This document discusses multimedia networks and properties of video and audio. It covers three types of multimedia network applications:
1) Streaming stored audio/video such as YouTube where content is pre-recorded.
2) Conversational voice/video over IP like Skype which is delay sensitive but loss tolerant.
3) Streaming live audio/video similar to broadcasting where a delay of up to 10 seconds is acceptable.
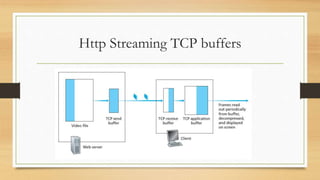
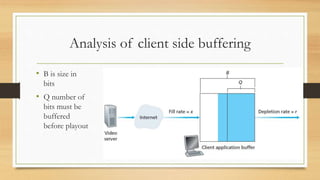
It also describes techniques for compressing, encoding, and transmitting video and audio over networks, including spatial/temporal redundancy, PCM encoding, MP3/AAC compression, and client-side buffering used in UDP, HTTP, and adaptive HTTP streaming.