The document discusses principles of user-centered design (UCD) including:
1. UCD focuses on meeting users' requirements and involving users in the design process.
2. There are different levels of user involvement from technical-centered to user-led design.
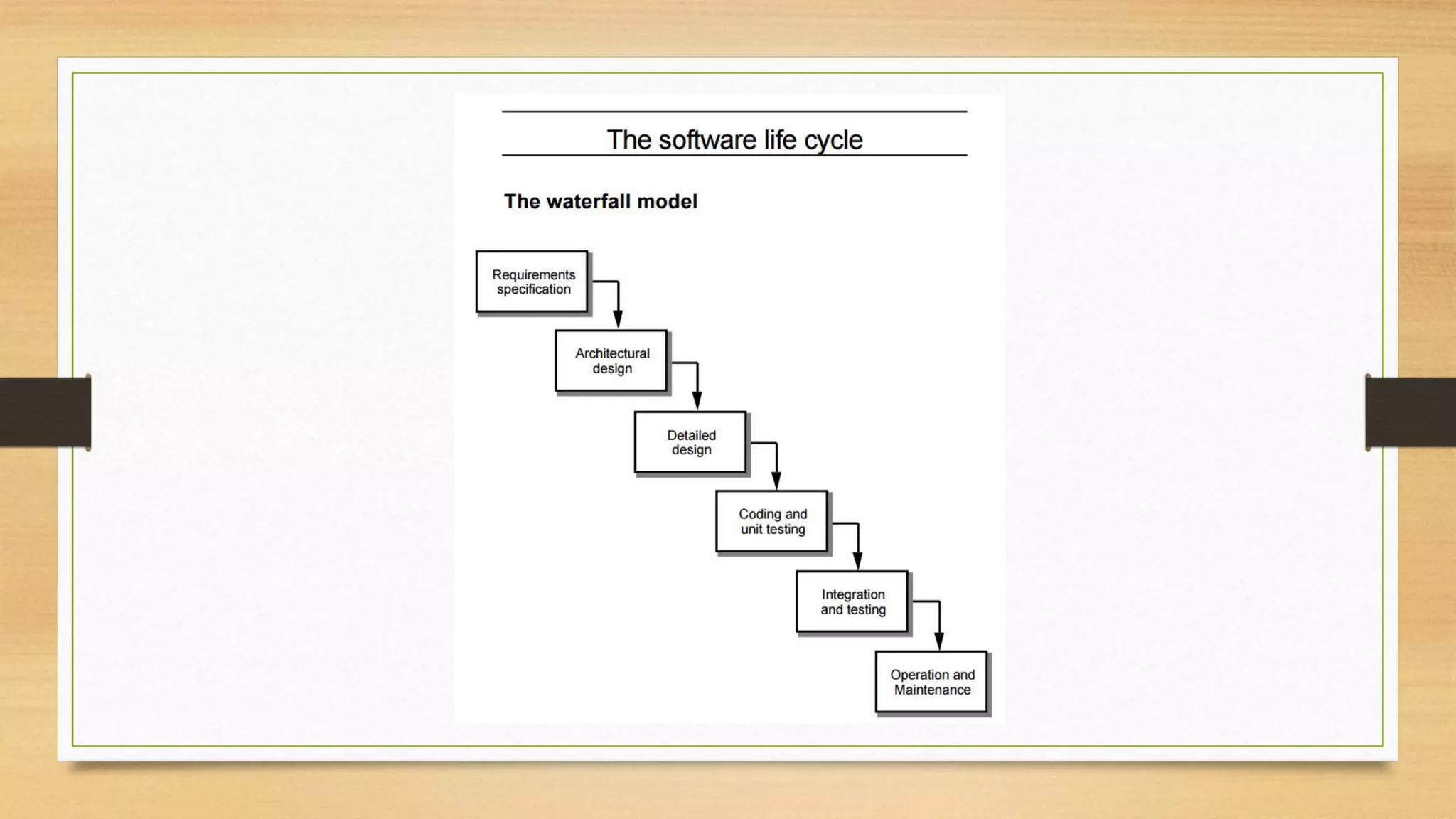
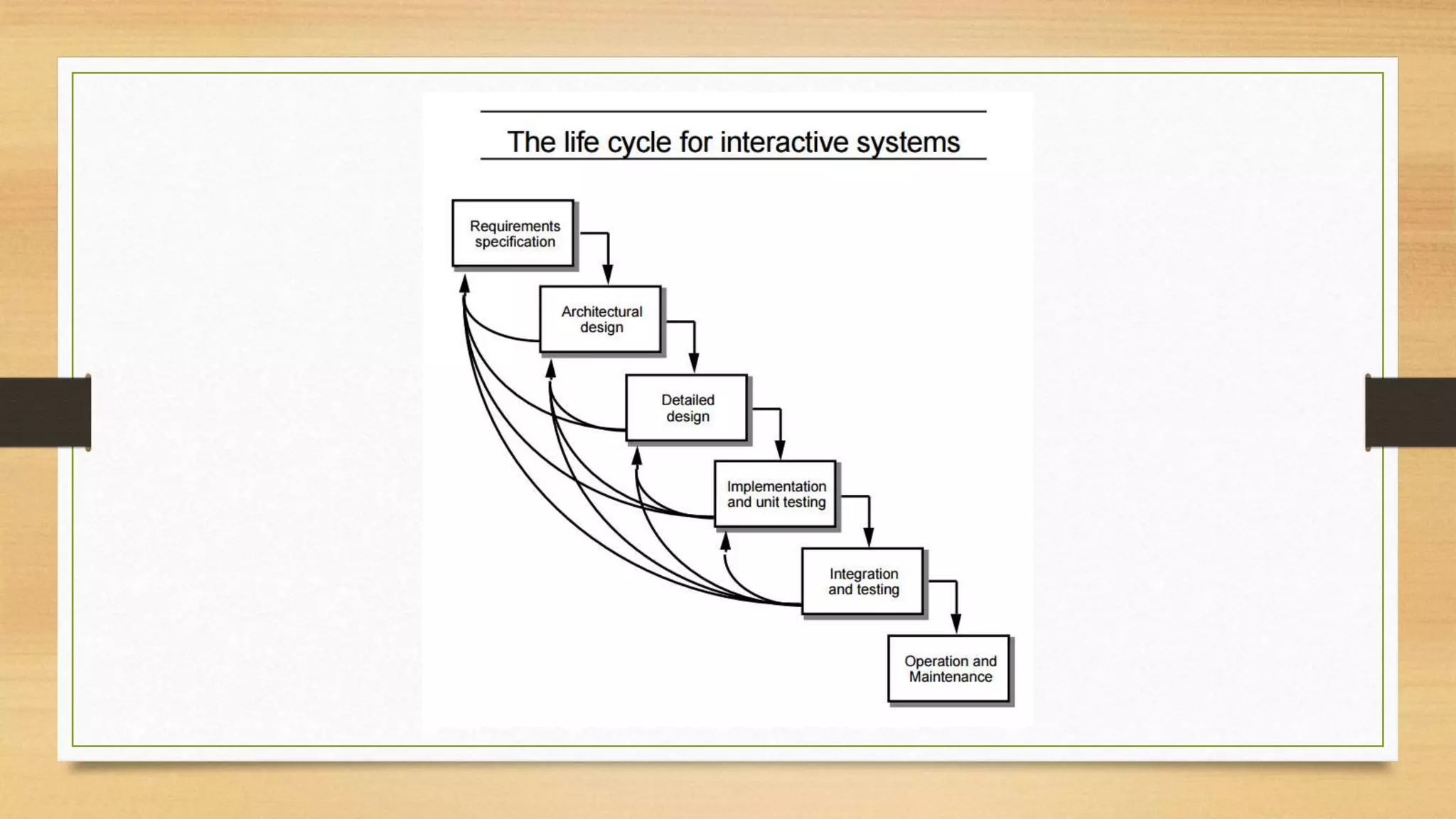
