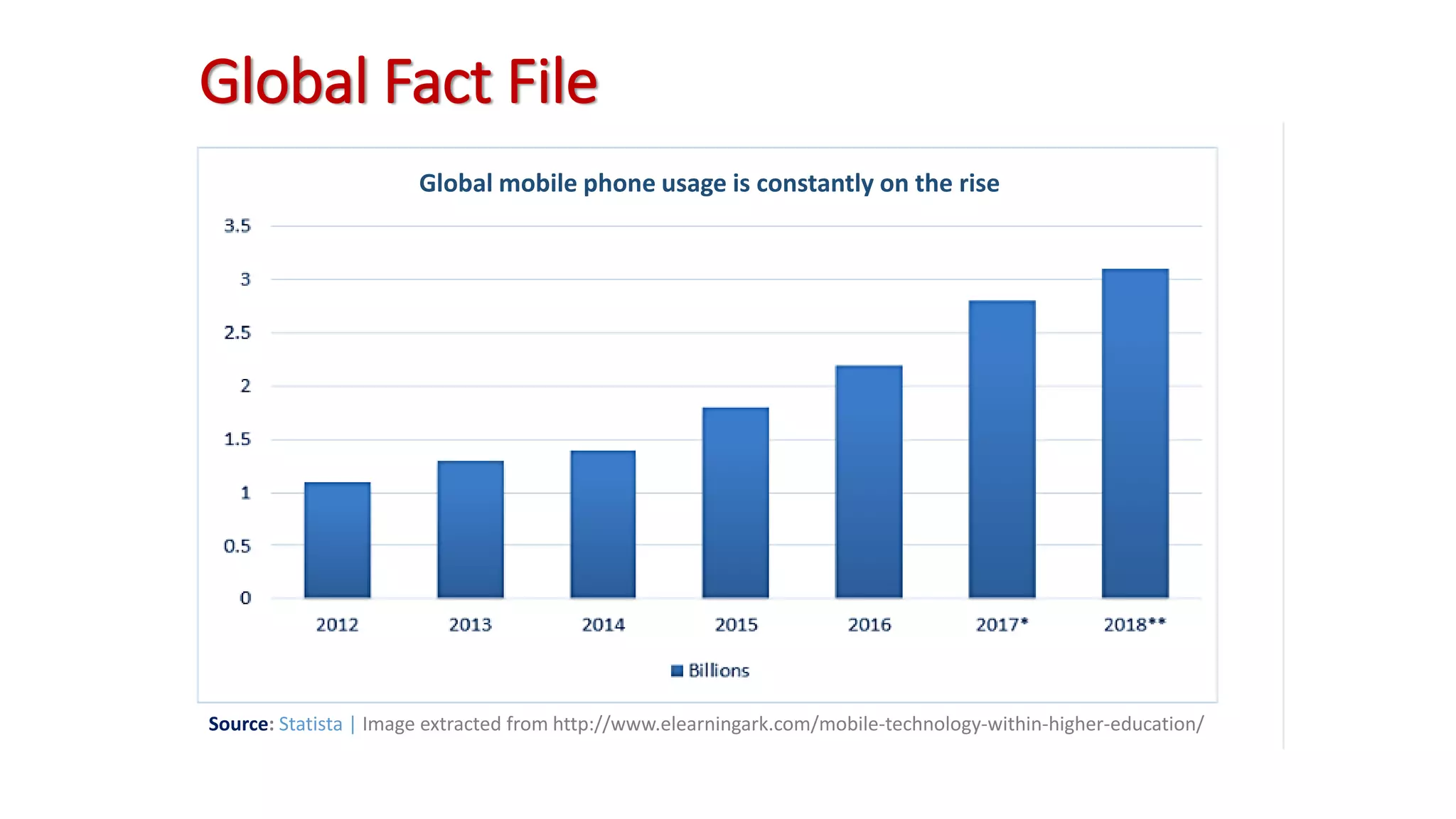
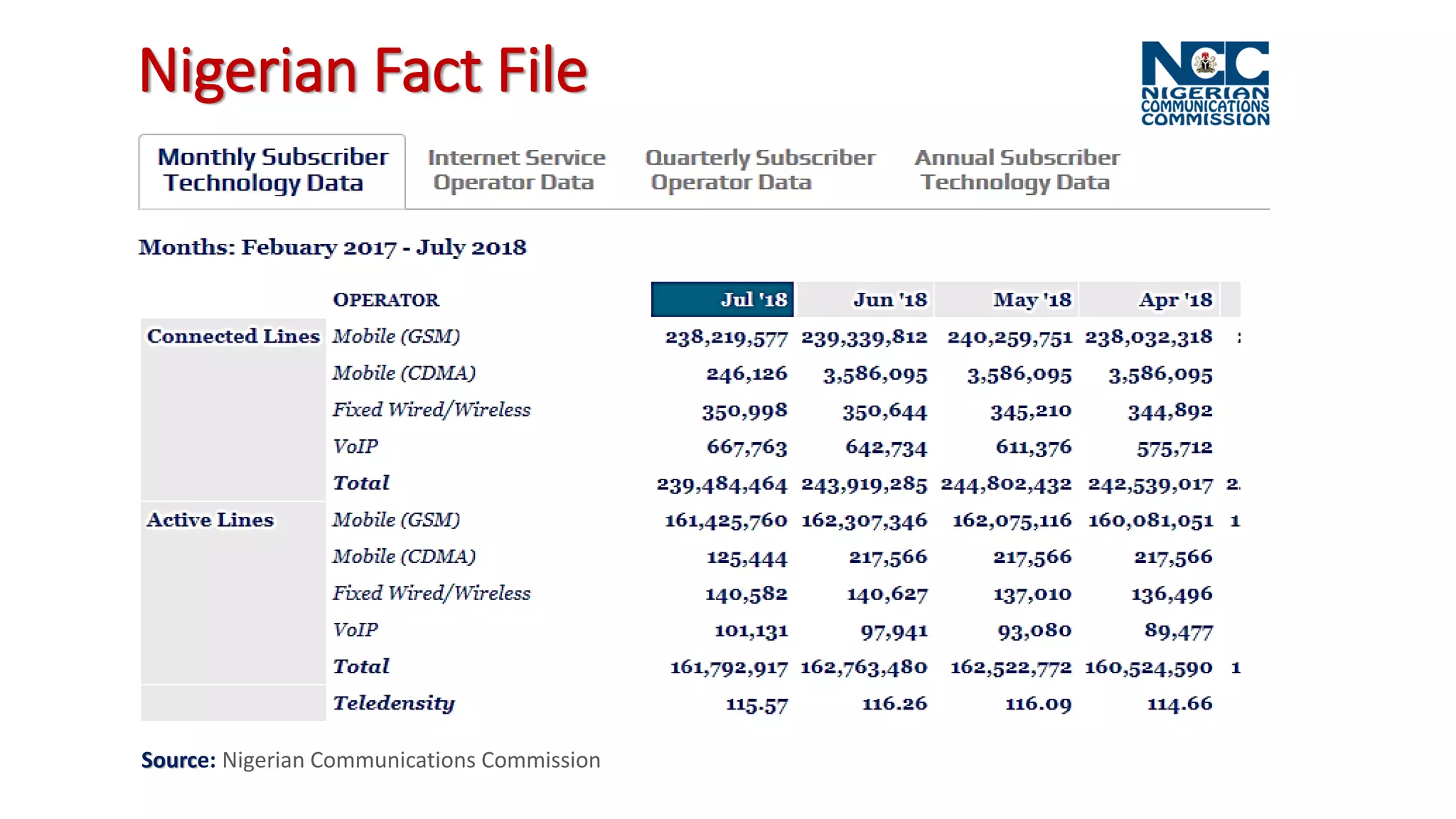
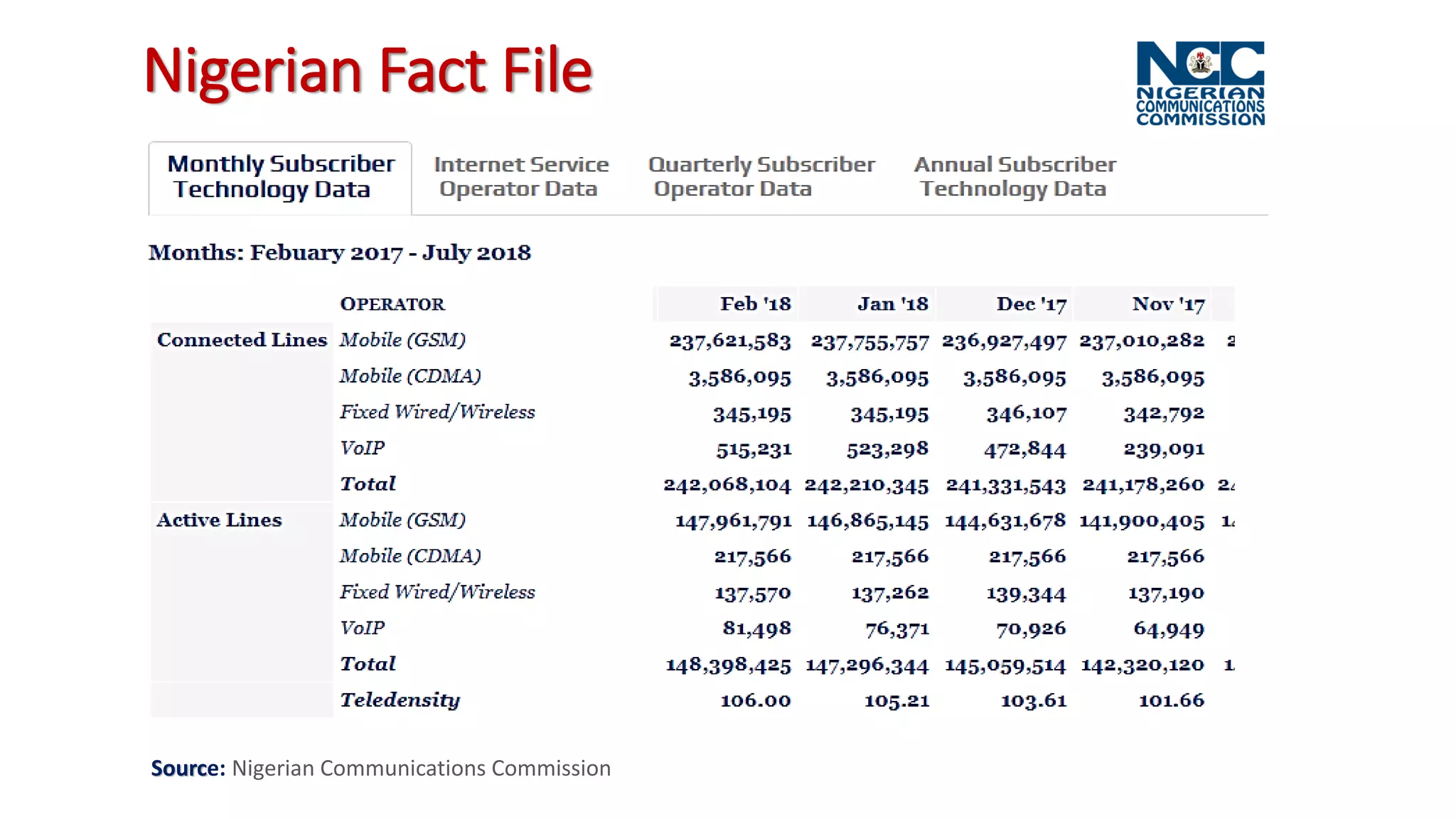
