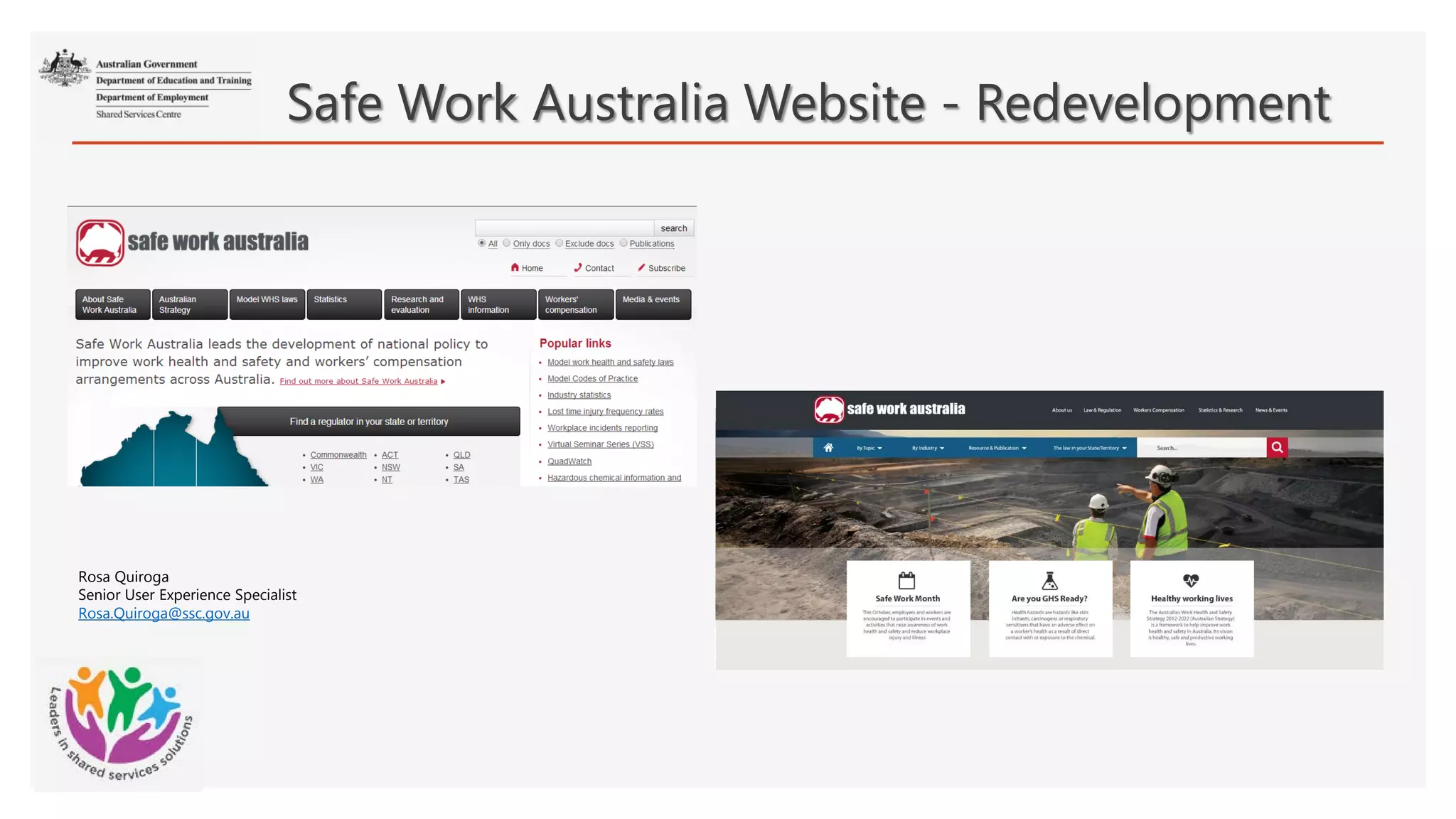
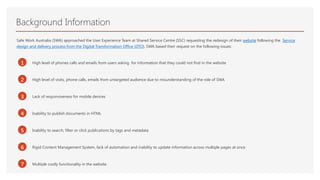
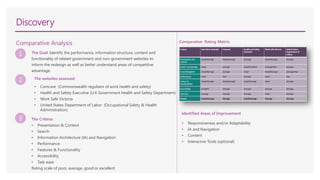
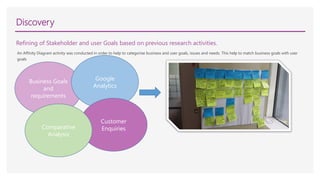
The document summarizes the process taken to redesign the Safe Work Australia website. It involved:
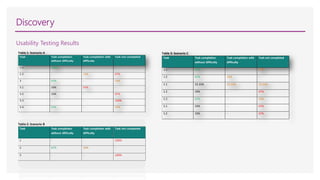
1) Analyzing user data and feedback to understand issues with the existing site like poor search and navigation.
2) Benchmarking other regulatory sites and identifying areas for improvement.
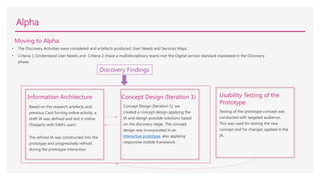
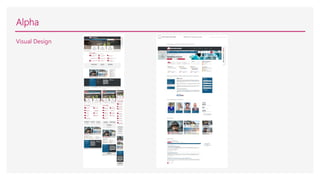
3) Creating user personas and testing prototypes with users to refine the information architecture and design.
4) Developing high-fidelity prototypes in HTML/CSS that dramatically improved task success rates in user testing.
5) Finalizing the redesign following the Digital Transformation Office process to create an optimal user experience for the new site.