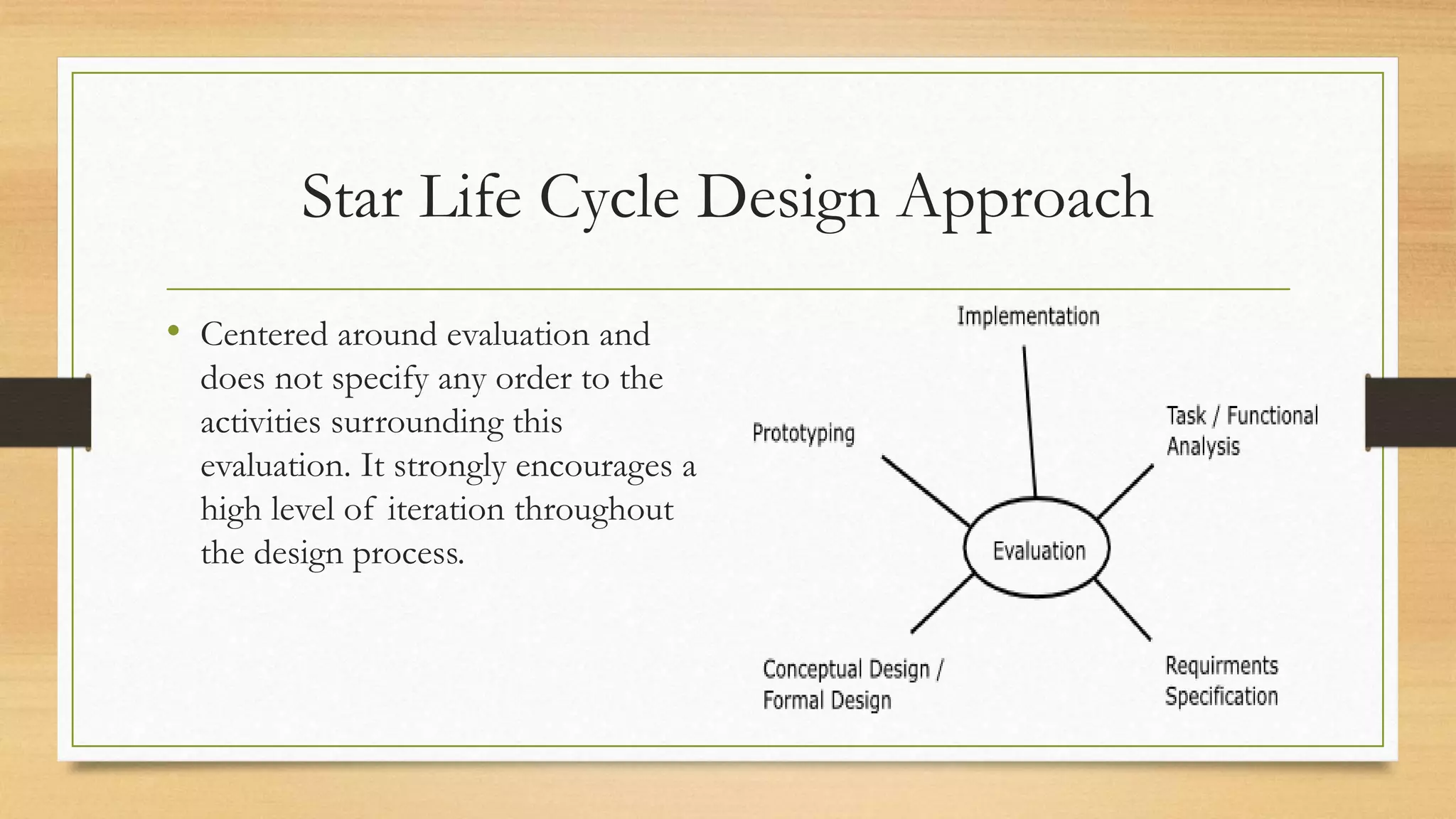
3. UCD methods gather user data and employ iterative design and testing to design systems based on user needs.