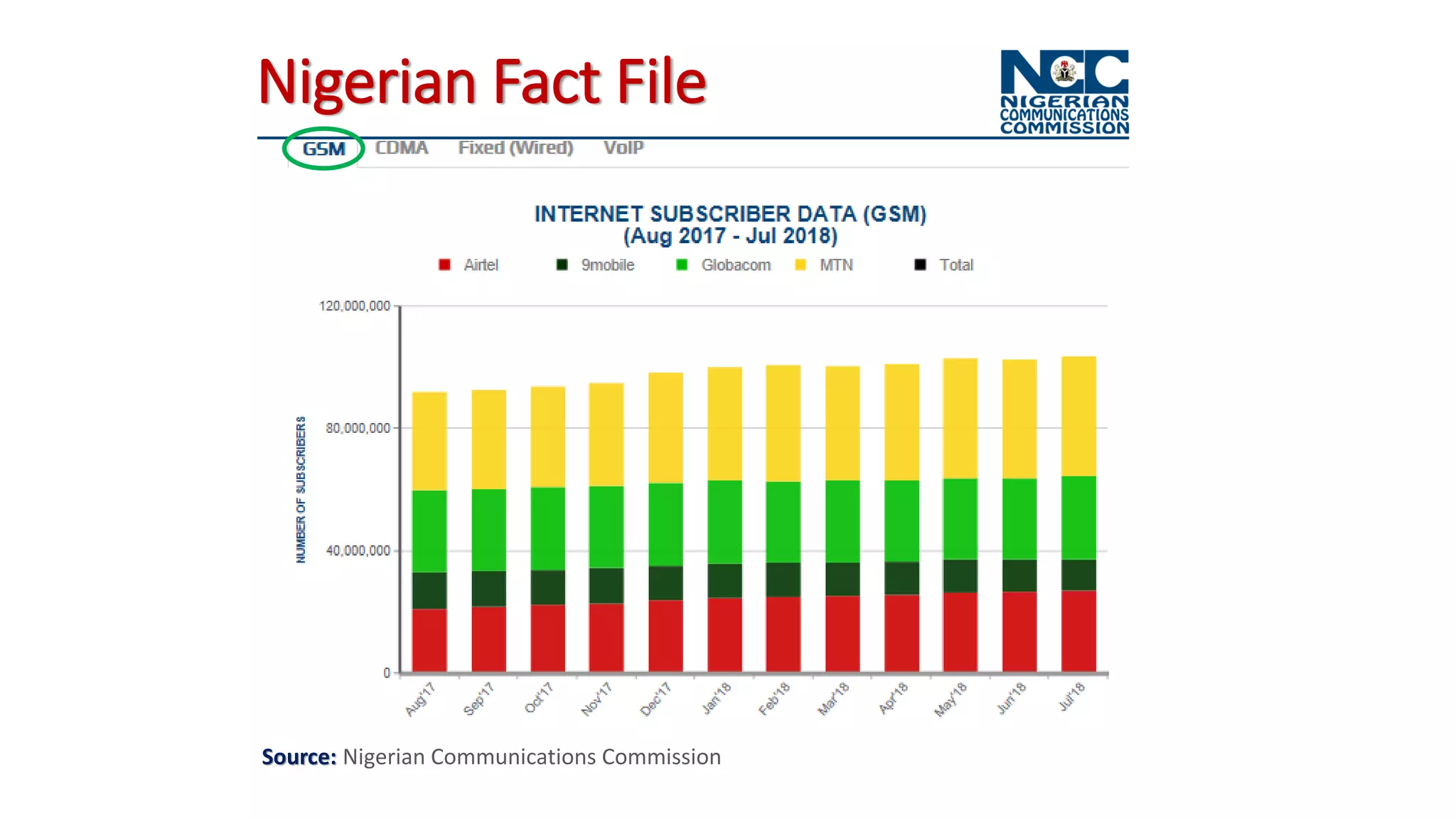
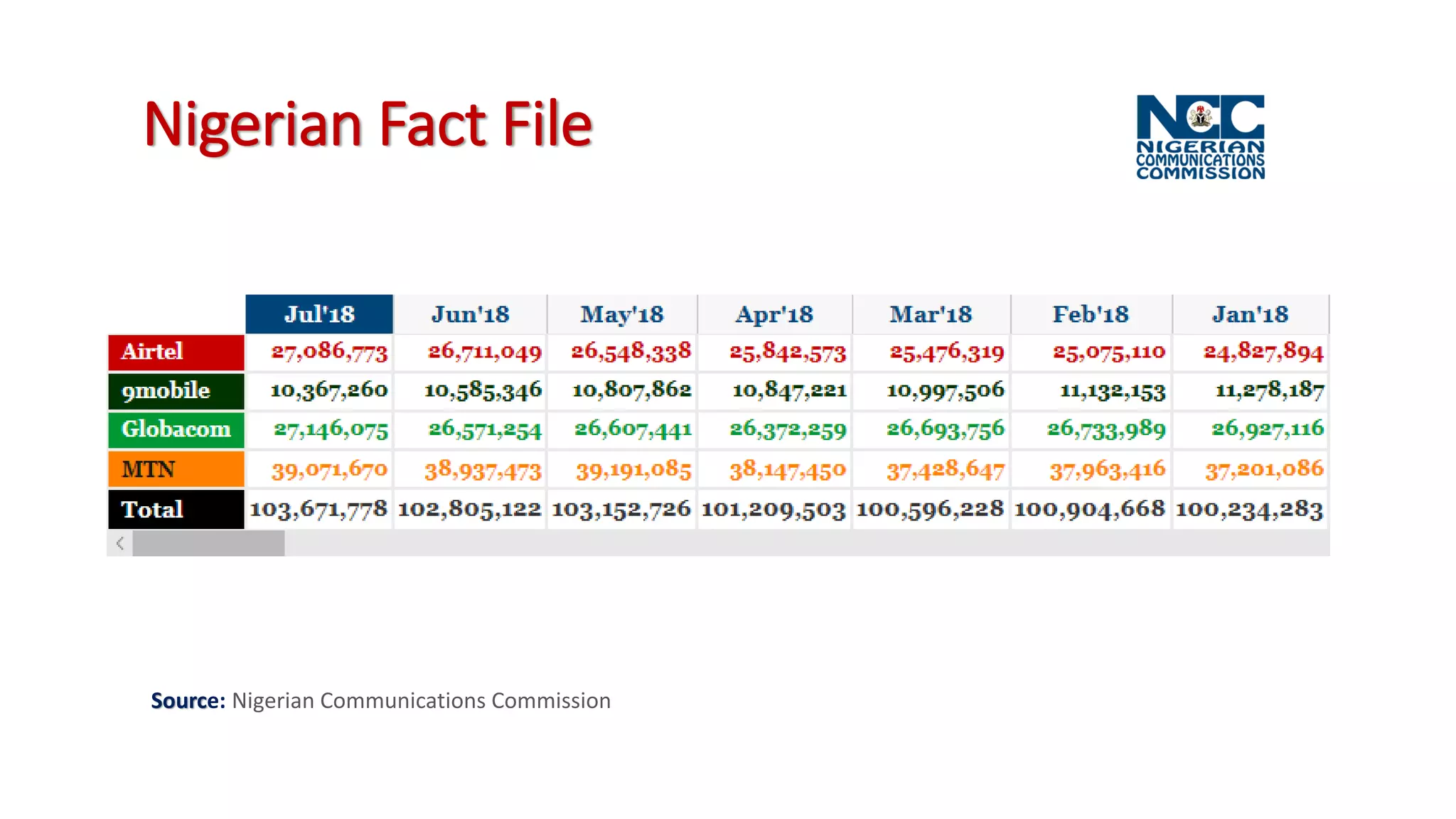
The document discusses the impact of mobile technologies on Nigerian libraries and highlights the necessity for librarians to adapt to these changes for better service delivery. It emphasizes the increasing reliance on smartphones and mobile internet for accessing information and suggests various mobile services that can enhance user experience. Ultimately, it advocates for libraries to integrate mobile technologies into their operations to remain relevant and effective.