Using mind maps in Business English
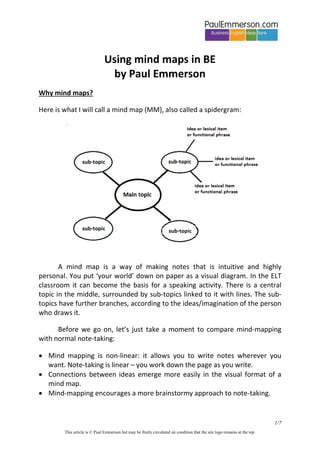
- 1. Using mind maps in BE by Paul Emmerson Why mind maps? Here is what I will call a mind map (MM), also called a spidergram: A mind map is a way of making notes that is intuitive and highly personal. You put ‘your world’ down on paper as a visual diagram. In the ELT classroom it can become the basis for a speaking activity. There is a central topic in the middle, surrounded by sub-topics linked to it with lines. The subtopics have further branches, according to the ideas/imagination of the person who draws it. Before we go on, let’s just take a moment to compare mind-mapping with normal note-taking: Mind mapping is non-linear: it allows you to write notes wherever you want. Note-taking is linear – you work down the page as you write. Connections between ideas emerge more easily in the visual format of a mind map. Mind-mapping encourages a more brainstormy approach to note-taking. 1/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
- 2. Mind mapping forces you to write just a few words as a summary, rather than continuous text. With mind-mapping you automatically structure your ideas. This is less easy in the process of linear note-taking. A mind-map has to fit onto a single page, so it encourages summarizing, overviews, thinking about which are the key points etc. And a word of warning before we come to our first practical activity. It is absolutely ESSENTIAL to give the students an example of a mind-map first, before asking them to produce one. Activity 1 below does this by including a live teacher model – the students see you sketch a simple example on the board first. Activity 1: MM to prepare a personalized speaking activity about jobs 1. Draw on the board a simple mind-map of your own job and professional world. Do it ‘live’ in front of the students as an improvised sketch, to give an idea of the whole approach. 2. Now ask the students to draw their own personal job MMs in class. Preexperience students can also do this, although it will be their wider world of study, part-time jobs etc. Remind the students that it is a summary, and set a time limit of five minutes. 3. When they finish their MMs, put the students into pairs or threes. They explain their jobs to each other, using the mind map as a prompt and as a structure. Encourage the listeners to ask questions. Don’t forget to circulate and take notes for language feedback. 4. Finish with a whole-class discussion to round up: ask the students what they found out. 5. Language feedback. That’s a zero-preparation, fun, personalized lesson of 50 minutes or so. It’s my standard first MM lesson, and it’s also a good lesson to have ready for when you have to cover for colleagues at short notice. As always, don’t forget to leave time for the language feedback: extending lexis, correcting grammar, working on pronunciation. You need this solid input at the end to balance the speaking/fluency part of the lesson. 2/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
- 3. Follow-up How could we follow up this first activity? These ideas all work well (and can be used after any MM): Work with a new partner The students regroup and work with a new partner. They use their MMs to explain their jobs again. Same task, but they will be much more fluent the second time, and the second partner will ask different questions. This activity could be done in the next class rather than the same class. Work with a new partner, but without using the MM the second time The students work with a new partner as before. But in this variation they do the second round without looking at their MM. Now the speaking will be more improvised and will move into different areas. “Explain your partner’s mind-map to a new partner” This is fun. Try it after the students have already done a more conventional activity as above. First warn students that after listening to their first partner they will have to explain what this person said to another student. This forces them to really check understanding with the first person. Note: when they move to work with the second partner they physically take their first partner’s MM with them as a guide and memory jogger. Writing activity Students discuss their MM in small groups as above, and then use it as the basis for a writing activity. Preparing ideas before writing is something we often encourage, and here the MM format is ideal. Not only are the ideas prepared as a structured diagram first, but the students then use the MM to discuss these ideas with a partner, further developing them. Students are now really ready to write - it’s not just abstract preparation starting with a blank sheet of paper. 3/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
- 4. Activity 2: MM to summarize an authentic text Use a MM to summarize an authentic text. I do this as a homework activity. Here is the procedure I use: 1. Decide where students are going to get their text from. There could be a short list of internet sites to look at, or a magazine or newspaper article which you give out in class (different articles for different students). Note that the text can be given by you or chosen by the student, and also for this particular activity the original can even be in L1. 2. Ask the students to produce a summary of the article in the form of a MM, for homework. So central topic in the middle, surrounded by a ring of the sub-topics in the article, and then the final braches of the MM are the individual points and ideas. Tell them to bring this MM to the next class (not the original text, which for this activity serves no further purpose). 3. In class, group the students into pairs and they take turns to explain their article to their partner, using their MM as a guide. Encourage the listener to ask lots of questions. 4. As usual, the teacher circulates, making notes, and at the end goes to the board for a language feedback slot. The follow-up activities mentioned in the last section all apply here as well, and this is a particularly good context to try the one called ‘Work with a new partner, but without using the MM the second time’. So, after the initial pairwork, you regroup the students into new pairs. Then, with a dramatic gesture, you go round the room turning over the students’ MMs face-down. The students laugh and immediately get the idea – they have to summarize the article again to the new person, but this time with no MM to help them. In fact, this follow-up is a fantastic fluency exercise and the students will be able to do it remarkably well. Why? Because they have processed the information a number of times: first reading the authentic text in order to decide on the main points and ideas, then actually drawing the MM, and finally referring to it as a guide while they summarized the contents to their first partner. Now they have the ideas and the language in their heads, ready to come out. You (and they) will be amazed at how well they speak when they repeat the activity with the new partner. It’s a real confidence-booster! 4/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
- 5. Activity 3: MM on board as a warmer for a business topic In activity 1 above the students prepared an individual mind map in class. In activity 2 they prepared an individual mind map for homework. In this activity the teacher is going to create the MM on the board, using it to summarize a class brainstorm. The teacher can feed in ideas as well. Here the MM is going to be a warmer for a business topic, such as Internet Marketing, or Globalization, or any topic coming up in the next coursebook unit. In General English (where all the ideas in this article are equally applicable) the topic might be Travel, or Family, or Films, or Money, or a current news item. Here is the procedure I use: 1. Write the main topic in an oval in the middle of the board with some lines coming out of it to suggest a MM that is about to be made. 2. Now ask the students to work in threes for a few minutes to brainstorm some subtopics for the inner ring, and also further individual words for the end branches. Circulate to keep them on track. 3. Take whole-class feedback: write up on the board the first sub-topic that one group calls out, and ask the class for suggestions for words for the end branches, possible ways that this sub-topic could be modified, etc. 4. Now write up a second sub-topic using another group as a starting point, and afterwards add to this in turn, again using suggestions from the class. 5. Continue until the board is full. What can you now do with this MM you’ve built up on the board? Well, I ask the students to personalize the topic. So if we’ve built up a mind map for Internet Marketing on the board, then I’ll ask the students to describe the activities of their own companies in this area. They can try this with no (or very little) preparation as the MM on the board will be a good structure for them to refer to as they speak. A variation is to use a MM on the board as an introduction to a text (reading or listening) that you want to work with. You obviously need to know beforehand which text you are planning to use, and it could be from a coursebook or an authentic source. Then you follow the procedure above – first writing the main topic in the centre of the board, and then building up the inner sub-topics and outer ideas by whole-class brainstorming. The students 5/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
- 6. haven’t seen the text yet – it is a prediction exercise for them. But you do know the text, and so you can feed in a few ideas of your own to steer the MM closer to it. Once the MM is complete on the board you have a ready-made task: read the text (or listen to the recording) and see which ideas in the MM are also in the text. After that, finally, you’re ready to have a discussion about the contents of the text. Activity 4: MM to elicit functional phrases In Business English we spend a lot of time on business communication skills: presentations, discussions, telephoning, social English etc. Each of these has a series of ‘functions’, and then phrases for each function. So, taking the example of ‘discussions’, some main functions might be ‘managing the topic’, ‘clarification’, ‘agreeing and disagreeing’ etc. Taking just the first one of these, ‘managing the topic’, key phrases might be: Right, let’s get down to business or Could I just interrupt for a moment? You get the idea, and Business English coursebooks are full of these functions and associated key phrases, often boxed off on the page. This whole approach lends itself very well to mind mapping: 1. Write the name of the communication skill in the middle of the board, as the centre of the MM, and establish some functions as the inner sub-topics. You will probably feed in the function names yourself as they are a teacher/coursebook way of looking at the world – students don’t think in terms of functions unless asked to, they just think of the phrases. 2. Now brainstorm key phrases with the class, and write them as the outer branches of the MM. If you wish, students could work in pairs first to think of some phrases, before sharing their ideas with the group. What can you now do with this MM you’ve built up on the board? Well, if you have a list of functions and phrases in your coursebook then you can open the book and look and compare. But most obviously you will now actually do a task, and the students will try to use the phrases on the board. So if you brainstormed phrases for telephoning, then do a telephoning role-play. Leave the MM on the board while the students are doing the activity – the phrases are there to refer to if the students want them. Also leave time for them to copy down into their notebooks. 6/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
- 7. Other uses of mind maps Here are a few other uses of mind maps. 1. Present a new/unfamiliar topic. The teacher can prepare a mind map for a topic that is on the syllabus, and have it ready as a photocopy to give an initial overview and introduction. 2. Organize grammar points. For example: irregular past tenses grouped by form; phrasal verbs with the main verb in the middle, the particles as the inner ring and example sentences as the outer branches; prefixes for negative adjectives etc. 3. Collocation revision. Put the main business topic in the middle (such as ‘financial markets’, individual key words as the inner ring (finance, financial, stock, market), and collocations with these words as the branches (finance sector, financial advice, stock index, money market). 4. Set up a role-play using ideas from the class. Create a RP situation with your students. First think of the name of company, products sold, reason for the meeting (or phone call), and write these ‘bare bones’ in the middle of the MM. Now write the Customer as one inner branch, and the Supplier as another. Then for the outer branches brainstorm with the students their names, further details of their roles, what they want from the meeting (or call), etc. 5. Review a lesson. In the final few minutes of a lesson use a MM to review what the students did and learned in that lesson. Conclusion I hope you feel inspired to try some of these ideas – I use them all the time in my own teaching. In a nutshell, a MM provides scaffolding for a fluency activity, preparing both ideas and language. The speaking activity that follows preparation with a MM will be richer in content and more focussed than speaking with no preparation at all. And it will be more spontaneous than if the students use linear notes. Paul Emmerson January 2014 7/7 This article is © Paul Emmerson but may be freely circulated on condition that the site logo remains at the top.
